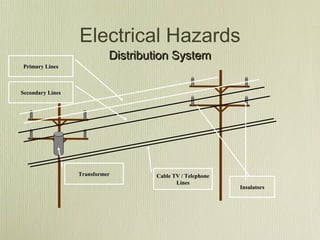
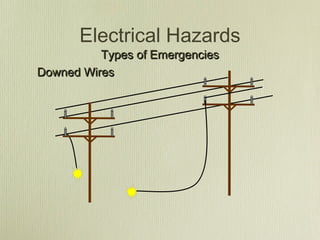
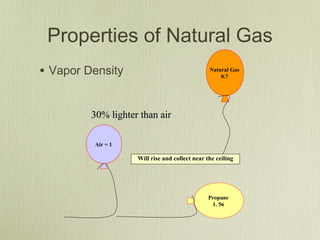
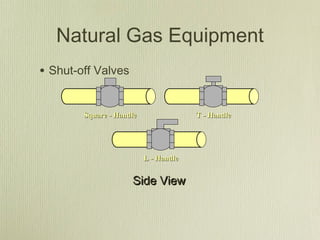
This document discusses utility emergencies involving electricity, natural gas, and propane. It provides information on electrical distribution systems, hazards of downed power lines, pole/transformer fires, vehicle accidents involving poles, and manhole fires. Guidelines are given for establishing safety zones, contacting utility companies, and safely responding to various emergency scenarios until utilities personnel arrive to isolate energy sources. Personnel are advised to treat all wires and gas/propane equipment as energized until proven otherwise and to avoid actions that could cause arcing or explosions.