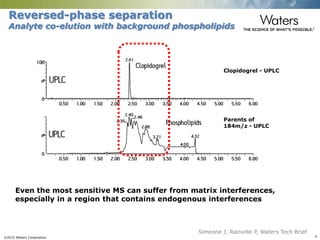
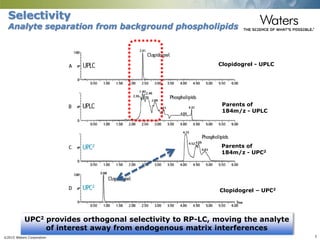
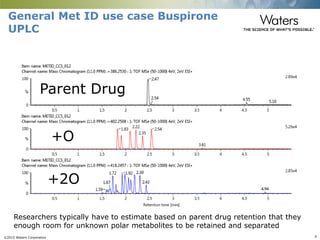
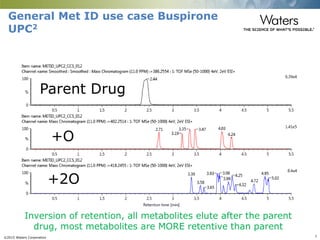
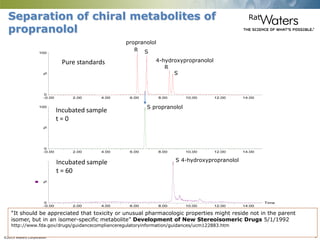
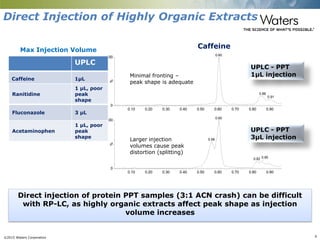
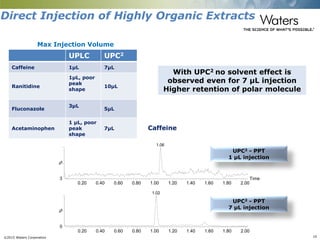
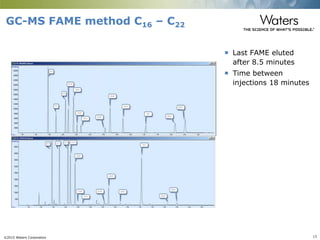
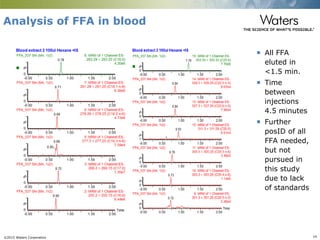
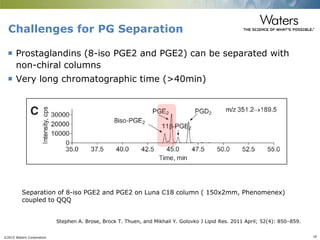
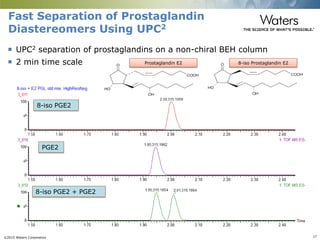
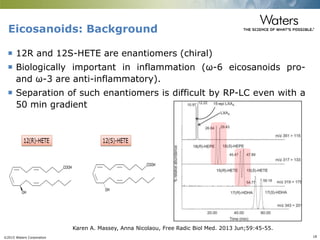
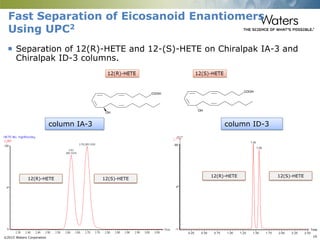
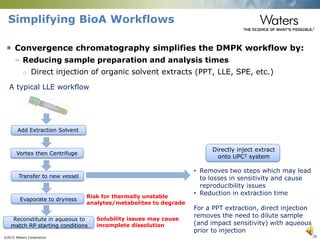
This document discusses the use of single column convergence chromatography/mass spectrometry (UPC2/MS) for bioanalytical studies. It provides examples of how UPC2/MS can simplify workflows by reducing sample preparation times through direct injection of extracts and improving selectivity over reversed phase chromatography. UPC2/MS also allows for faster separation of challenging compound classes like isomers and lipids compared to traditional techniques like gas chromatography. The document concludes that UPC2/MS provides an orthogonal separation method and combines multiple techniques into one analytical platform for streamlining quantitative bioanalysis in drug discovery and development.