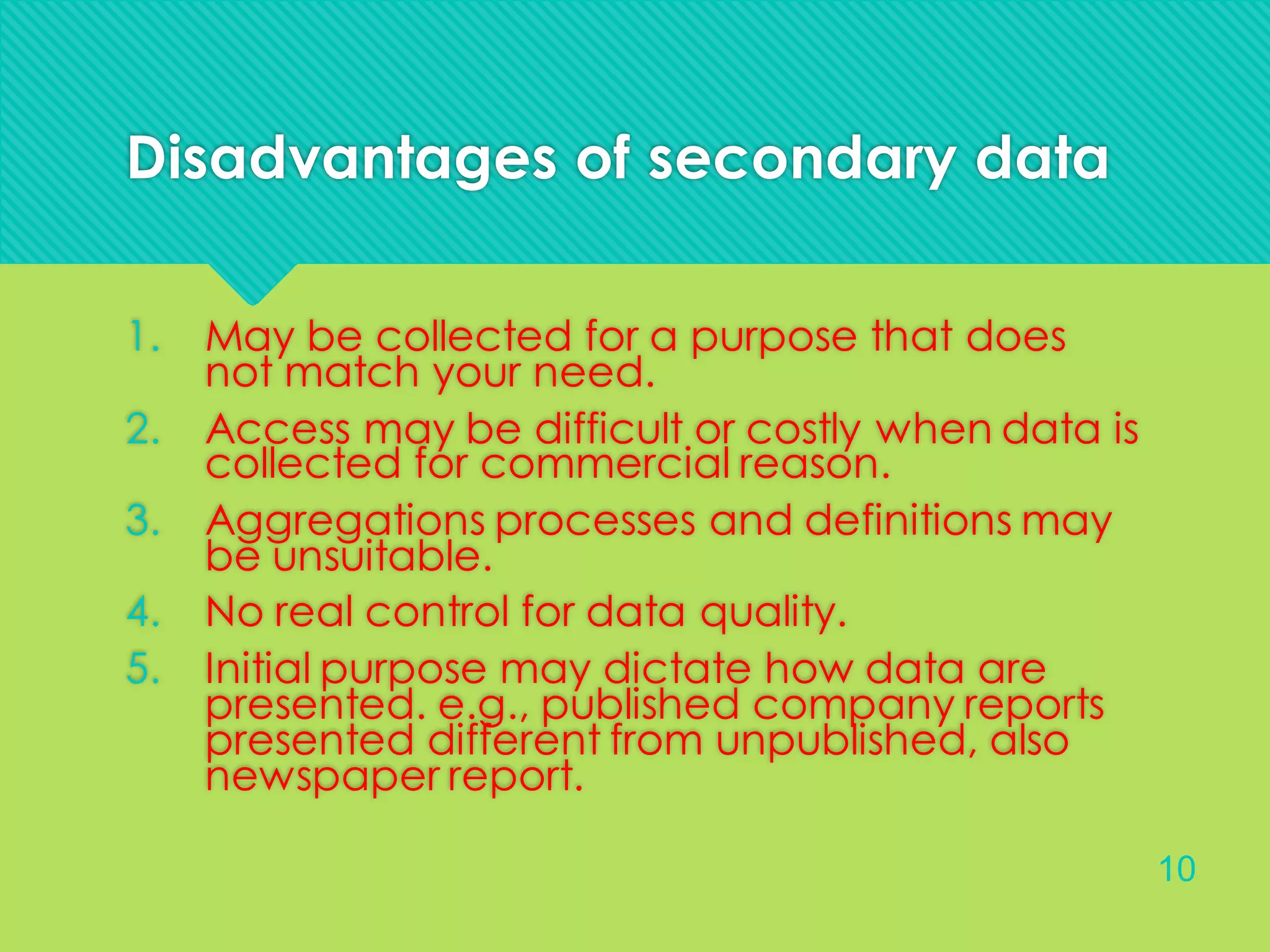
This document discusses the use of secondary data in research. It defines secondary data as data that has already been collected by someone else for another purpose. There are three main types of secondary data: documentary, survey-based, and multiple-source. Documentary data includes written materials like reports and non-written materials like photographs. Survey-based data refers to data collected from questionnaires by censuses, regular surveys, or ad-hoc surveys. Multiple-source data can be based on documentary or survey data and includes area-based and time series data. The document outlines advantages of secondary data like being less expensive and allowing longitudinal studies, but also disadvantages like data not matching the researcher's needs or lack of control over data quality.