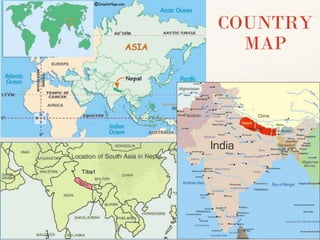
Nepal is a landlocked country located in South Asia with a population of over 30 million people. The capital and largest city is Kathmandu. Nepal has experienced much political upheaval in recent decades, transitioning from a monarchy to a democratic republic. It remains one of the poorest countries in the world, with many people working in agriculture and industries like clothing production. Hinduism and Buddhism are the dominant religions.