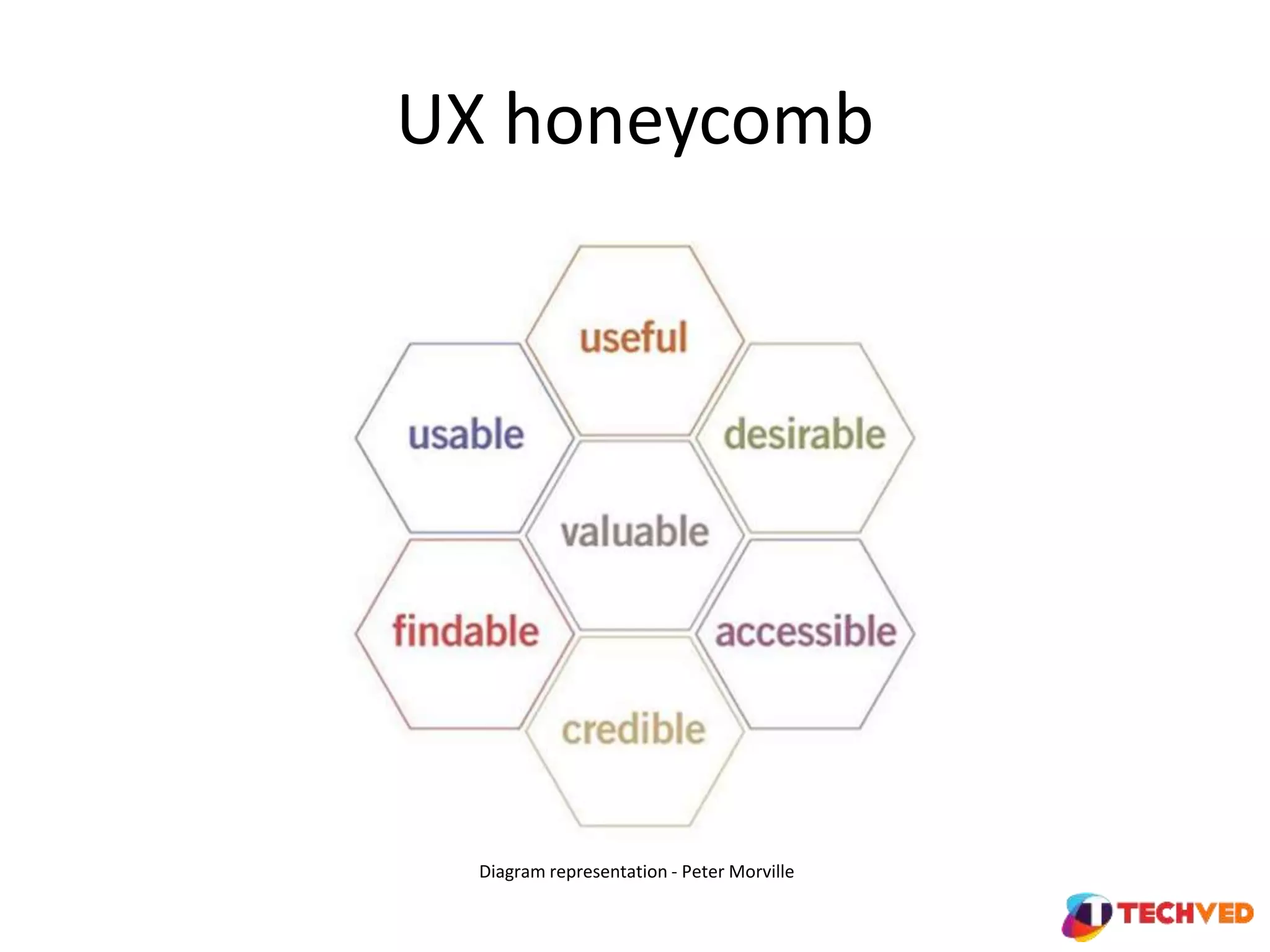
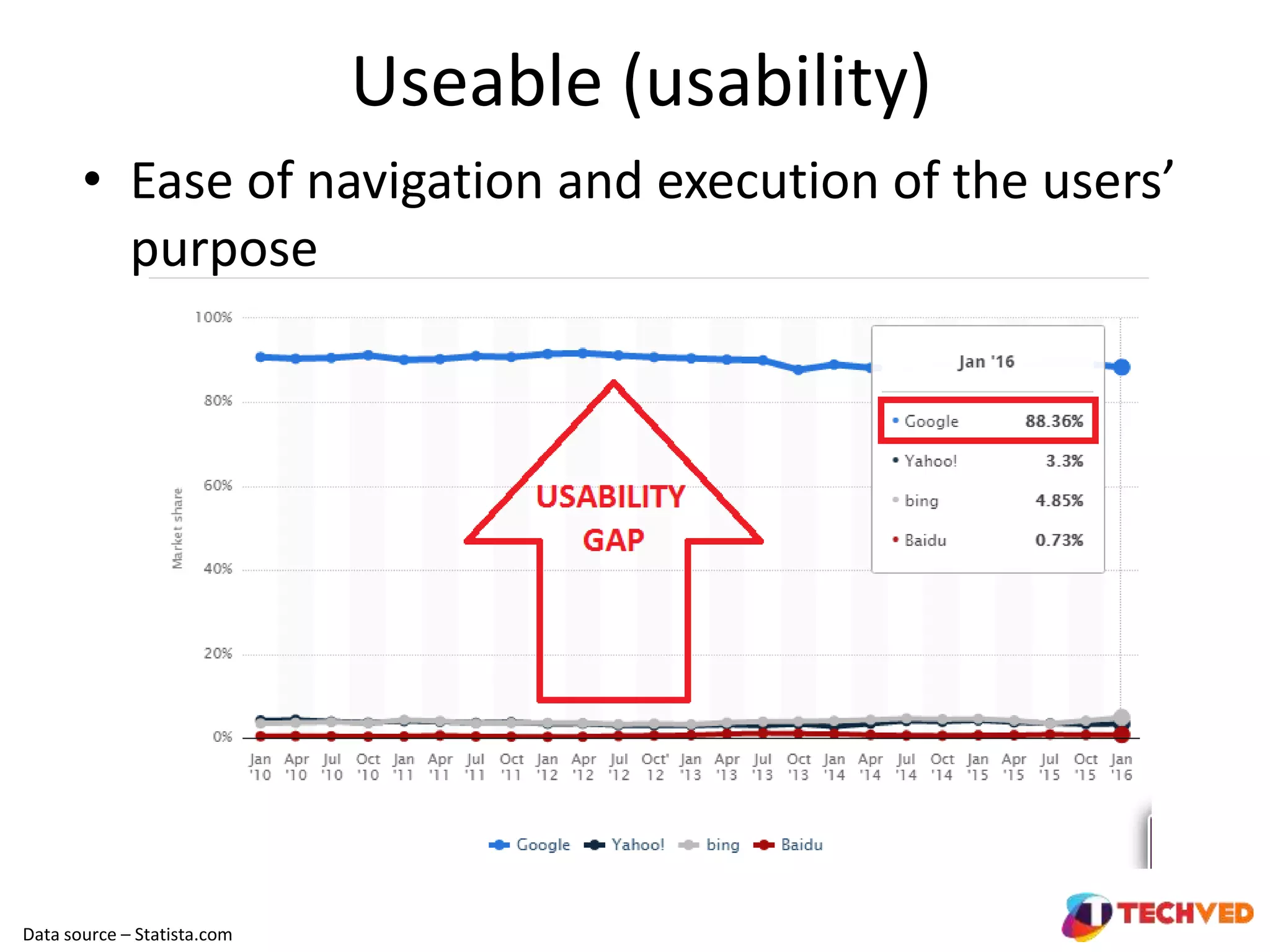
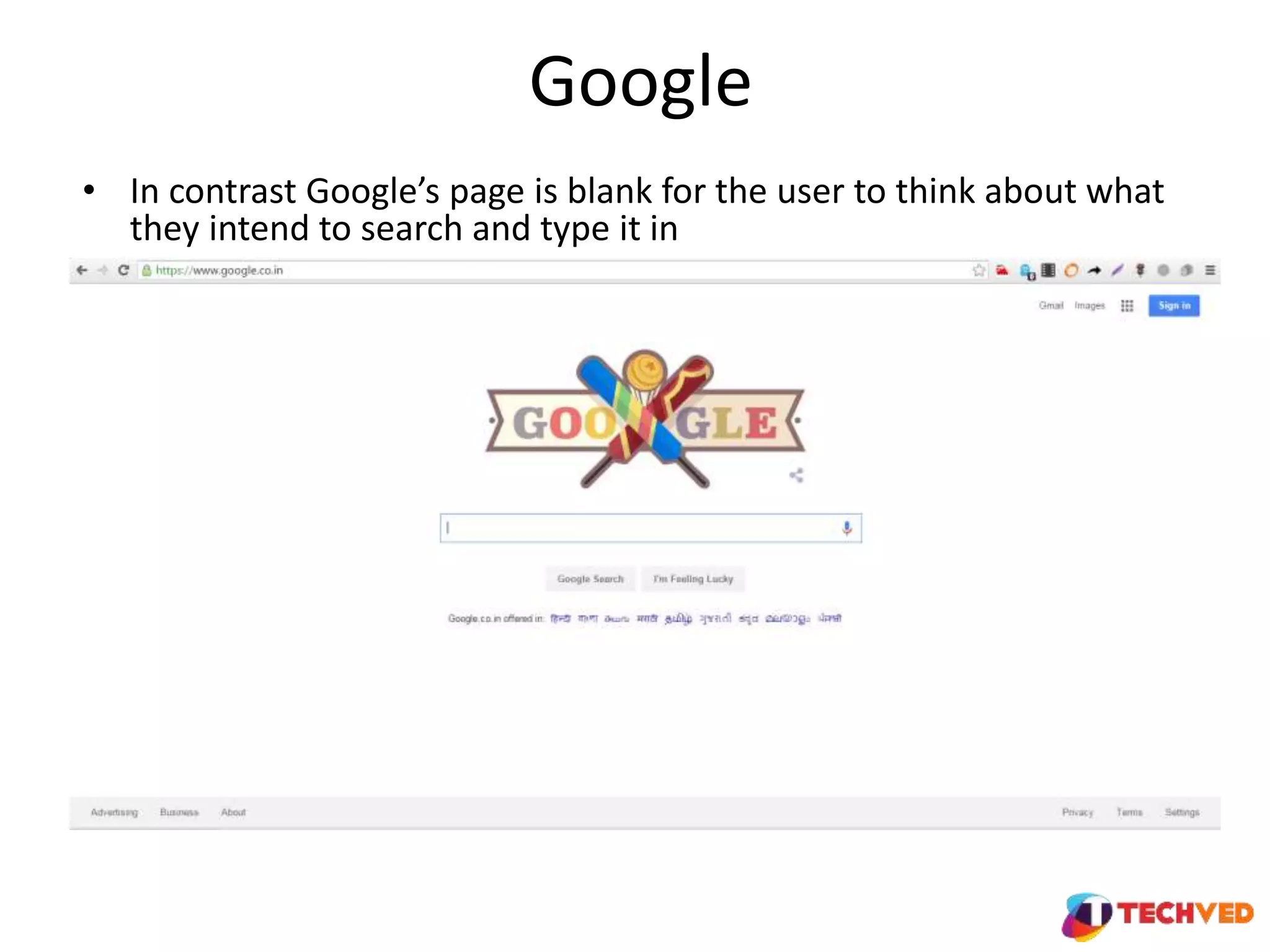
