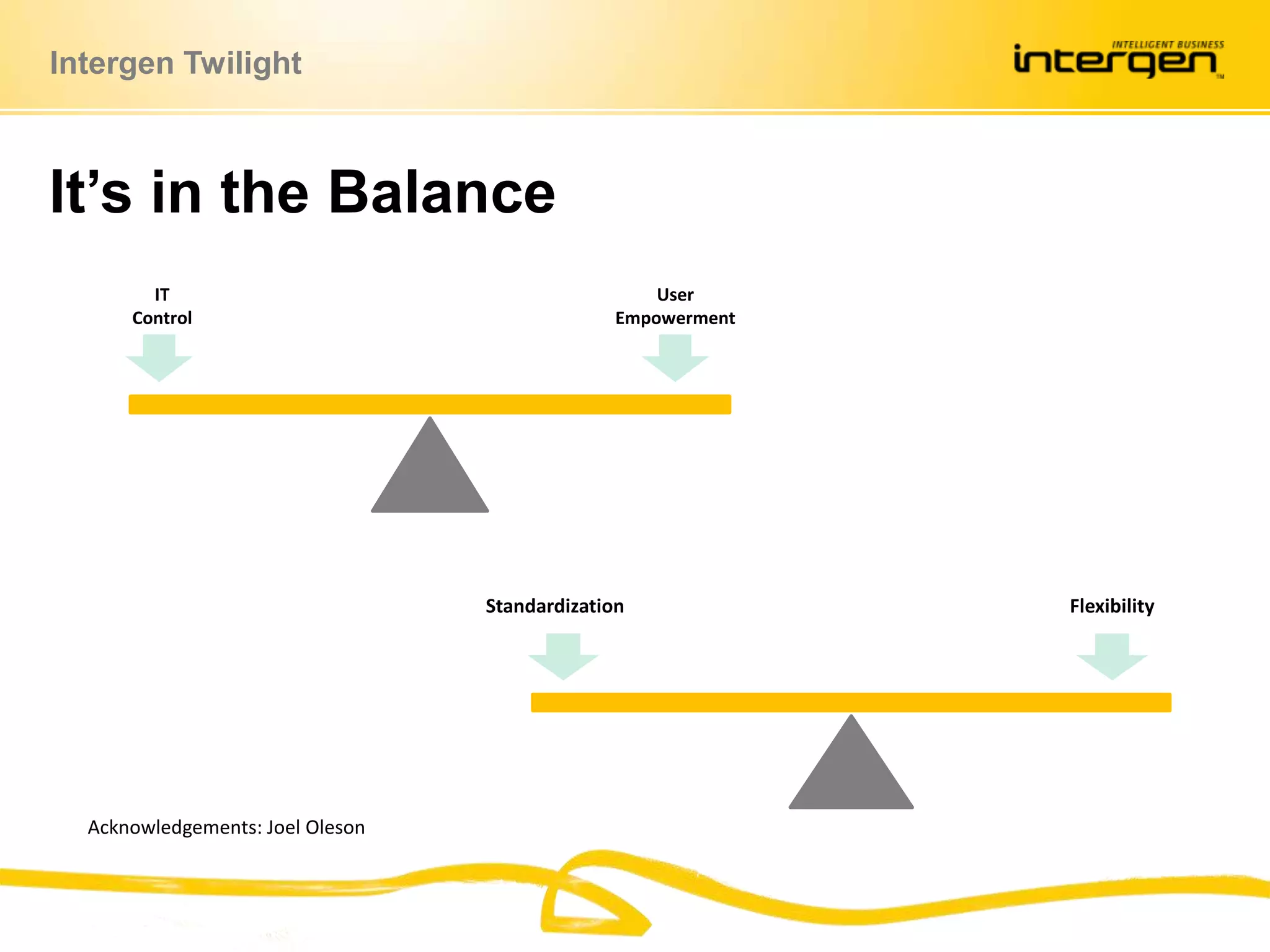
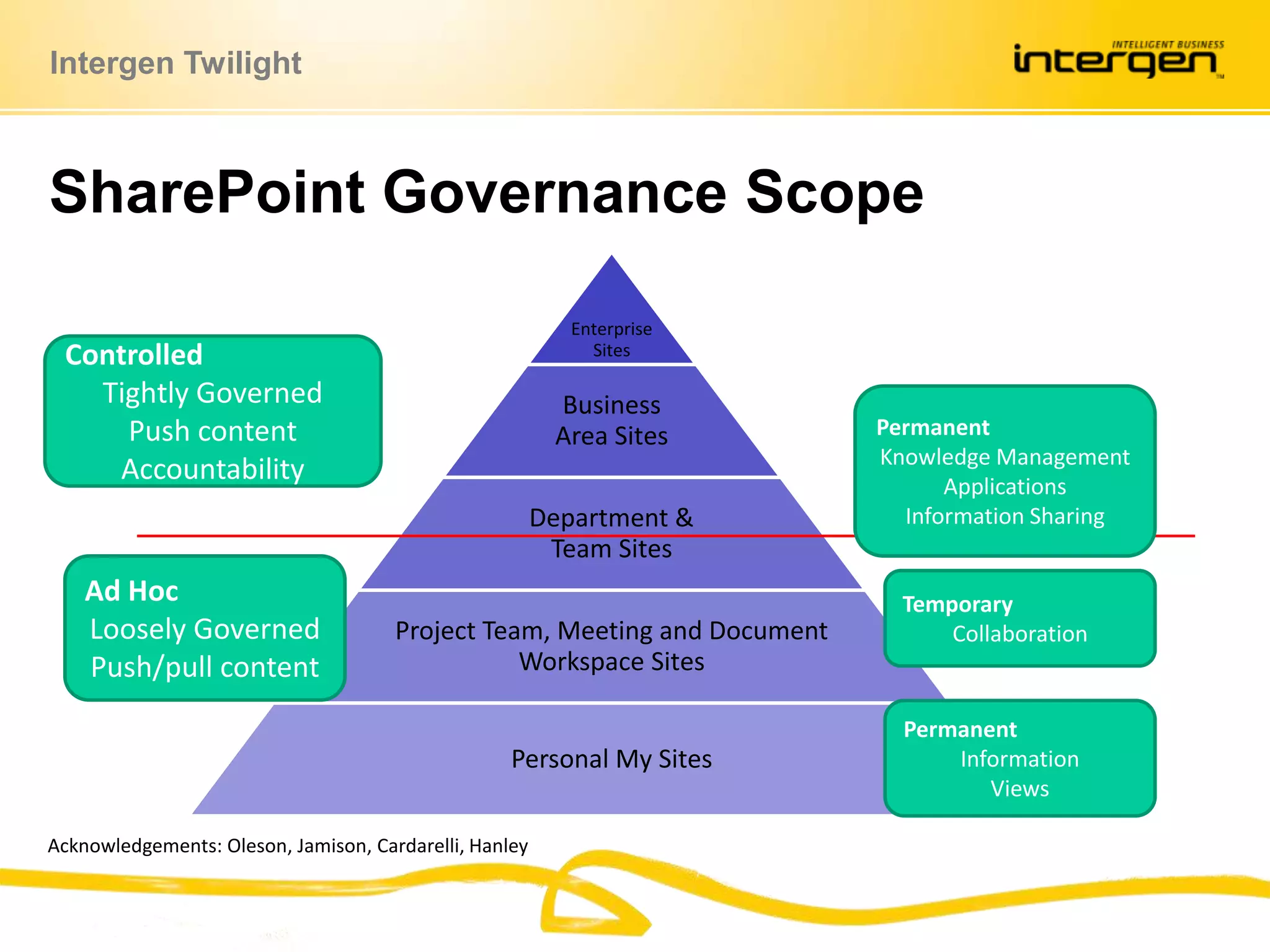
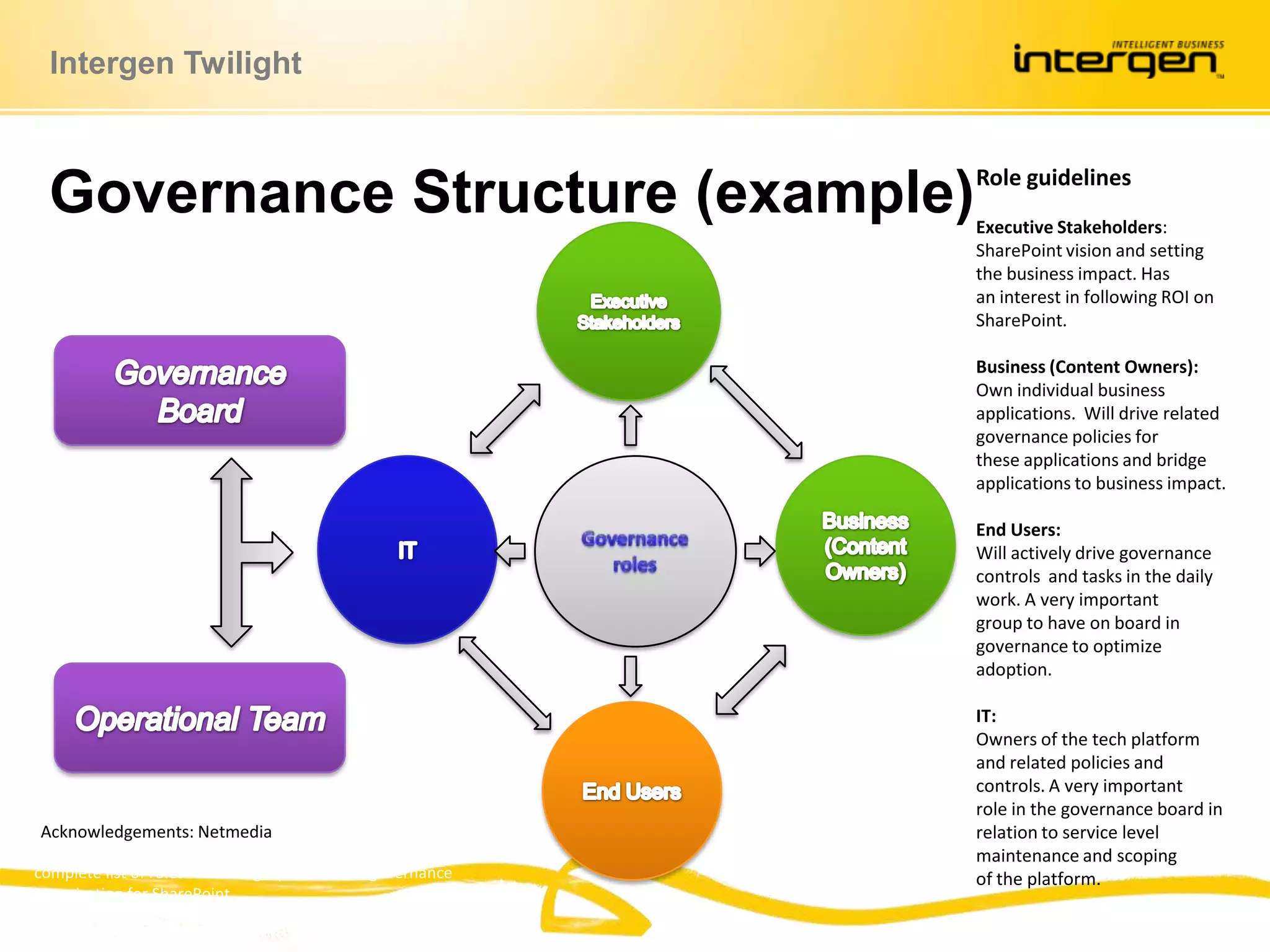
