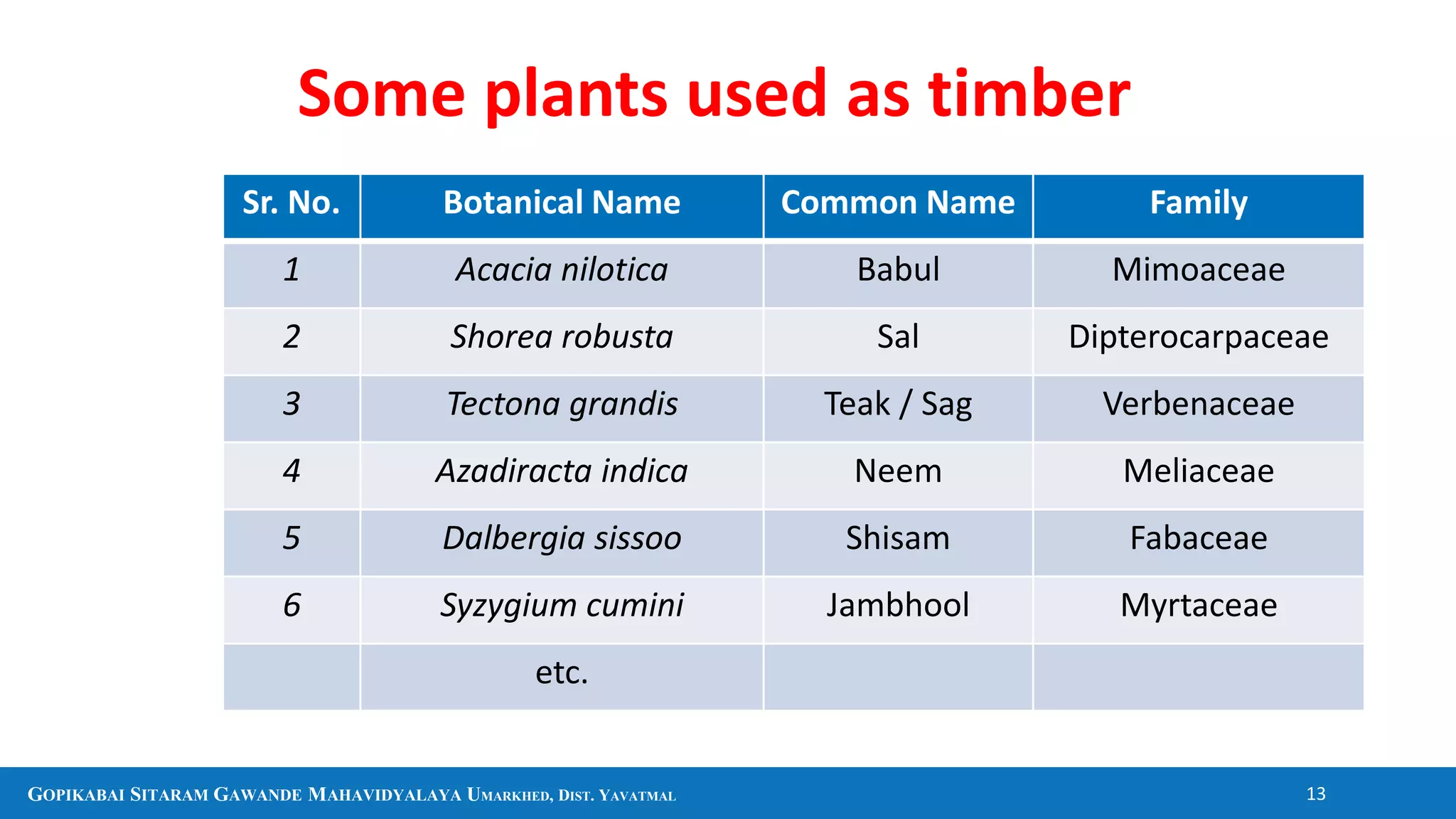
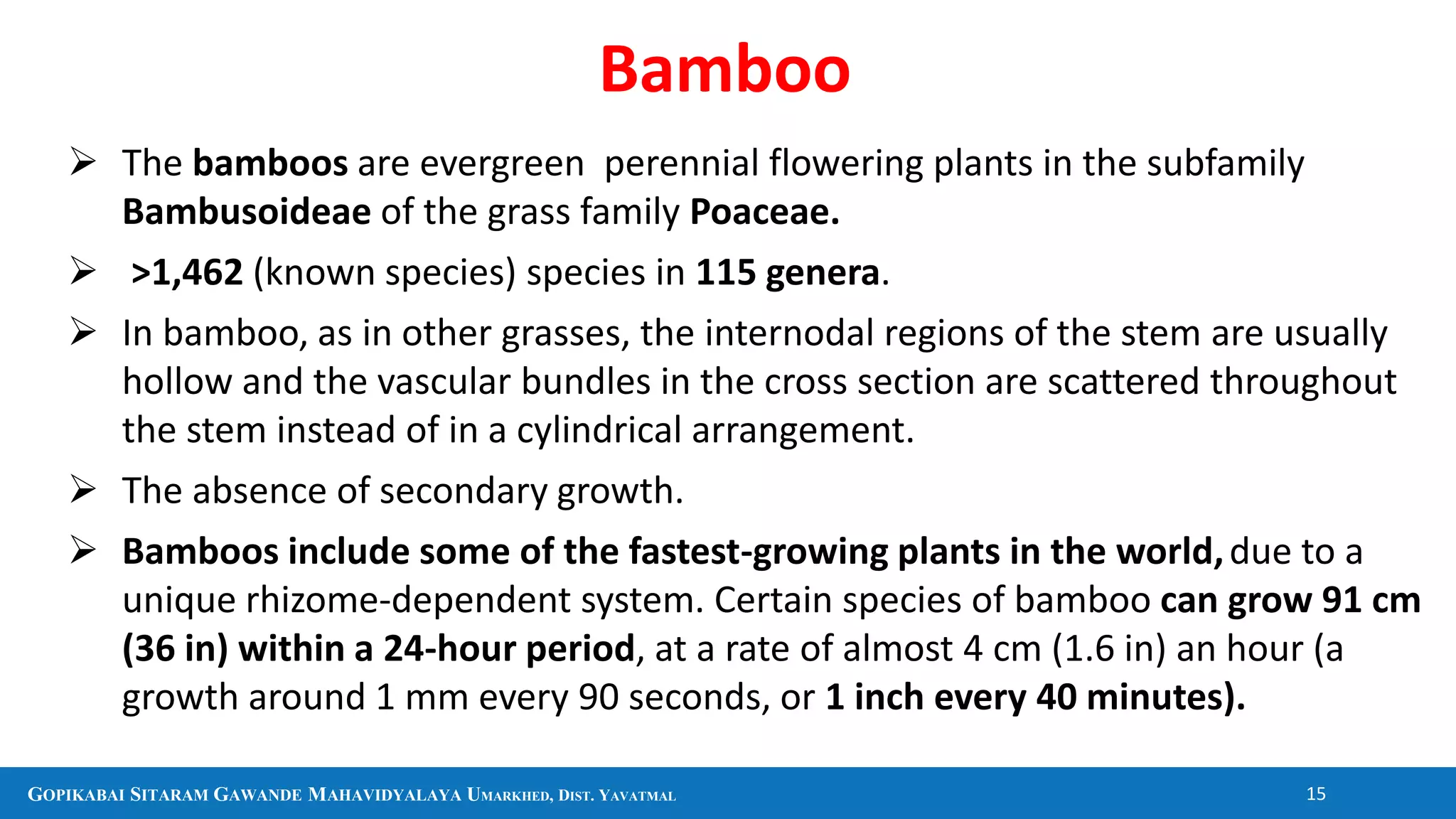
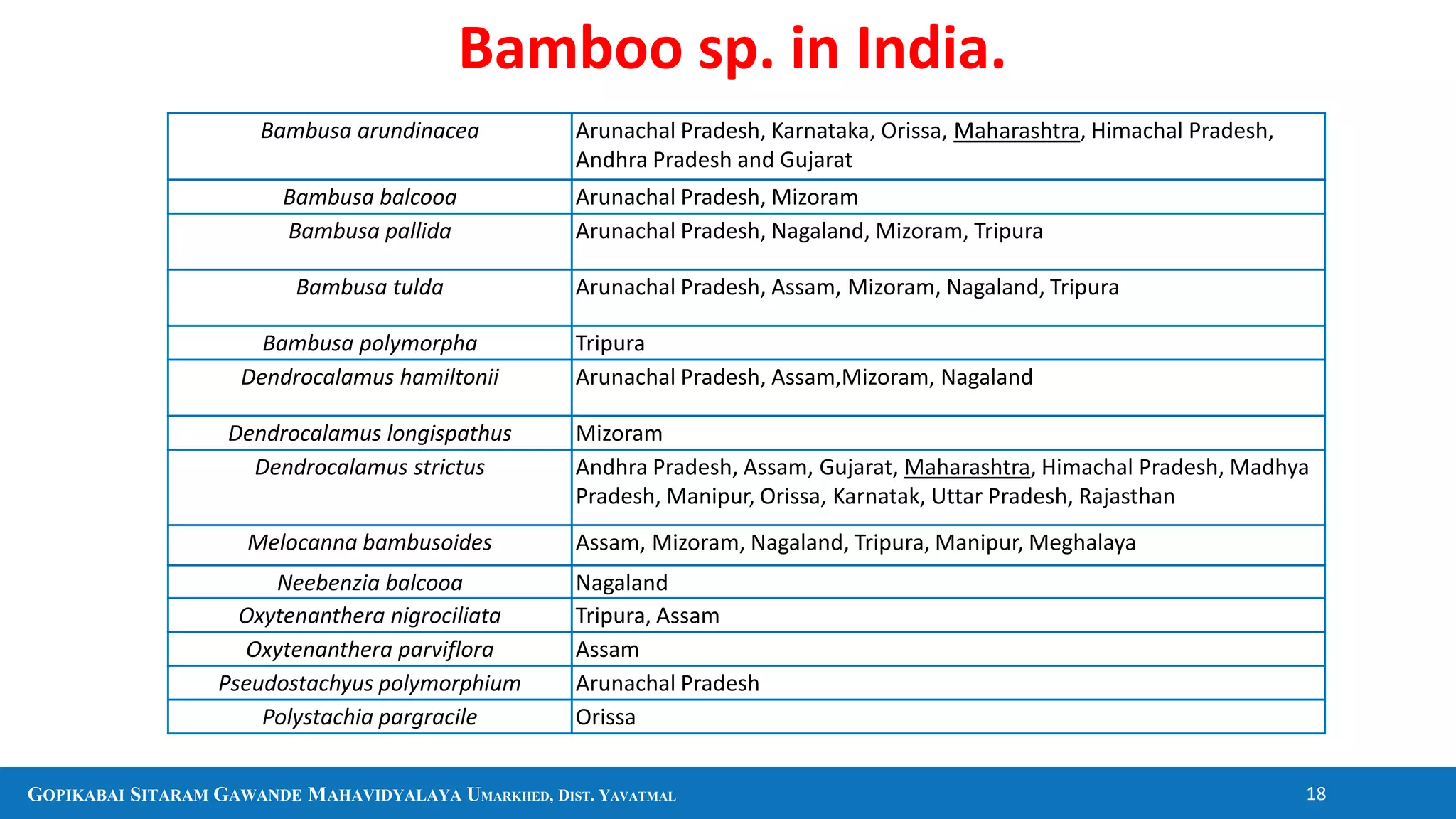
