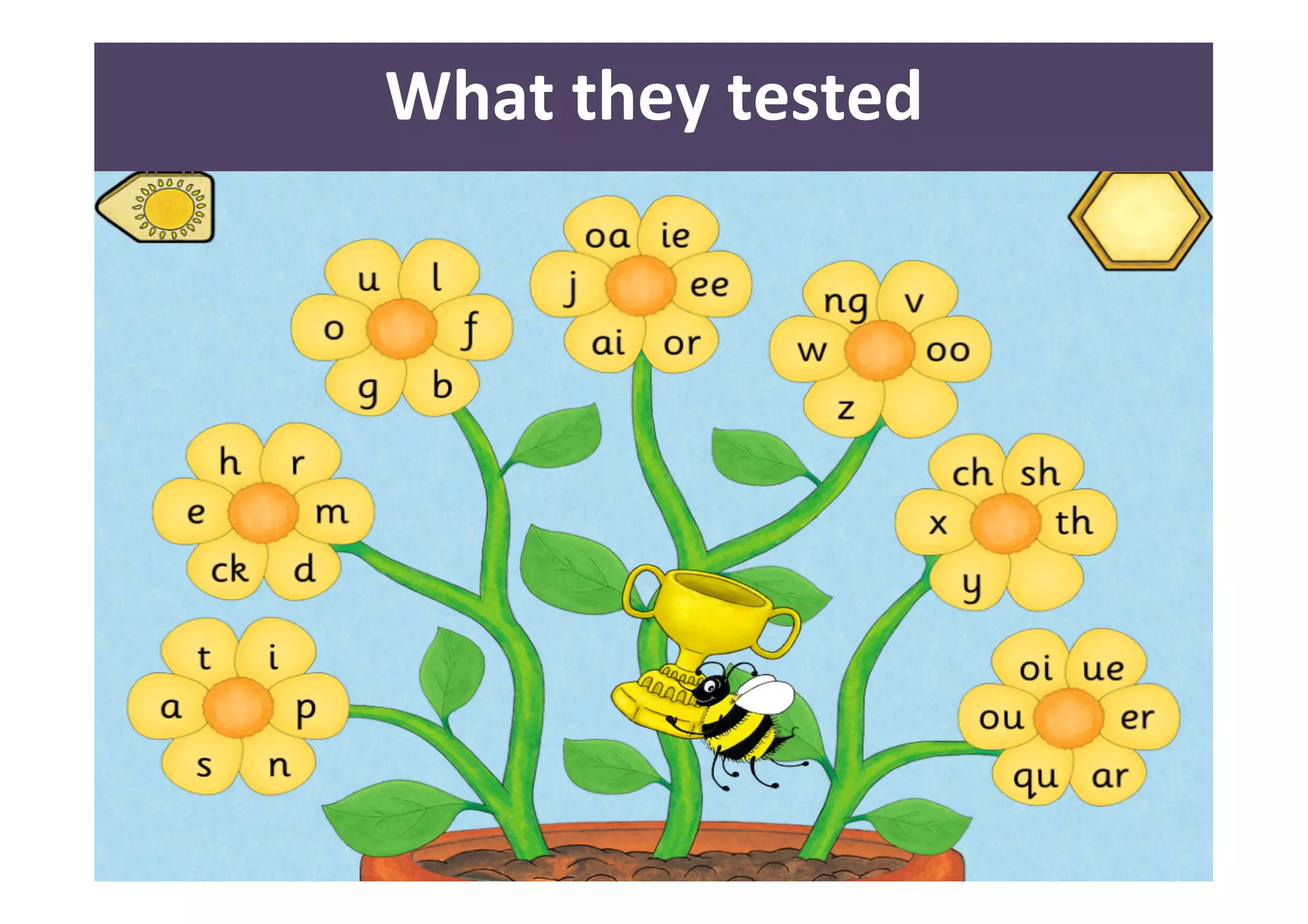
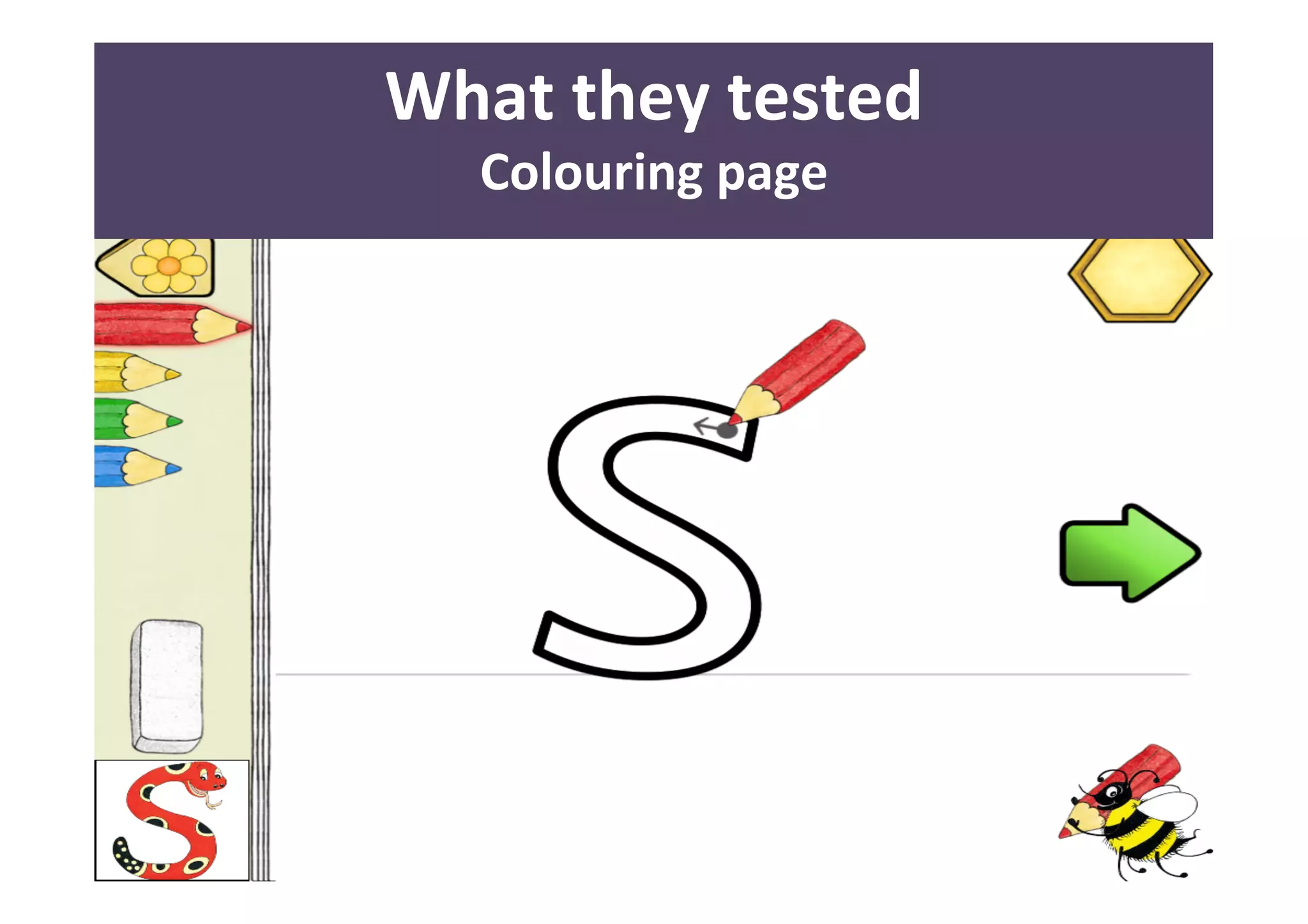
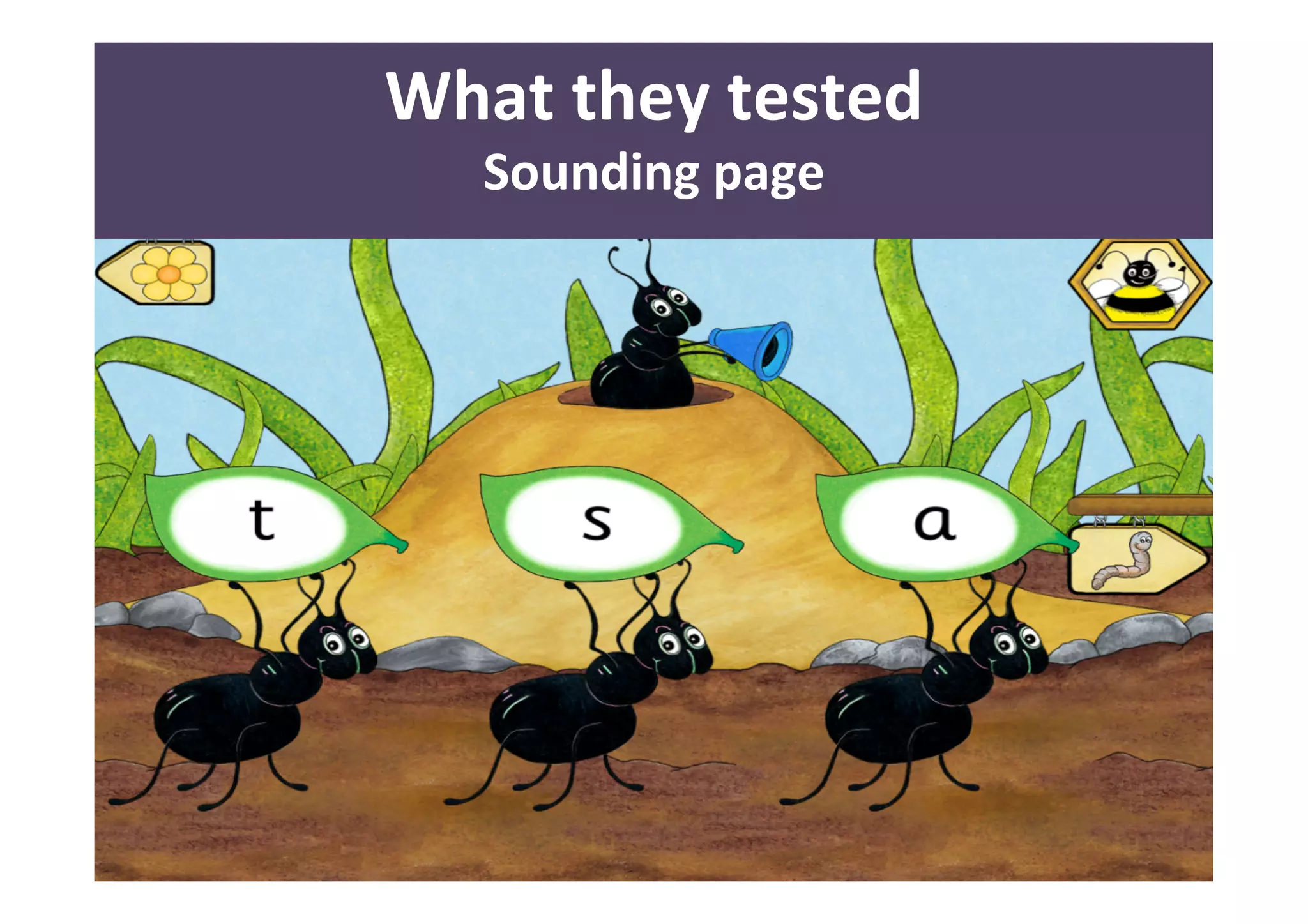
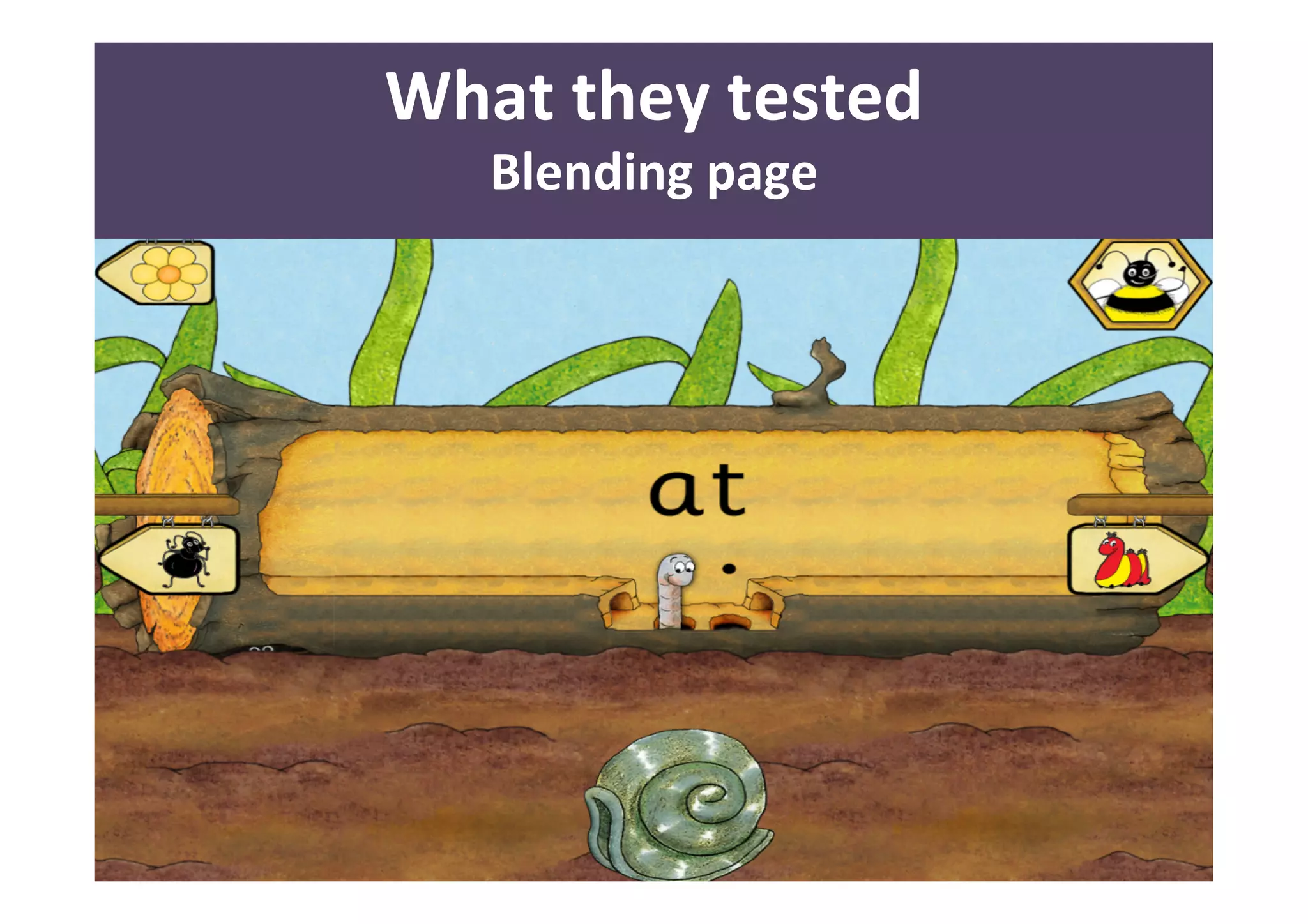
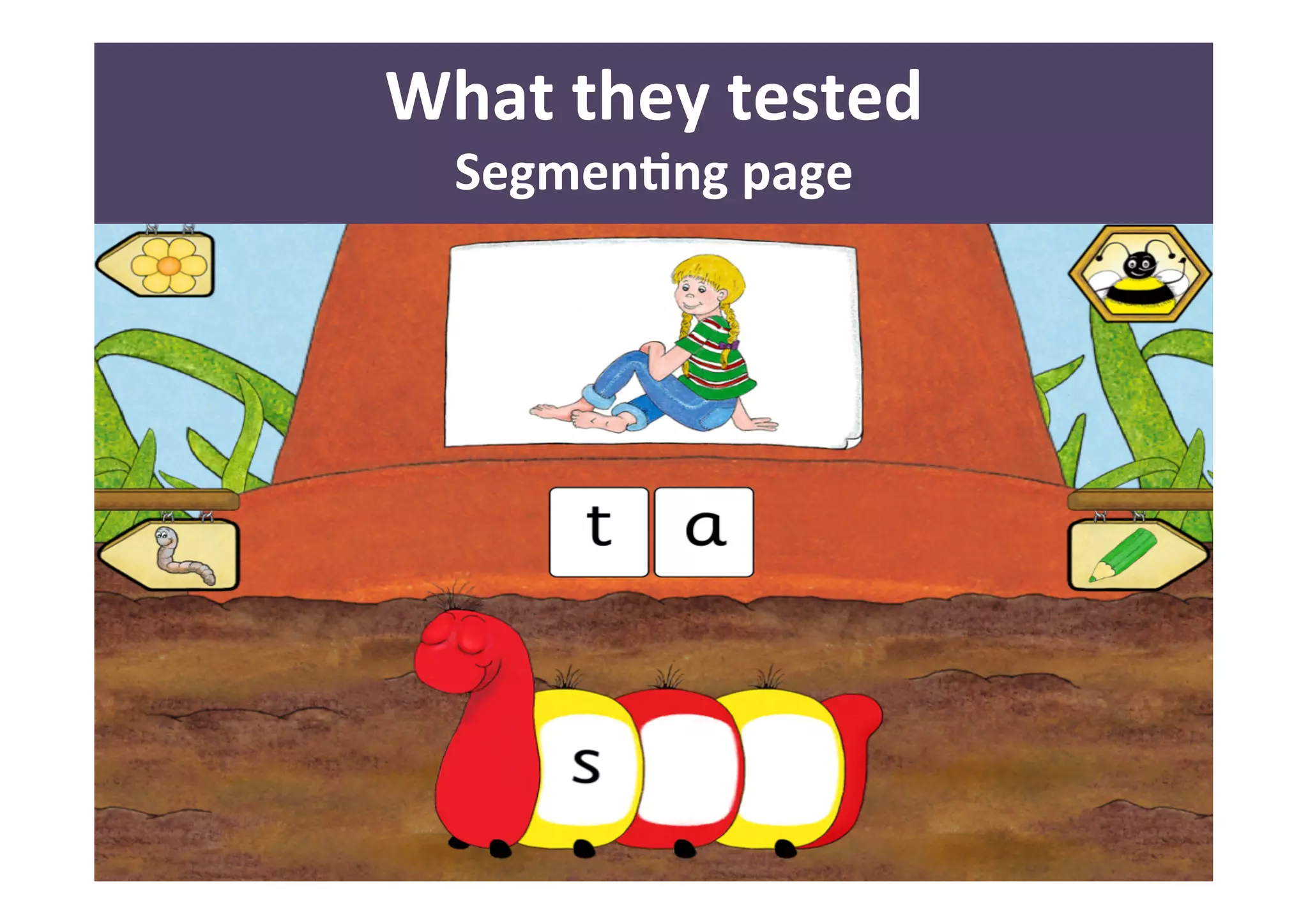
The document presents a case study on usability testing of the Jolly Phonics app with children aged 3-6, highlighting their developmental stages and how these affect