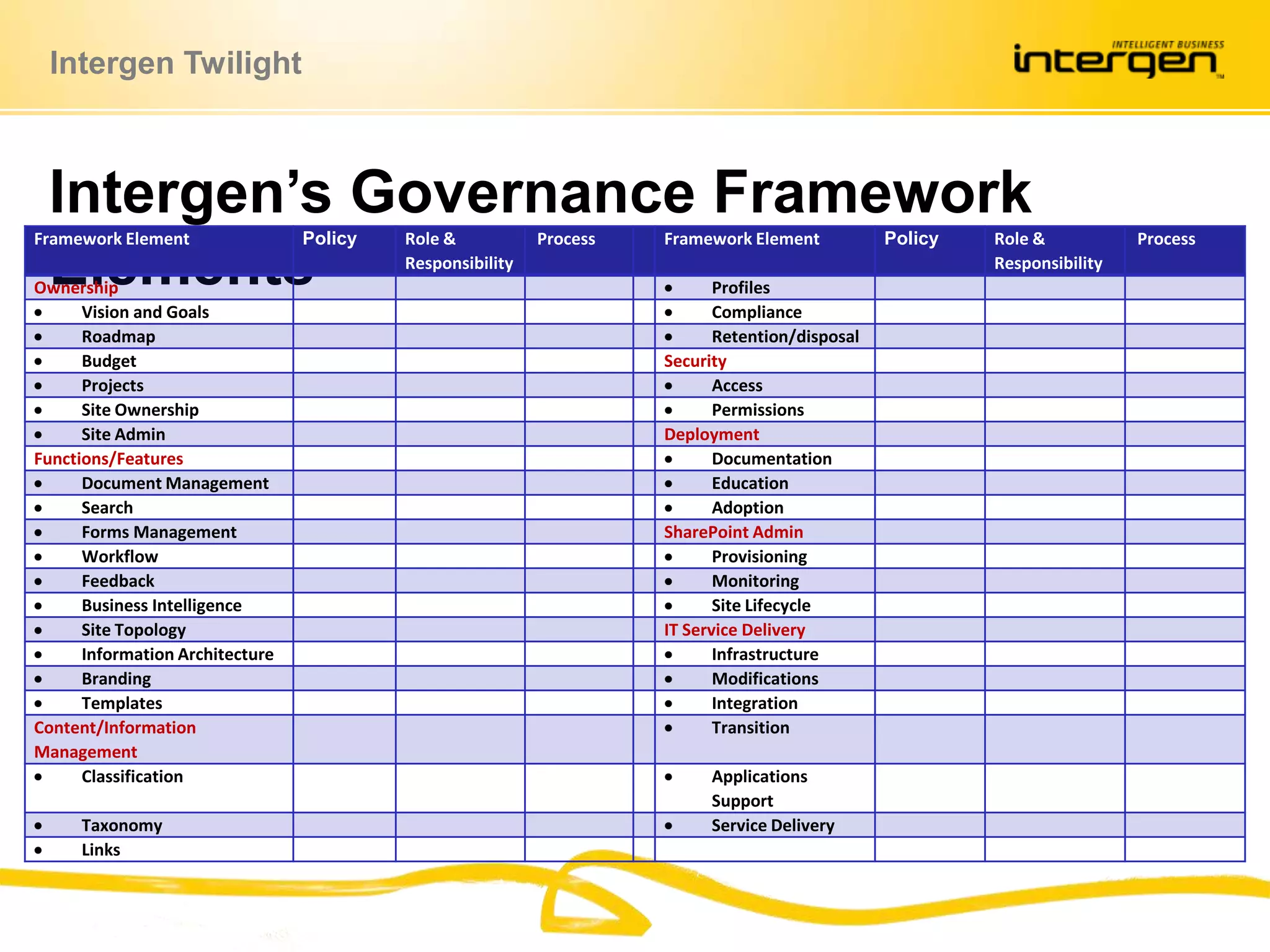
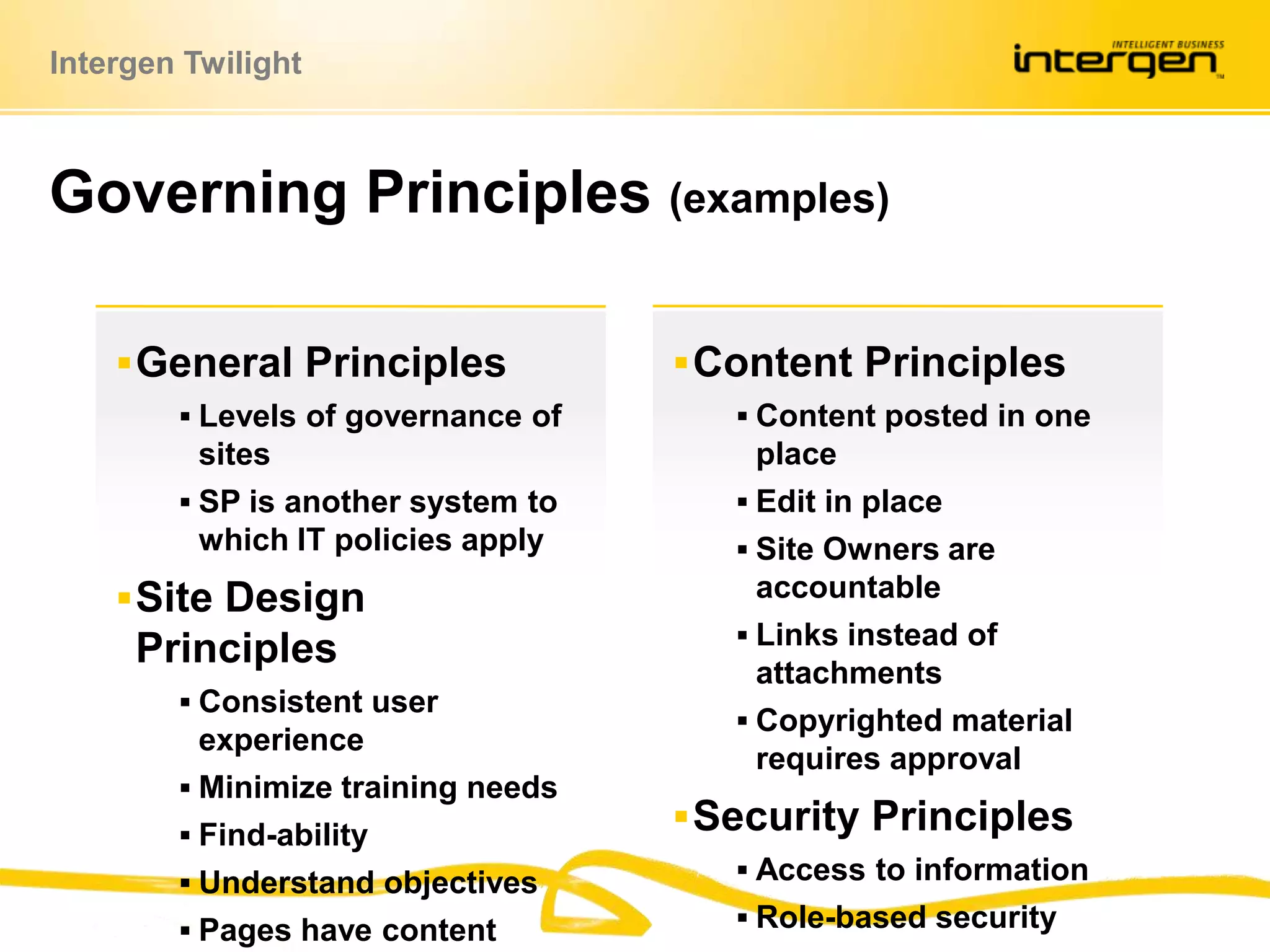
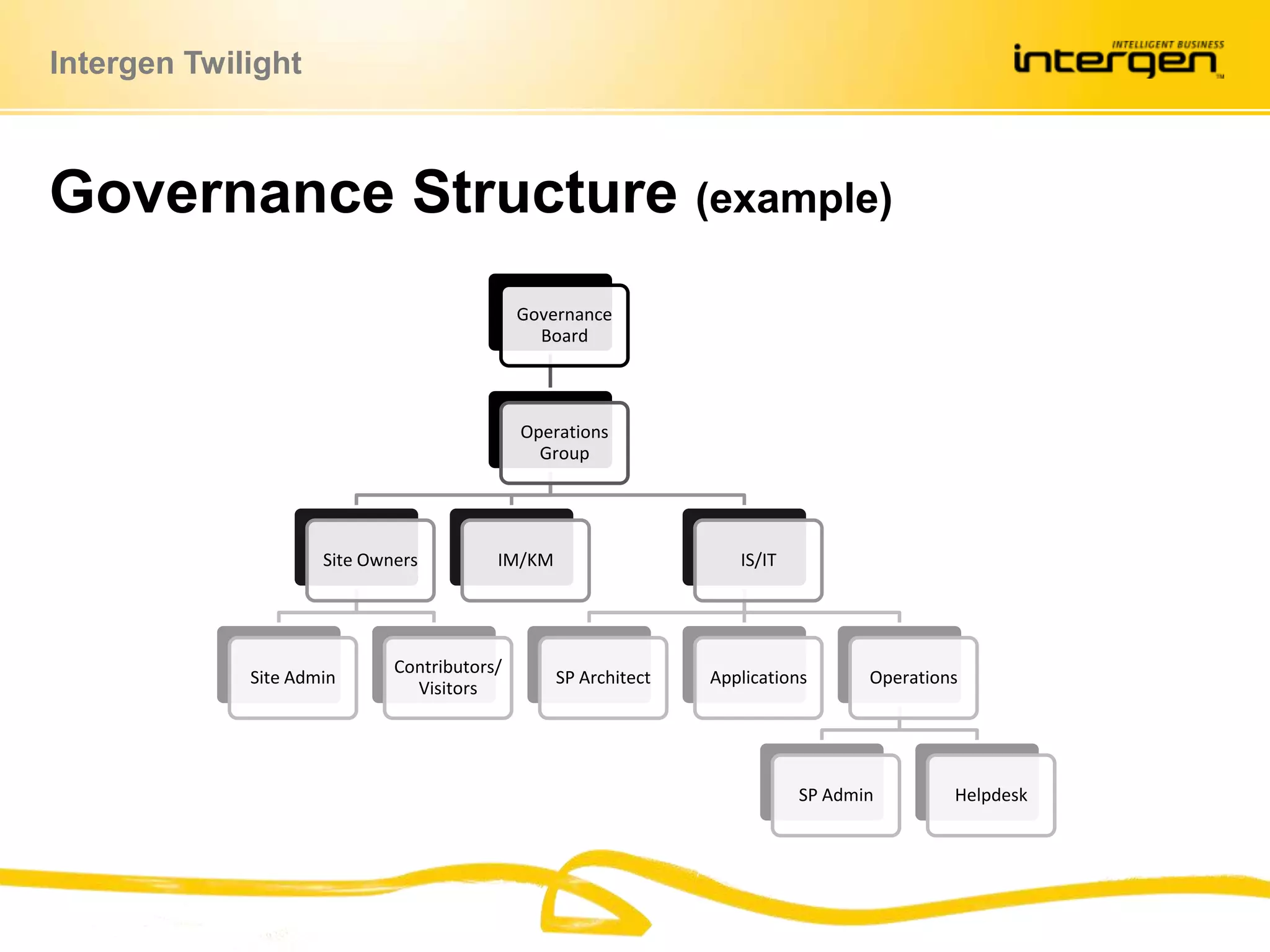
