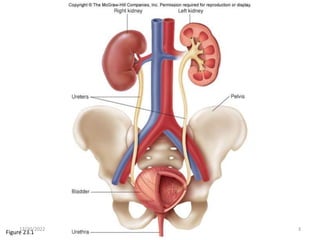
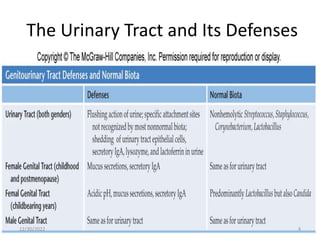
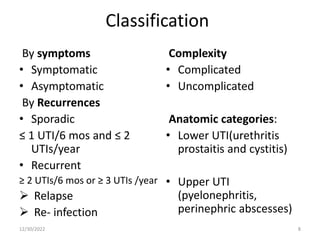
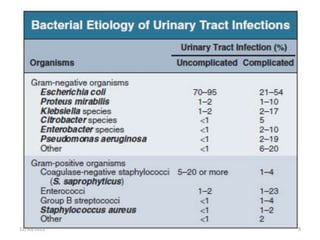
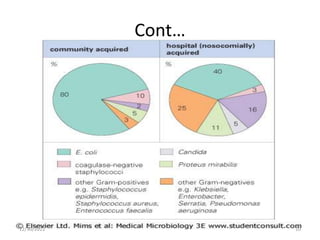
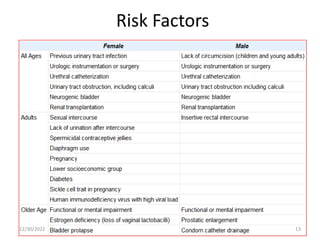
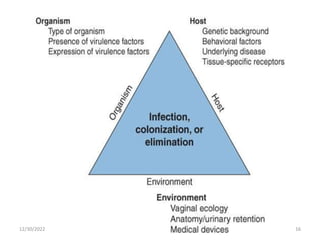
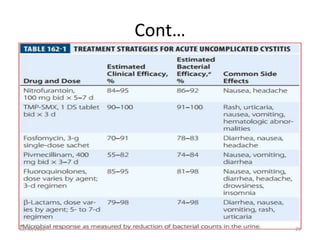
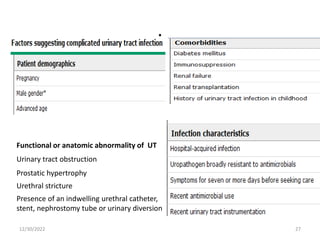
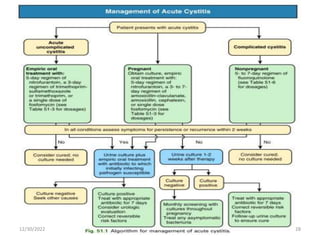
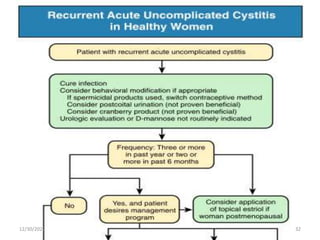
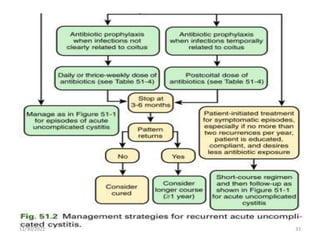
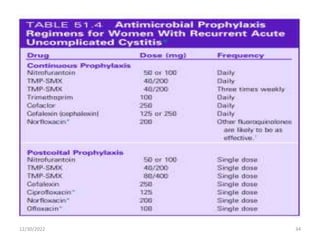
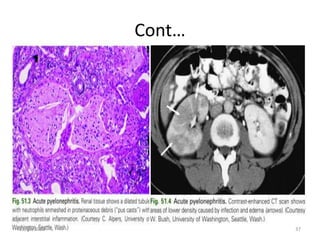
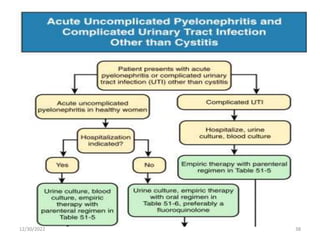
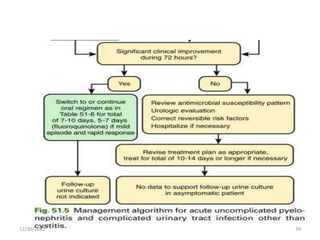
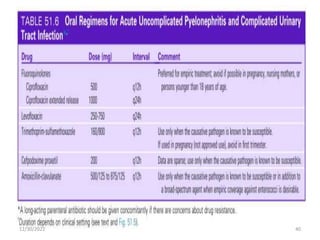
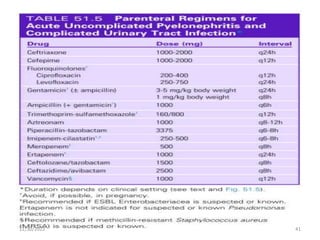
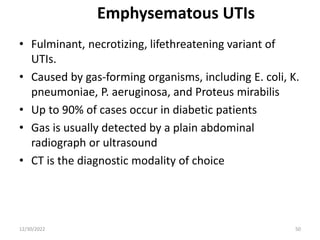
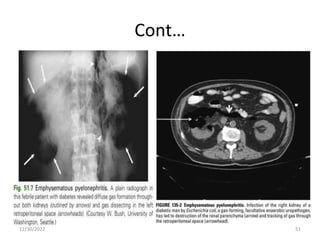
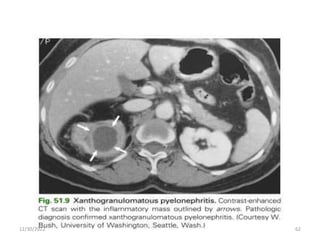
This document provides an overview of urinary tract infections. It discusses the epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, pathogenesis, diagnosis, clinical presentation and management of various urinary tract infections. The types of infections covered include asymptomatic bacteriuria, cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatitis, catheter-associated UTIs, recurrent UTIs and emphysematous UTIs. Diagnosis involves urine culture and microscopy. Management depends on the specific clinical syndrome and includes antibiotic treatment tailored to the identified organism.