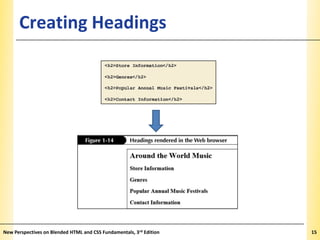
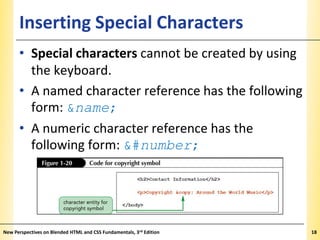
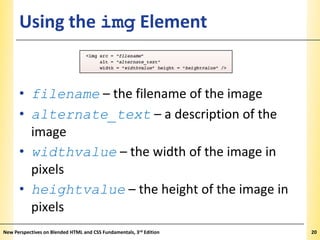
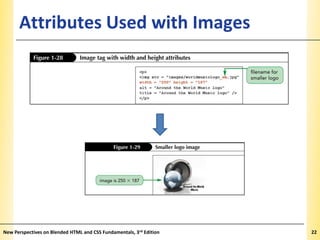
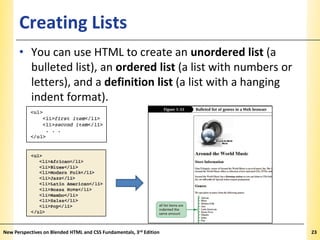
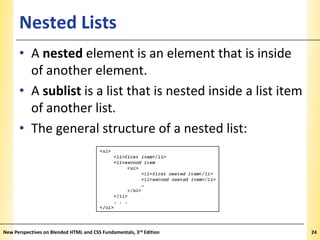
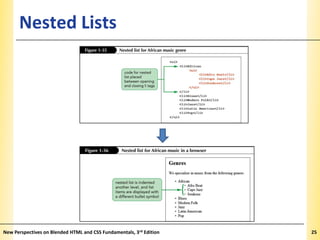
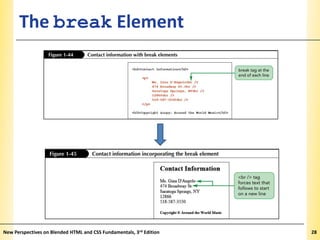
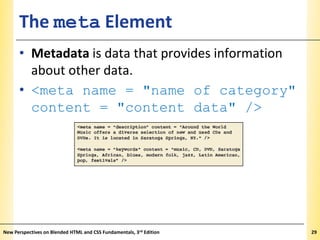
This document provides an introduction to HTML and creating web pages. It covers the basics of HTML including important tags like <html>, <head>, and <body>. It describes how to add headings, paragraphs, text formatting, images, and lists to a web page. The document also discusses validating code and using comments. The overall purpose is to teach students how to structure an HTML document and basic elements to include on a web page.