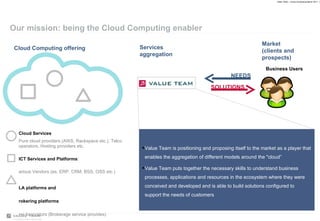
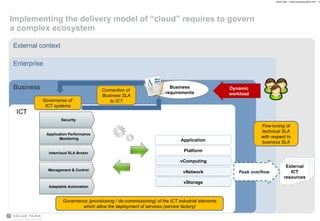
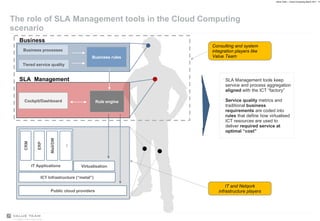
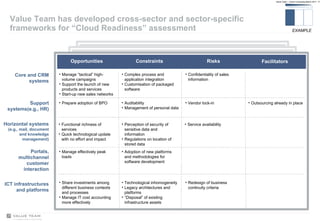
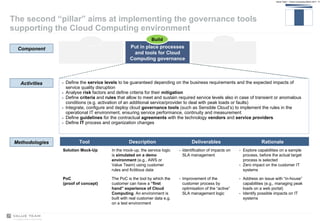
Value Team helps organizations adopt cloud computing by serving as a cloud services enabler. It evaluates opportunities and risks of cloud adoption, addresses issues like quality of service and security, and supports implementing effective cloud governance through tools that align service levels with business goals while optimizing cloud resource usage.