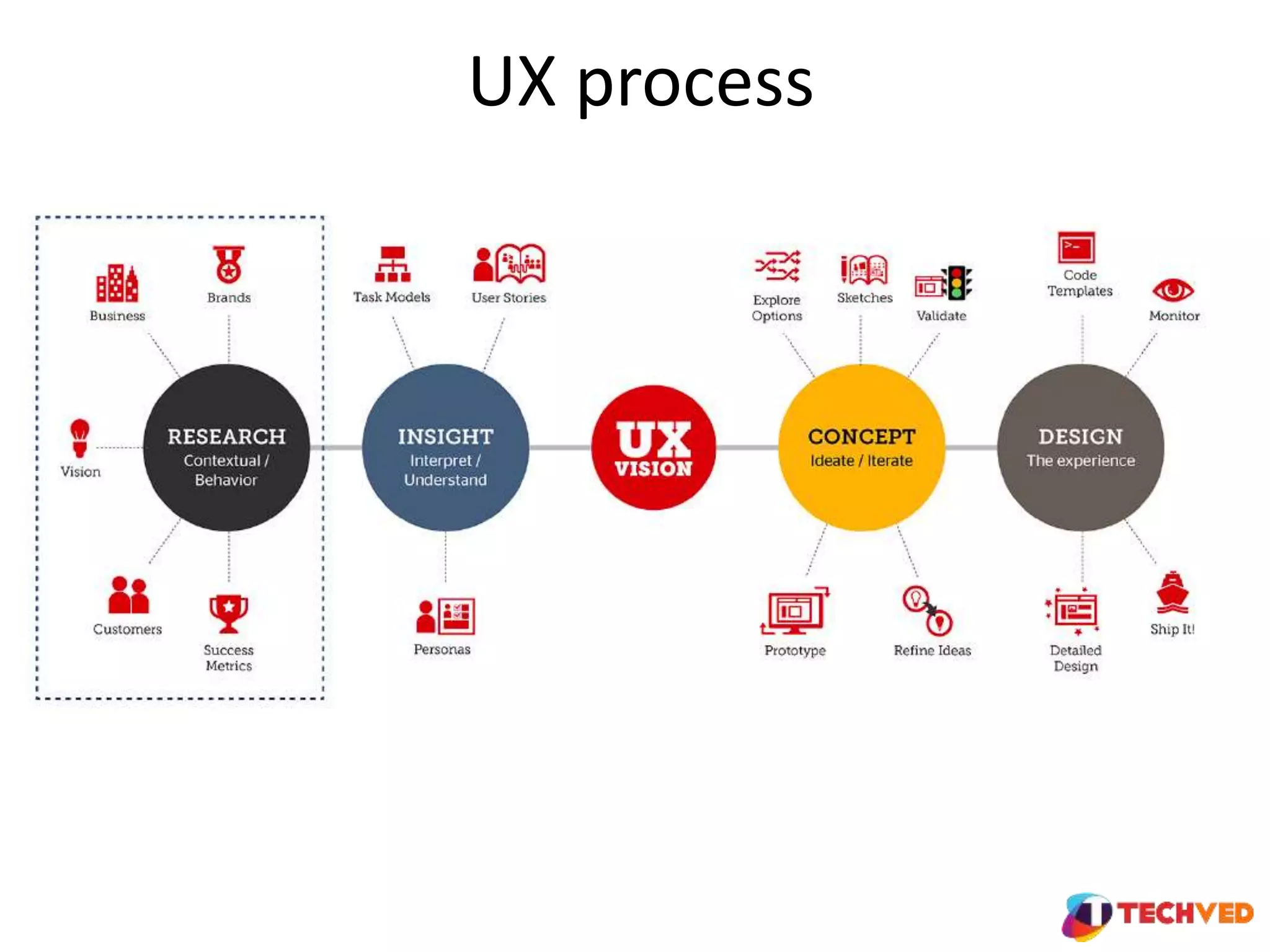
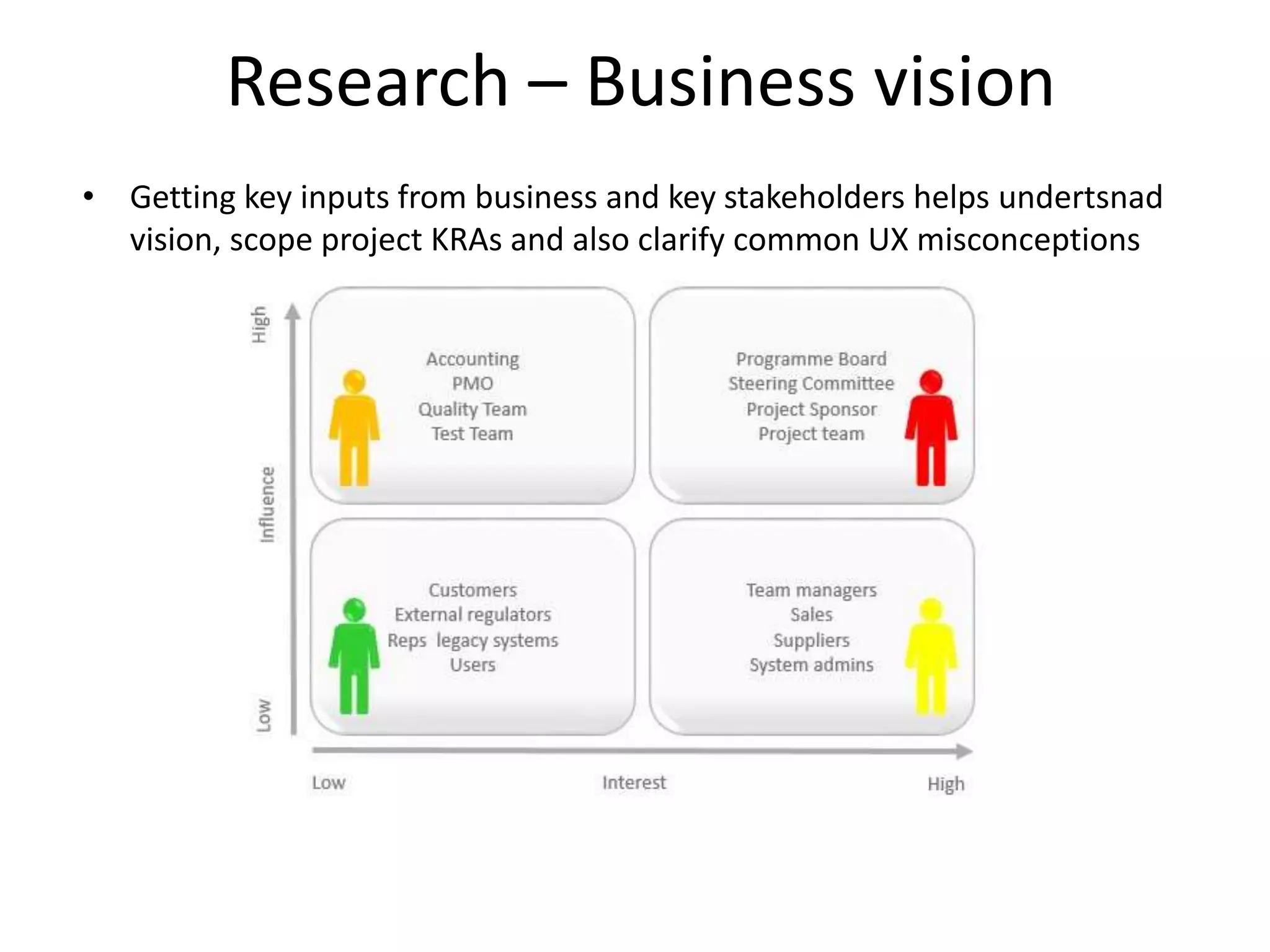
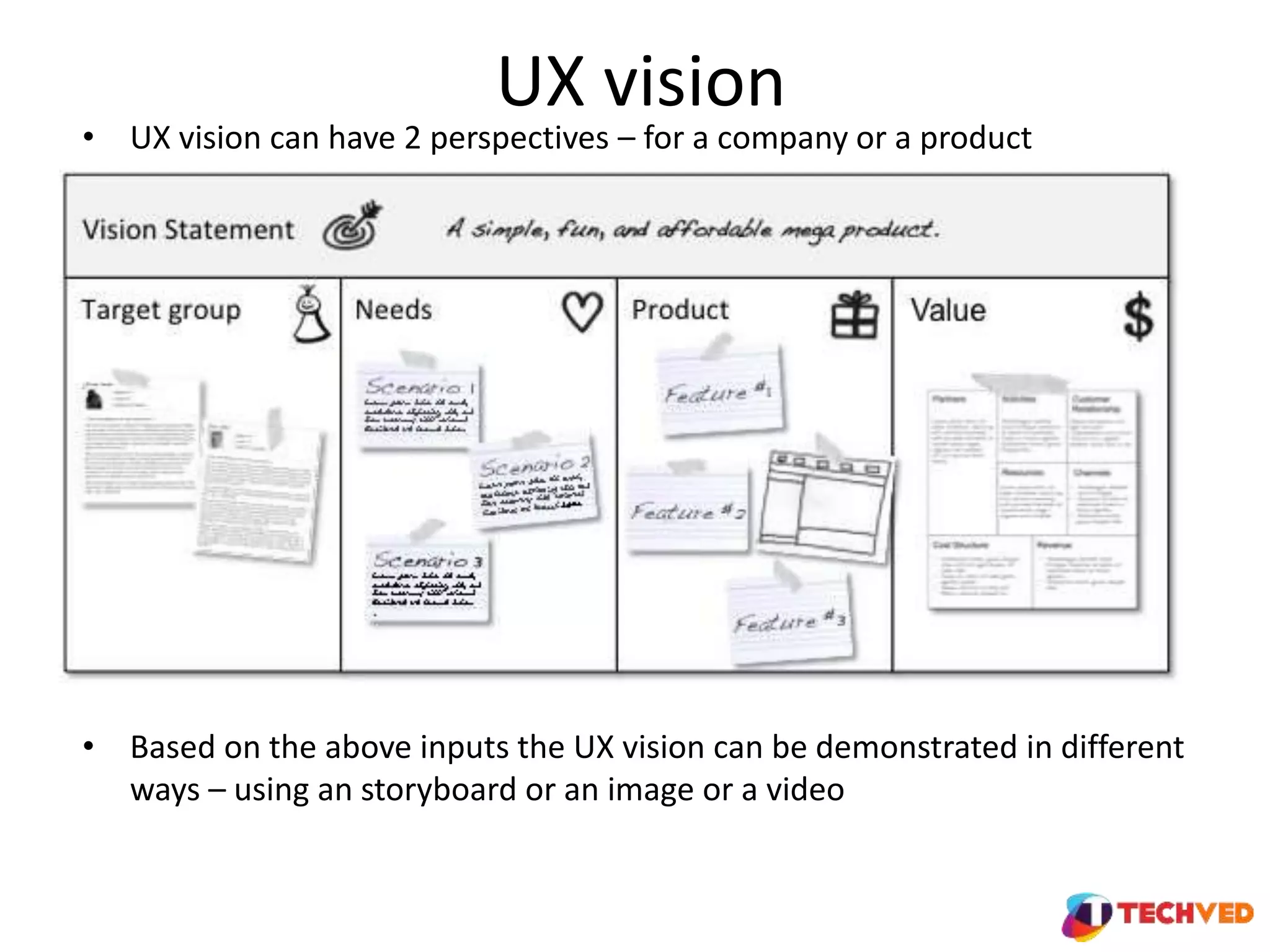
The document discusses essential UX design principles, emphasizing user needs, usability, and design elements that drive user engagement. It outlines a collaborative approach to comparative analysis of website usability, credibility, and user research practices that inform design strategies. The importance of mobile-first design and continuous testing is highlighted, alongside the necessity for a clear UX vision based on comprehensive research and insights.