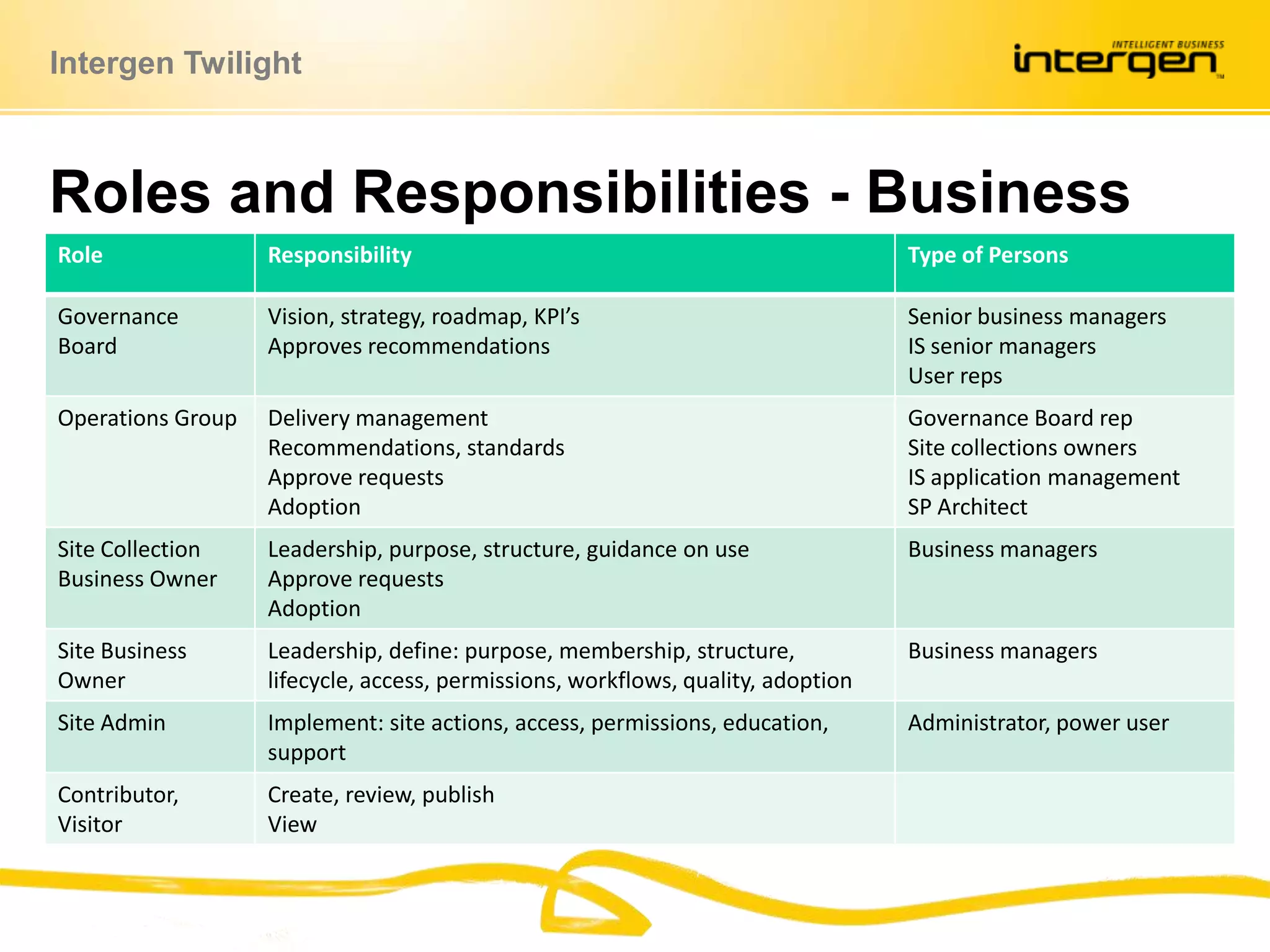
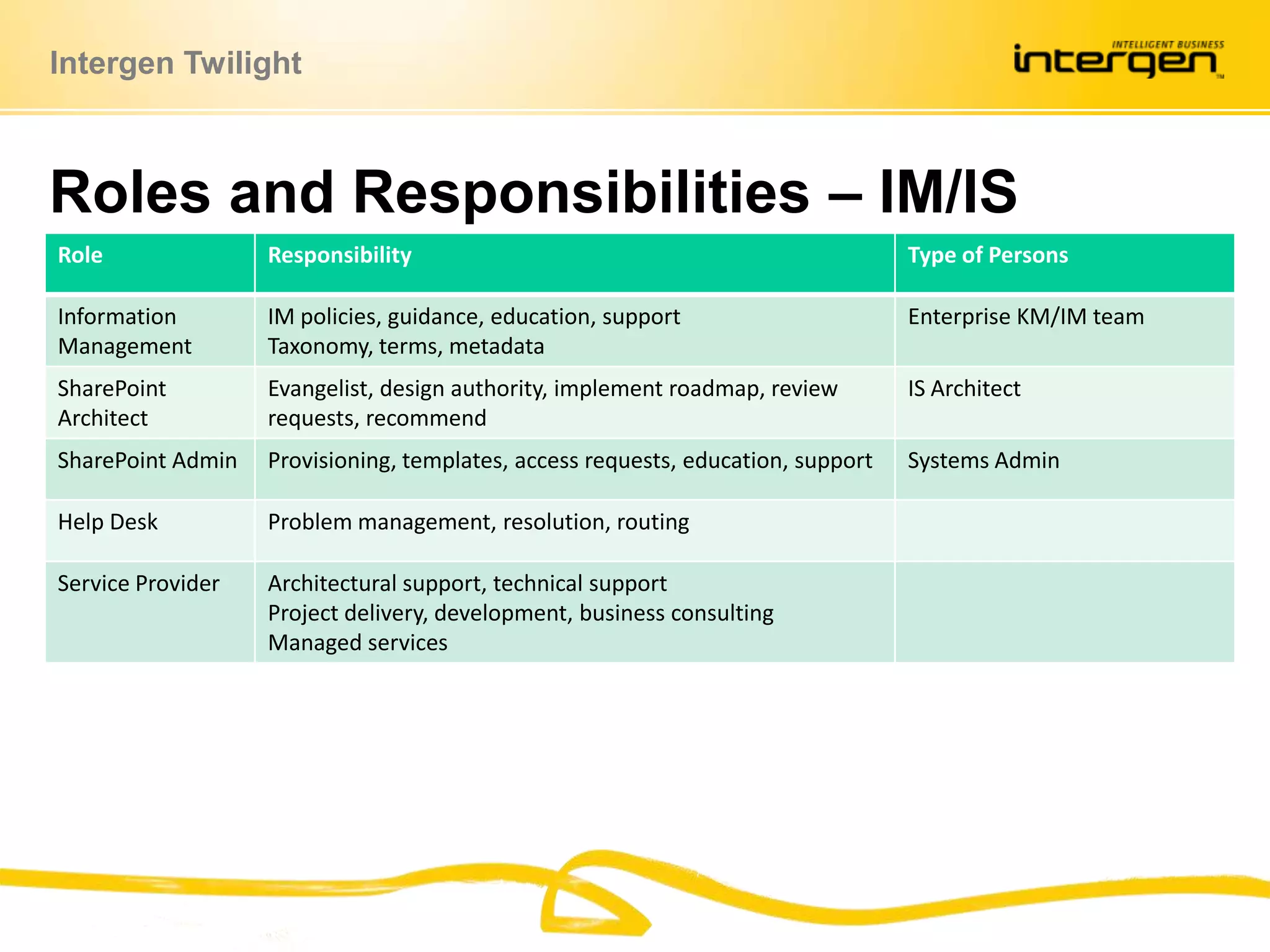
This document discusses establishing governance over SharePoint implementations to ensure value and manageability. It finds that only 50% of SharePoint projects have a business case and many organizations lack experience, guidance and policies. The presentation recommends developing a governance framework with principles, roles, processes and policies to provide structure and control over SharePoint use. An example framework outlines governance at different levels, and divides roles between executive, business, IT and end users. Questions are taken at the end regarding establishing a governance program.