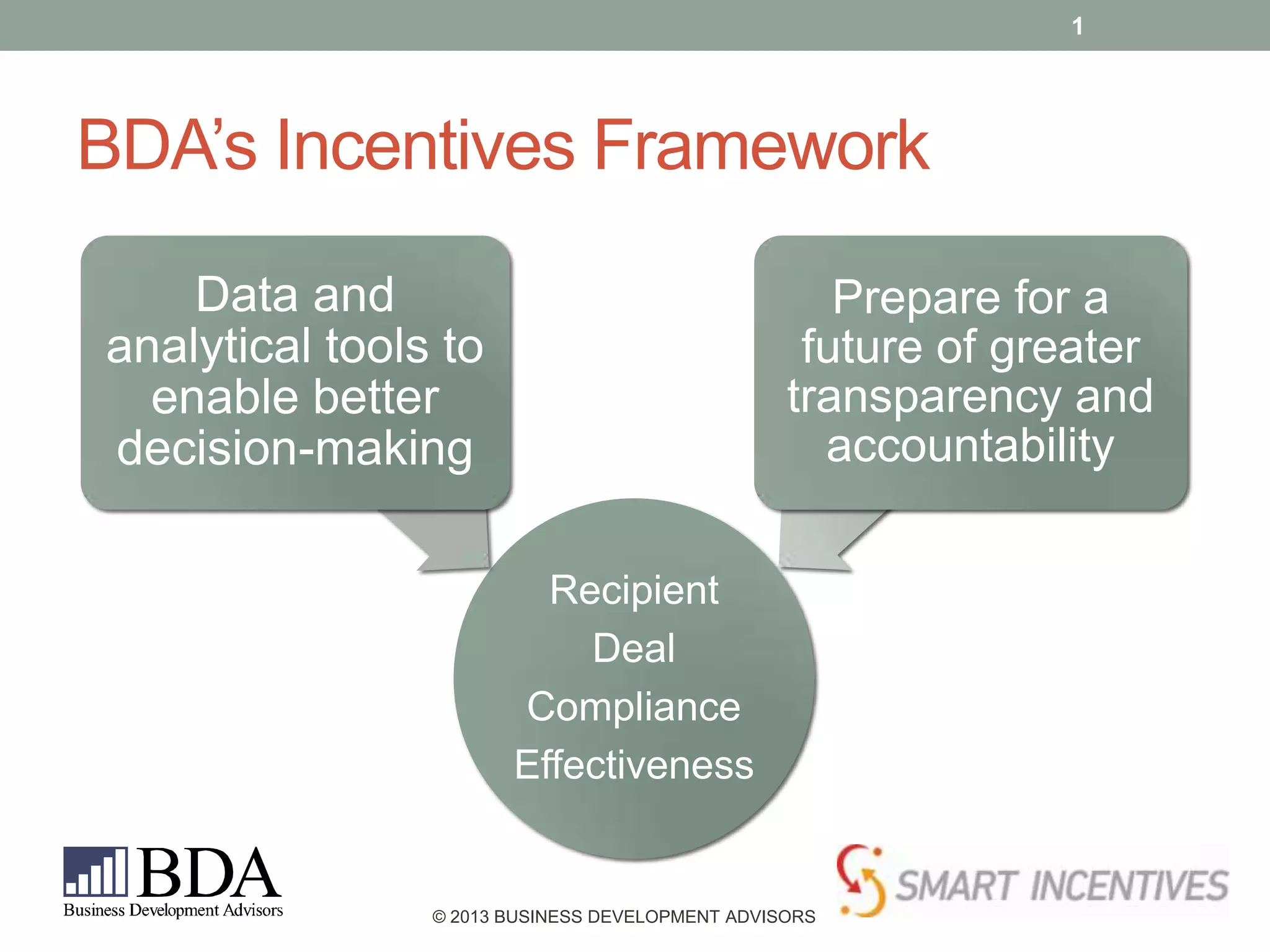
The document outlines a framework for using incentives in community economic development, emphasizing the importance of effective decision-making and compliance monitoring. It describes various incentive categories, assesses potential project benefits, fiscal and economic impacts, and provides guidelines for managing and evaluating effectiveness. The need for transparency and accountability in incentive usage is highlighted, alongside shortcomings in current reporting practices.