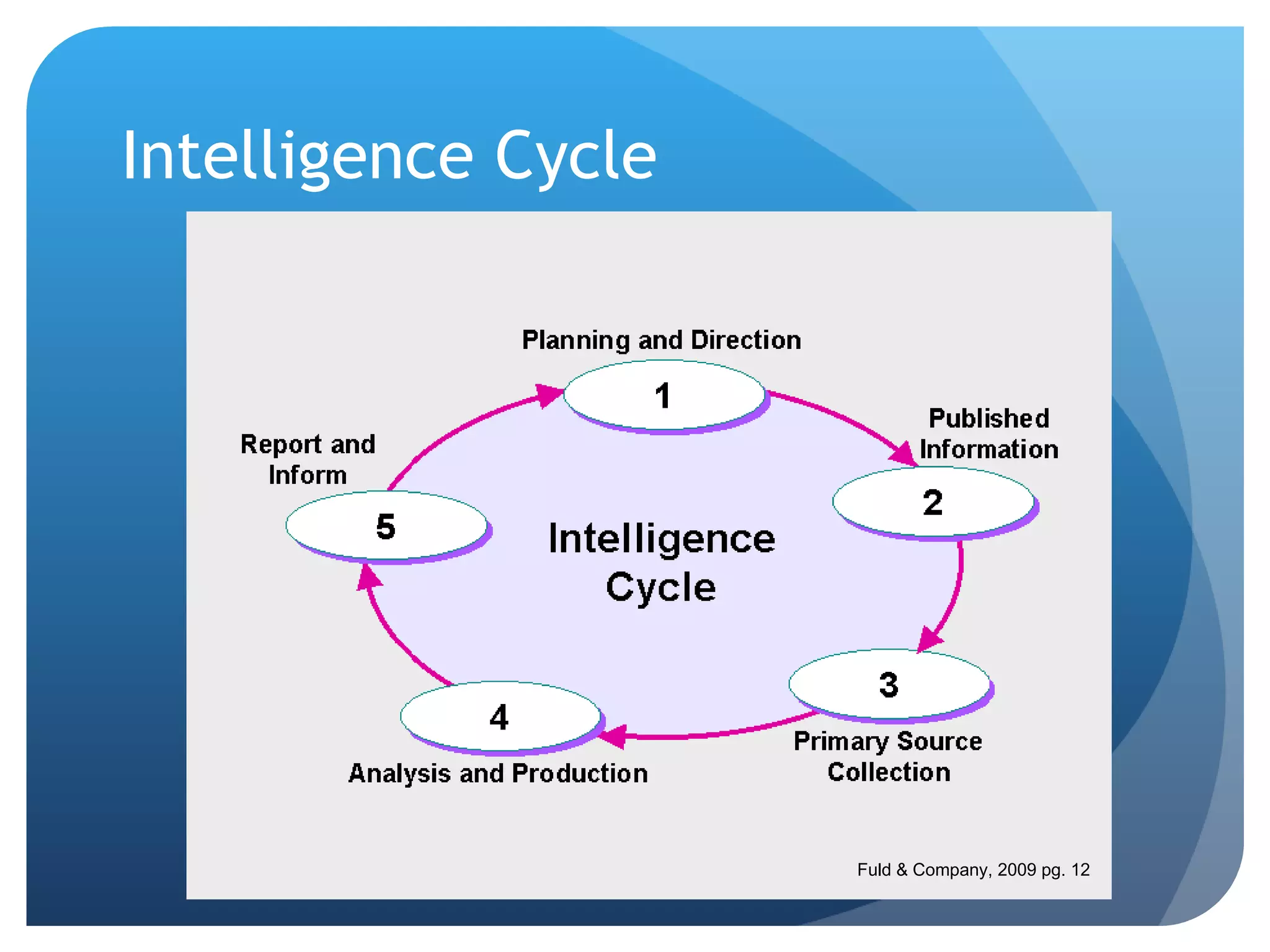
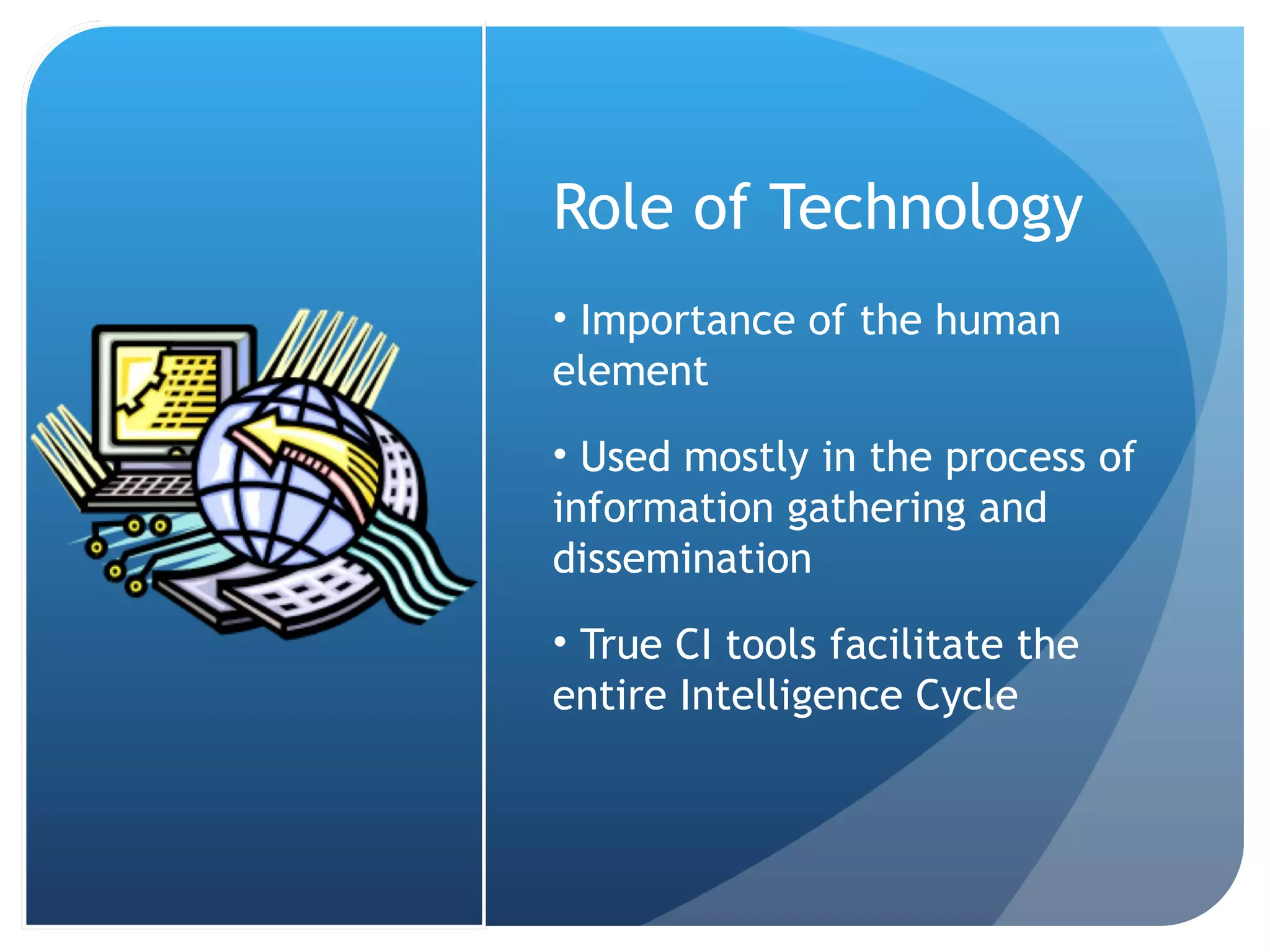
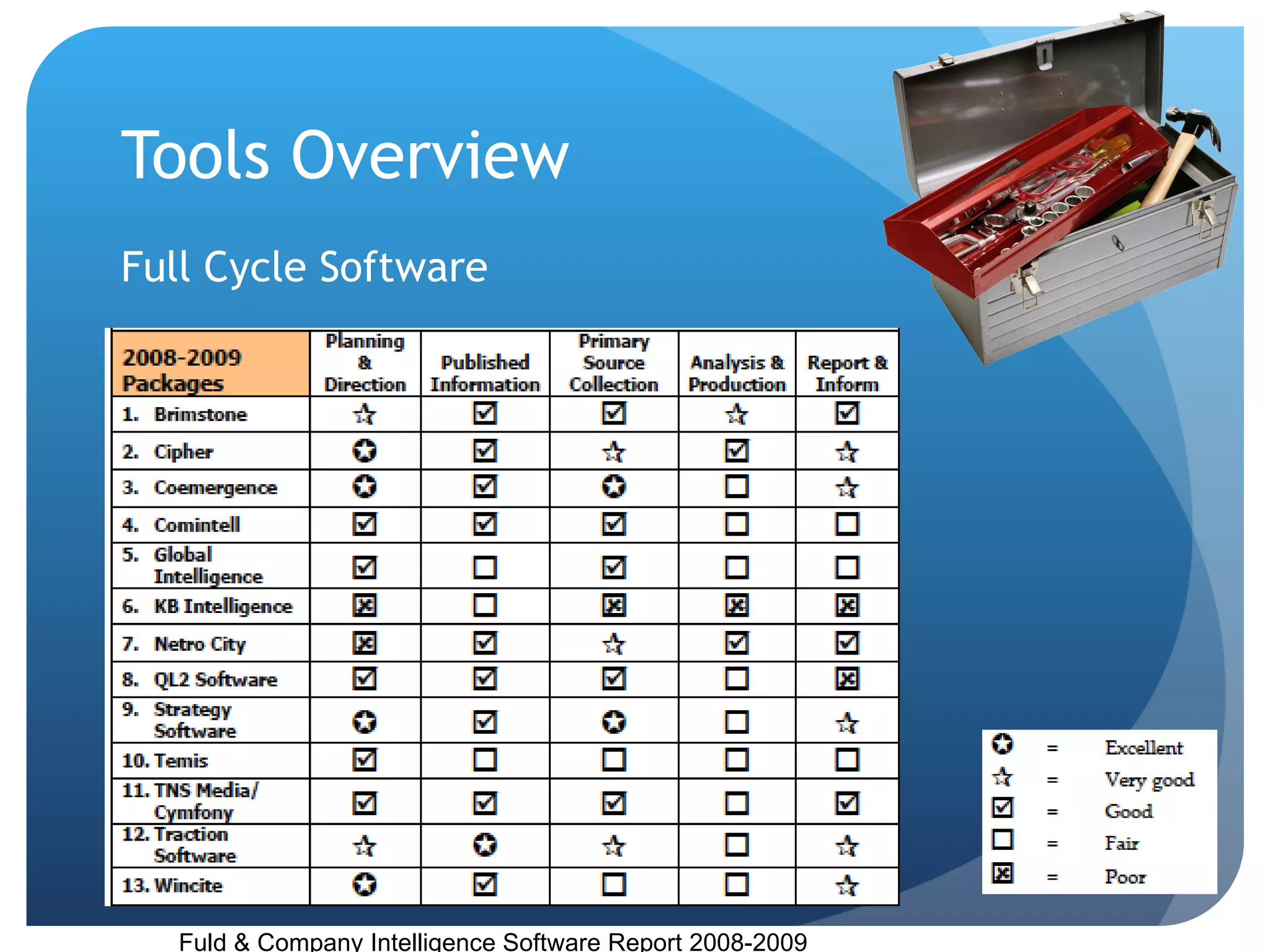
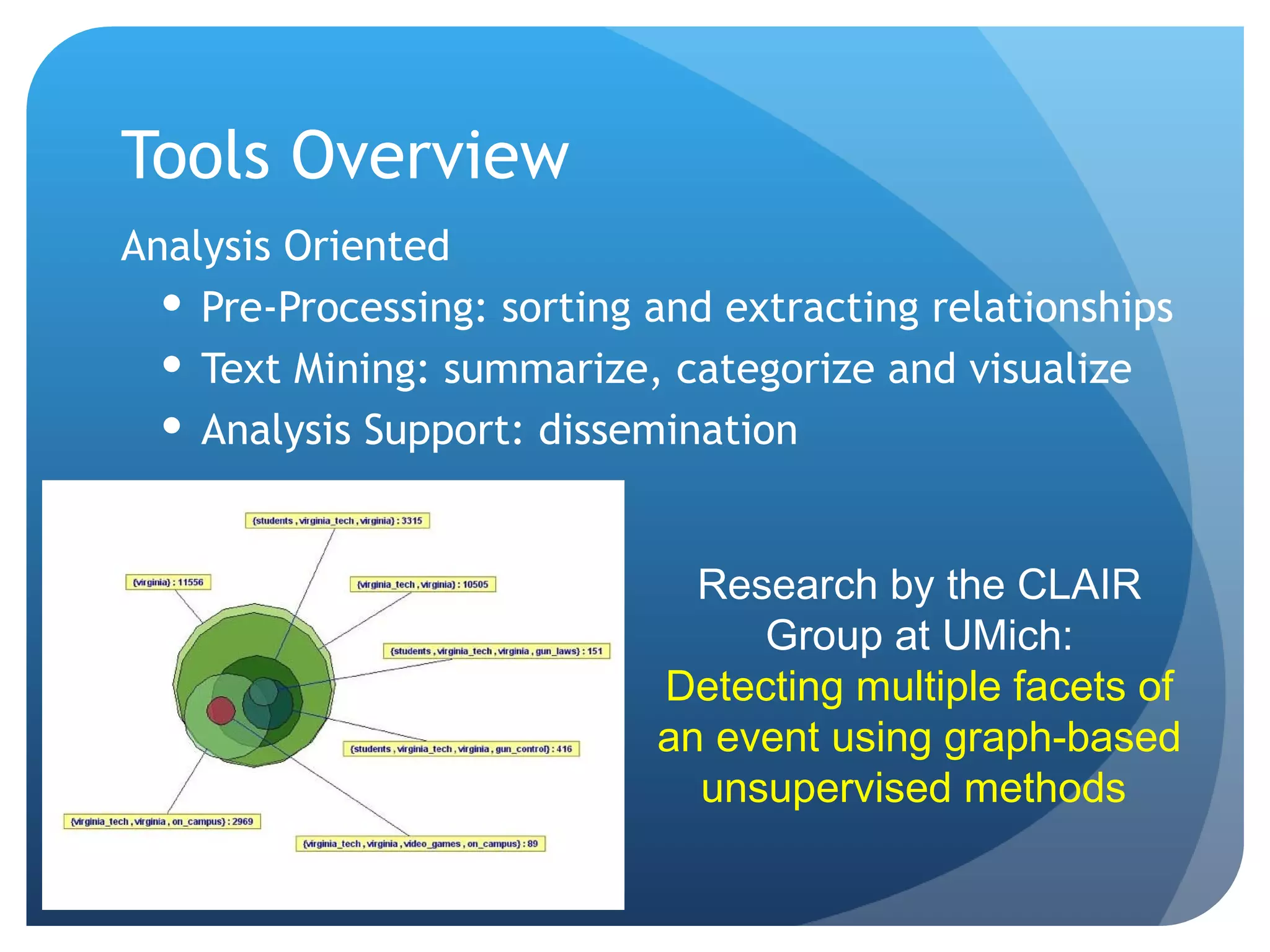
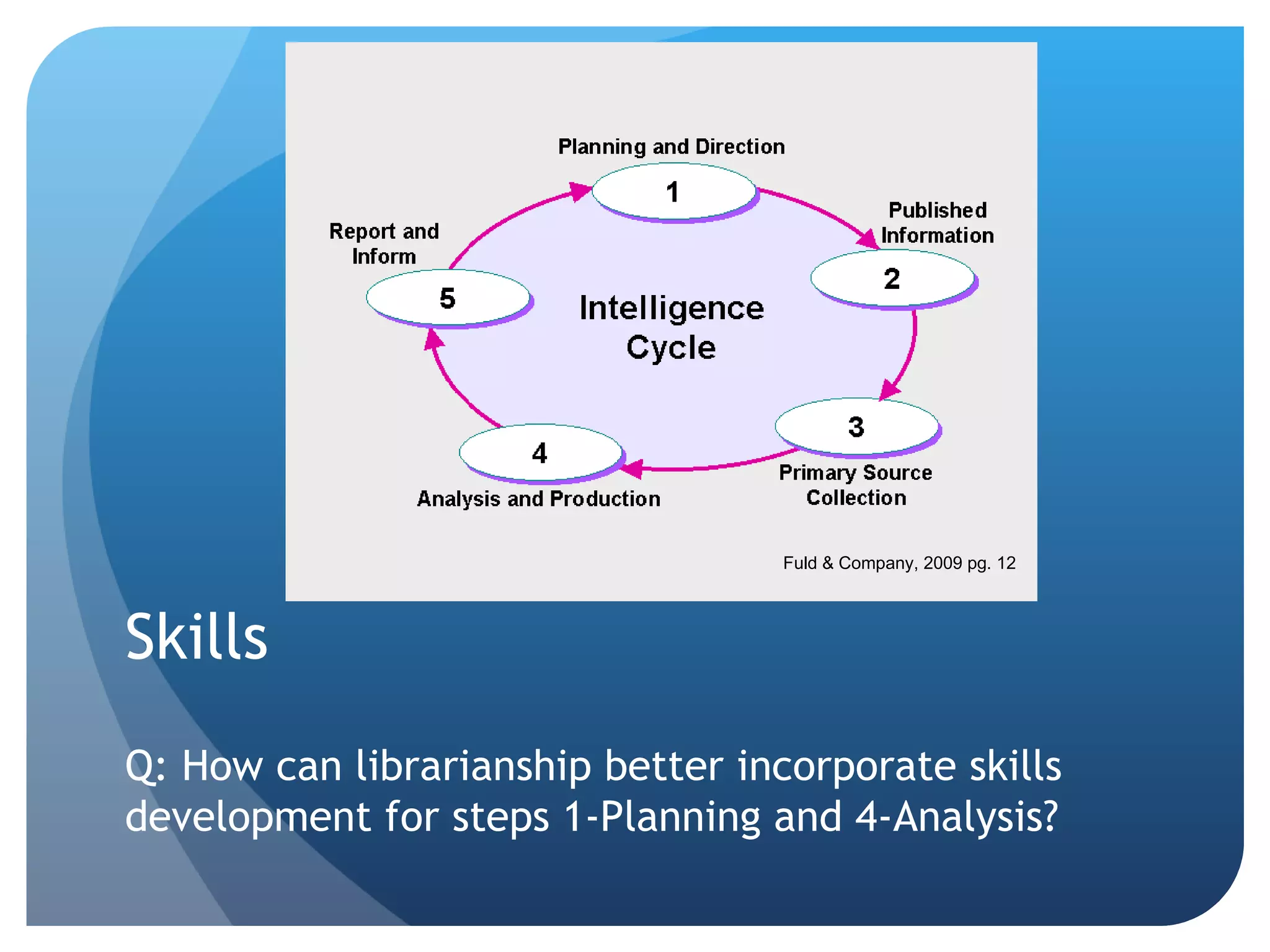
This document discusses the role of librarians in competitive intelligence (CI) and the skills needed to be effective CI practitioners. It outlines the CI process and compares the library information science (LIS) approach to CI with the traditional business approach. The LIS approach emphasizes information gathering and dissemination over planning and analysis. For librarians to truly practice CI, training in business administration is important. Key skills identified for CI work include knowledge of information sources, research methods, technology, disseminating information, connecting people, and analytical and people skills.









![SLA CI Division Member Profiles Correia, Cynthia Cheng. (January 2008). Members Survey: General Profile [Electronic Version]. Intelligence Insights, vol. 4:1, 4-12. Total of 134 Respondents 43% work in Information Centers 21% work in Business or Consulting Services 12% Pharmaceutical, Biomedical or Health Sciences 10% Law 8% Academic / Higher Education 35.2% spend less than ¼ of their time on CI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lipscombproject2ci-090309000945-phpapp01/75/Lipscomb-Project2-Ci-16-2048.jpg)



