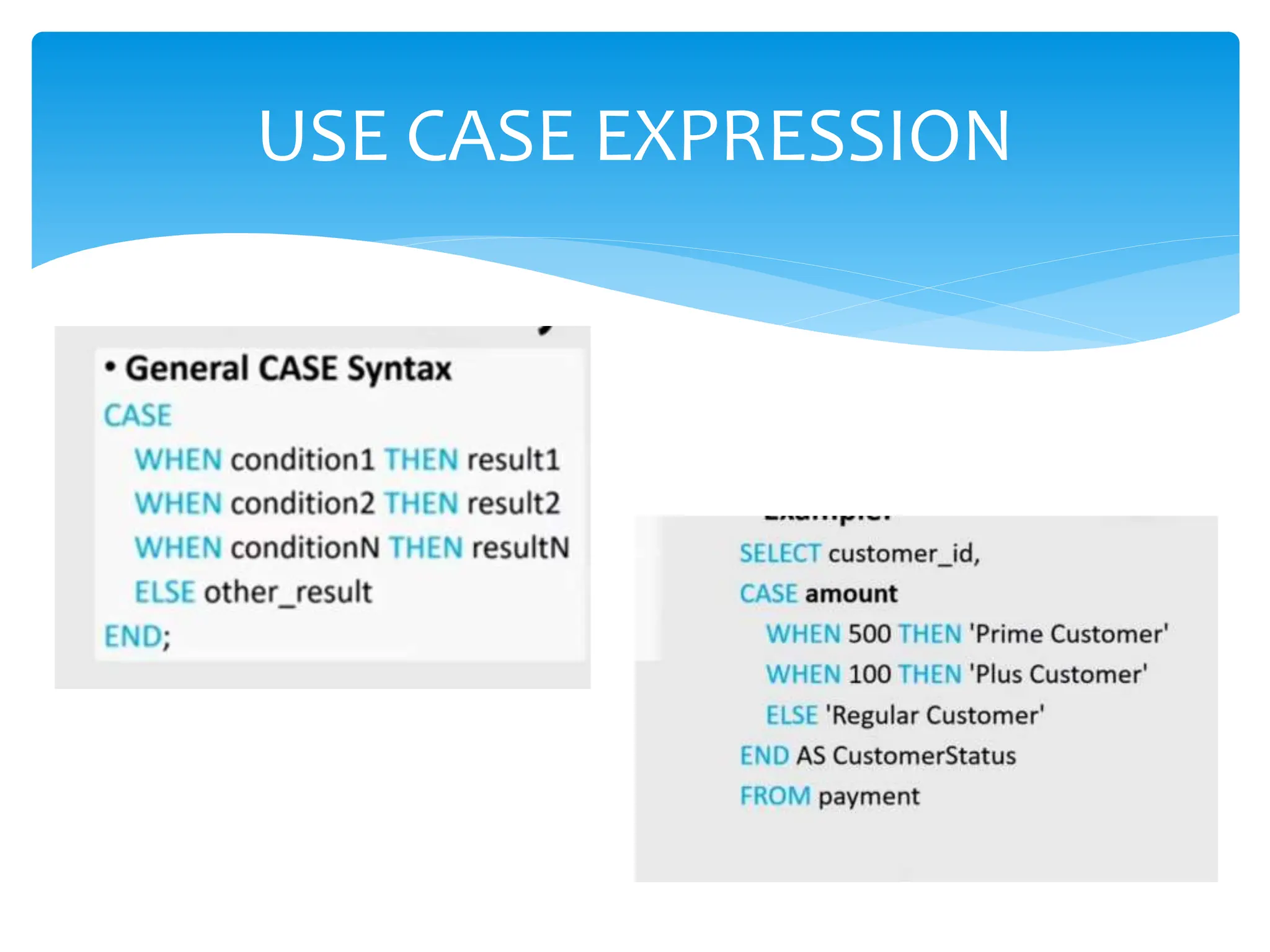
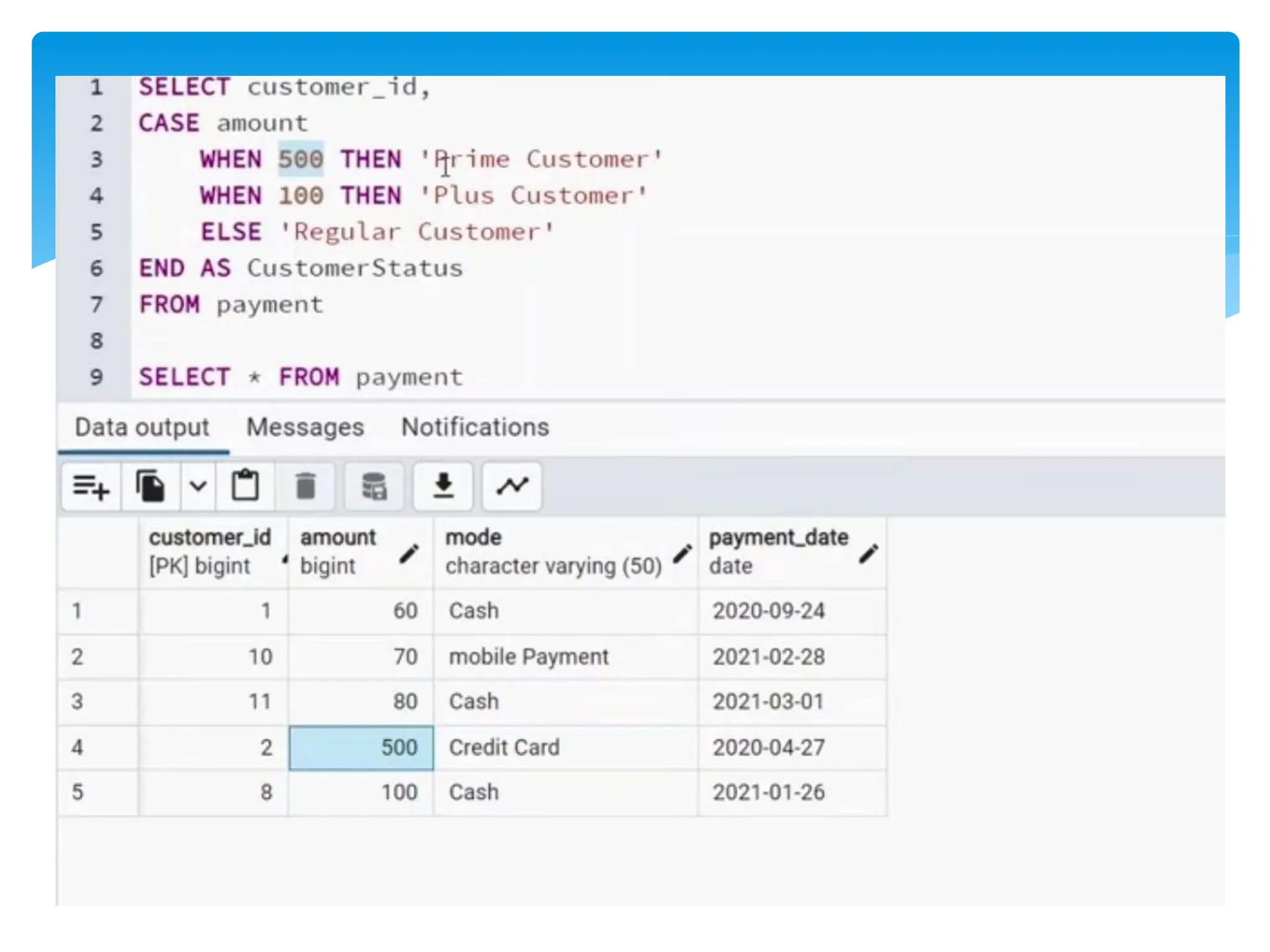
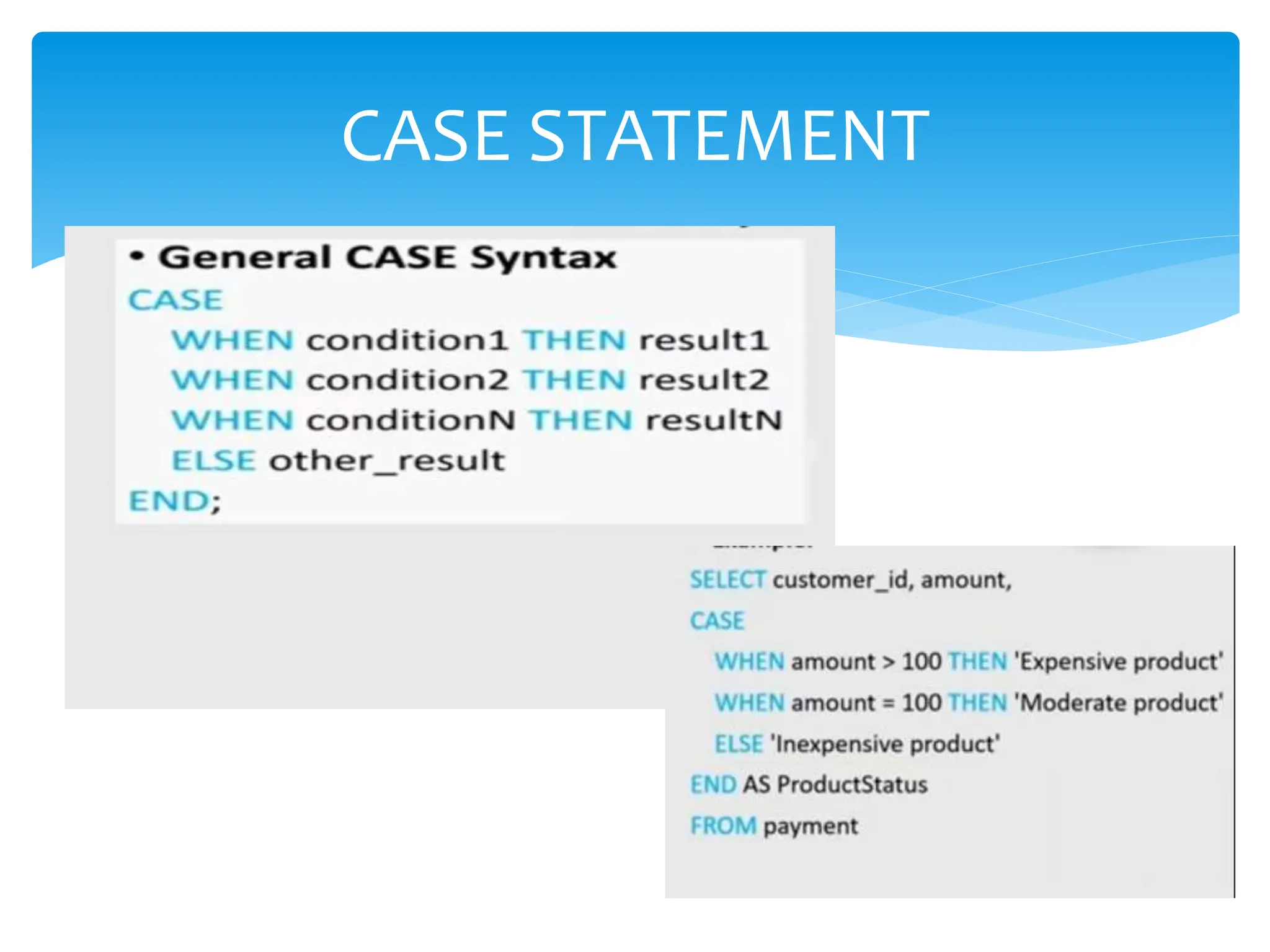
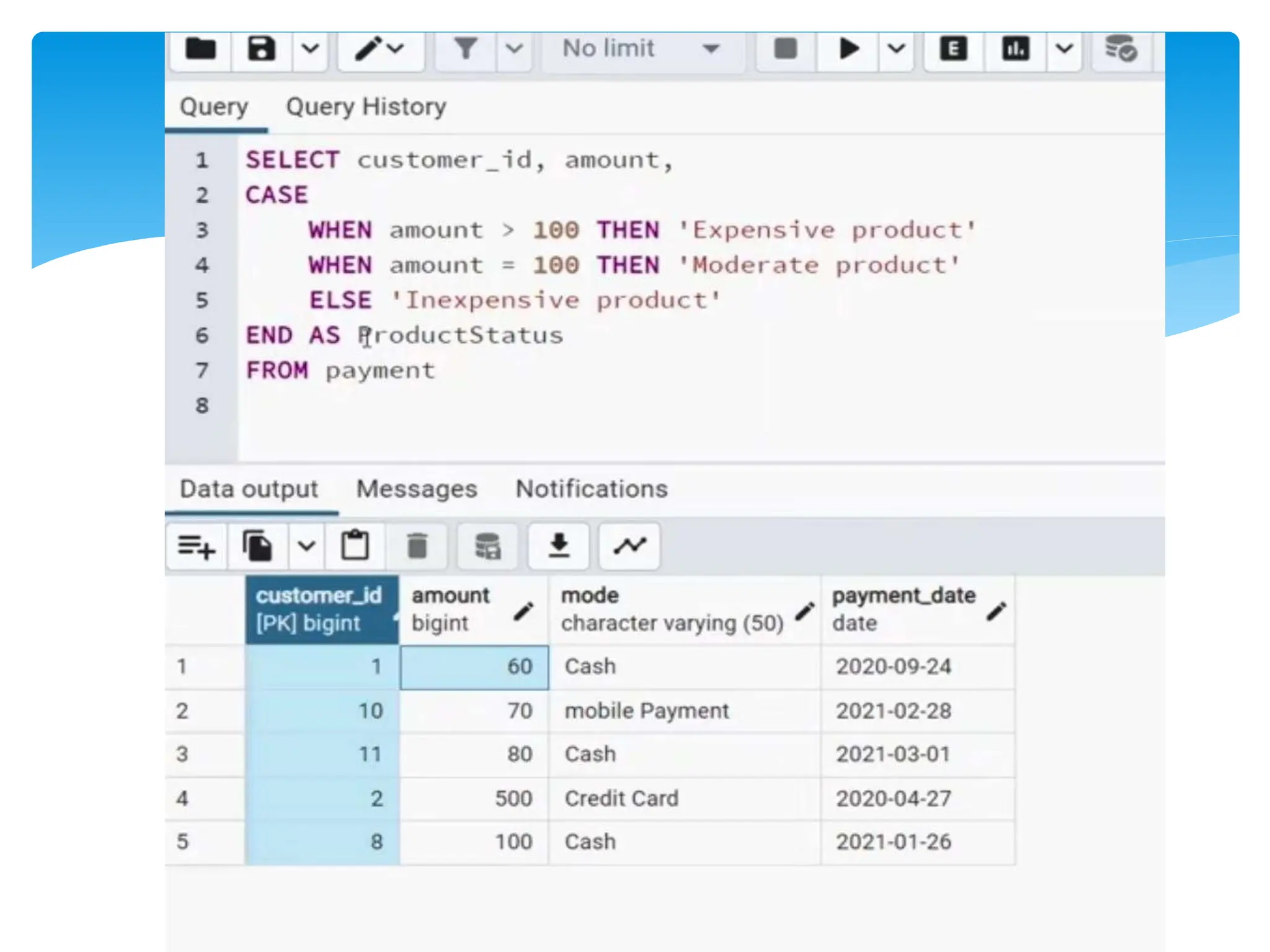
The document discusses use cases in SQL, highlighting scenarios such as data retrieval, manipulation, and analysis. It addresses scalability strategies including indexing, partitioning, caching, load balancing, and data sharding to enhance performance. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of query optimization, appropriate data types, and well-designed database architecture for improving SQL performance.