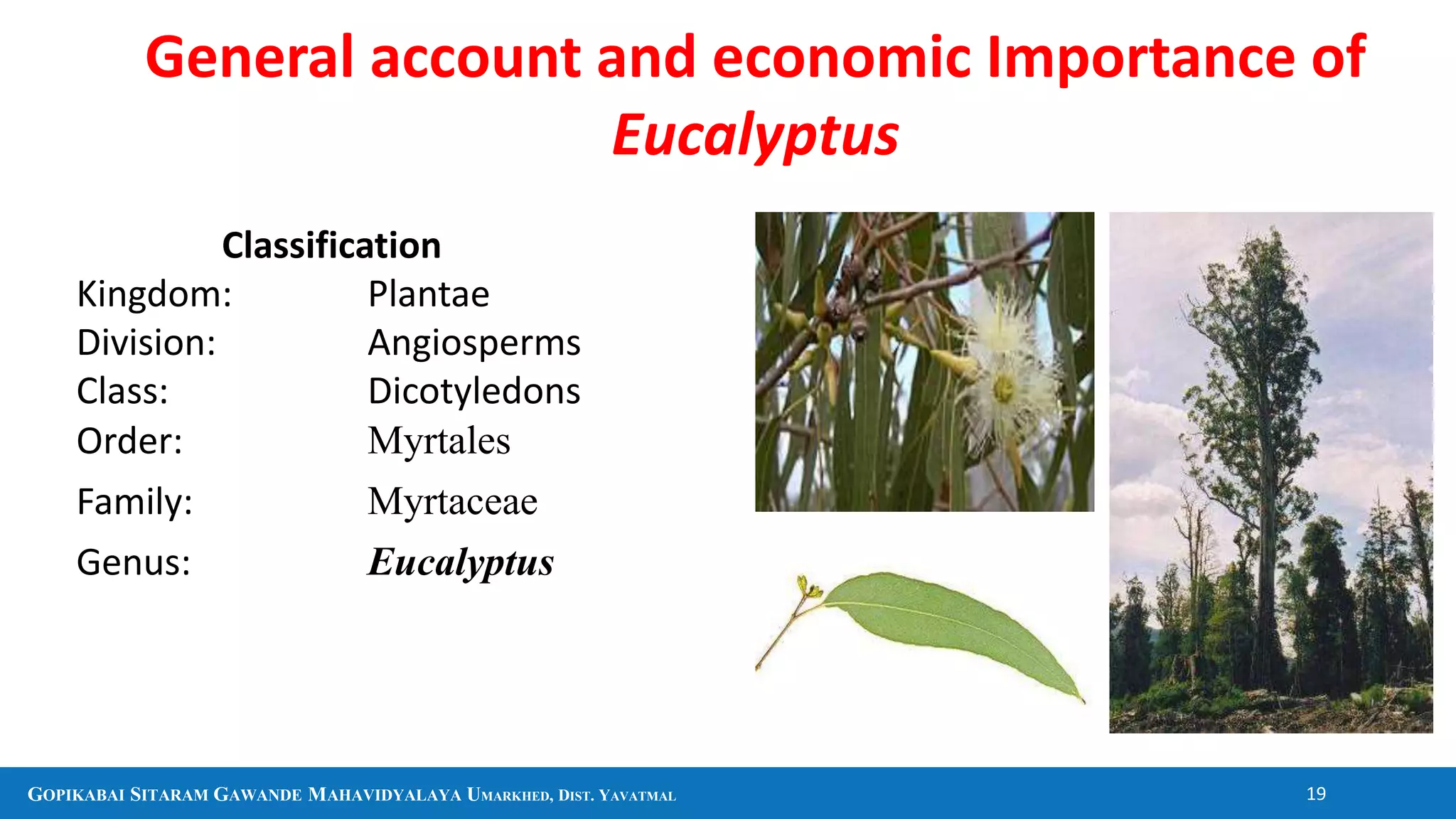
The document discusses several plants and their uses including black pepper, clove, cinnamon, cardamom, eucalyptus, and aloe vera. It provides information on their botanical classification, traditional medicinal uses, economic importance as spices or other products, and in some cases chemical constituents. It also covers general topics like sources of firewood, timber, bamboo, and pharmacognosy.