technology engagement. It emphasizes the importance of user testing with children, the challenges they face while interacting with apps, and the insights gained for improving design. Key lessons include the need for clear goals, organization, and making children feel valued during testing sessions.


















![21
Se]ngs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxcambridge2014monicaferraropresentation-140915083502-phpapp01/75/UX-Cambridge-2014-Usability-testing-with-young-children-21-2048.jpg)
![22
Se]ngs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxcambridge2014monicaferraropresentation-140915083502-phpapp01/75/UX-Cambridge-2014-Usability-testing-with-young-children-22-2048.jpg)
![23
Se]ngs
“…Kids say the darndest things:
they just need to be confortable enough
to open up!”
- Bill Cosby](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxcambridge2014monicaferraropresentation-140915083502-phpapp01/75/UX-Cambridge-2014-Usability-testing-with-young-children-23-2048.jpg)
![24
Se]ngs
• Introduce yourself
“…Hi! I’m Monica and this is Alex…”
• Breaking the ice
• Give them importance
“…we have designed a new game to learn the
letters and we need your help to understand if it
works or not…would you like to help us please?...”
“…but remember…the design is till “top secret”!...”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uxcambridge2014monicaferraropresentation-140915083502-phpapp01/75/UX-Cambridge-2014-Usability-testing-with-young-children-24-2048.jpg)