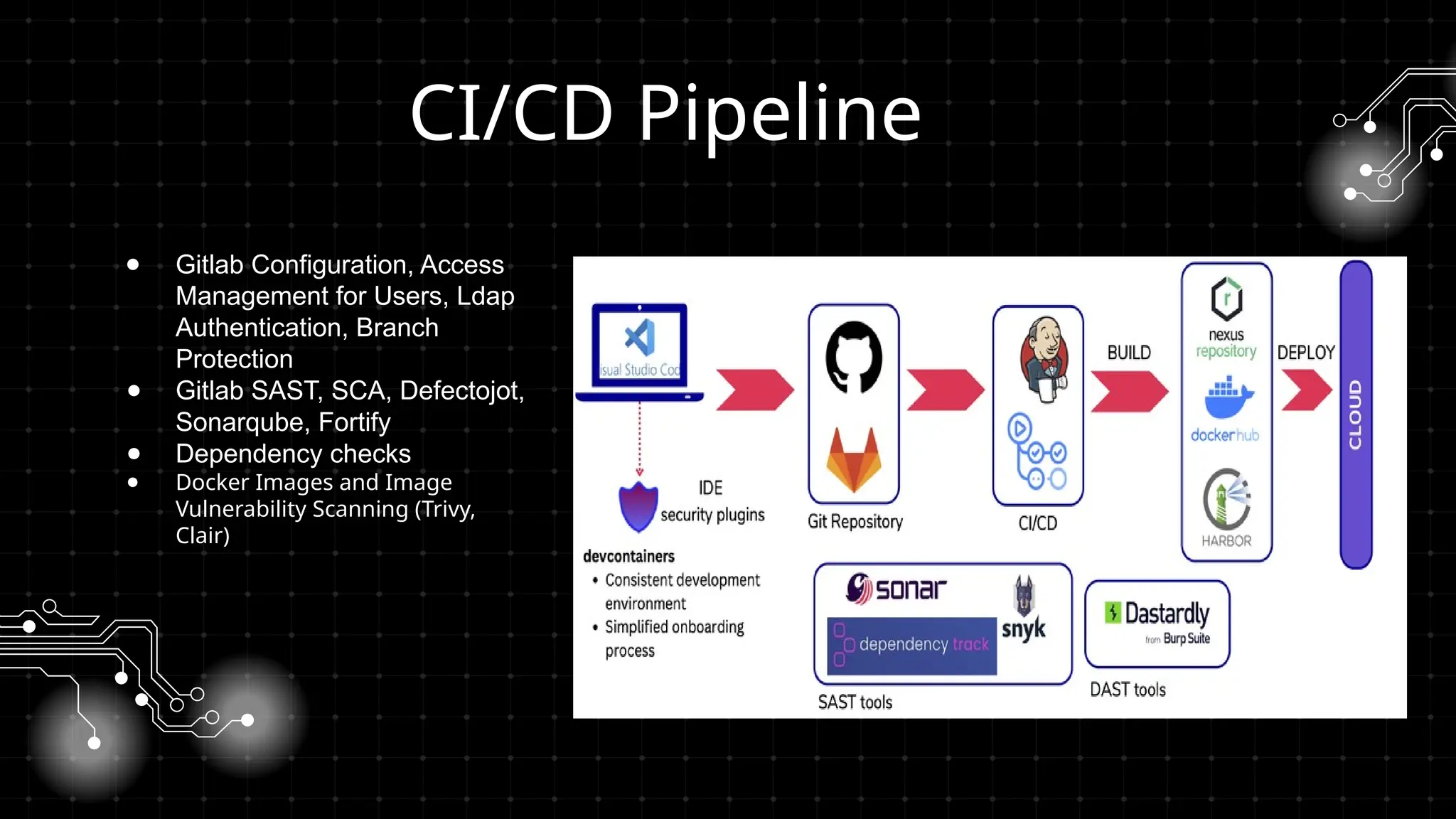
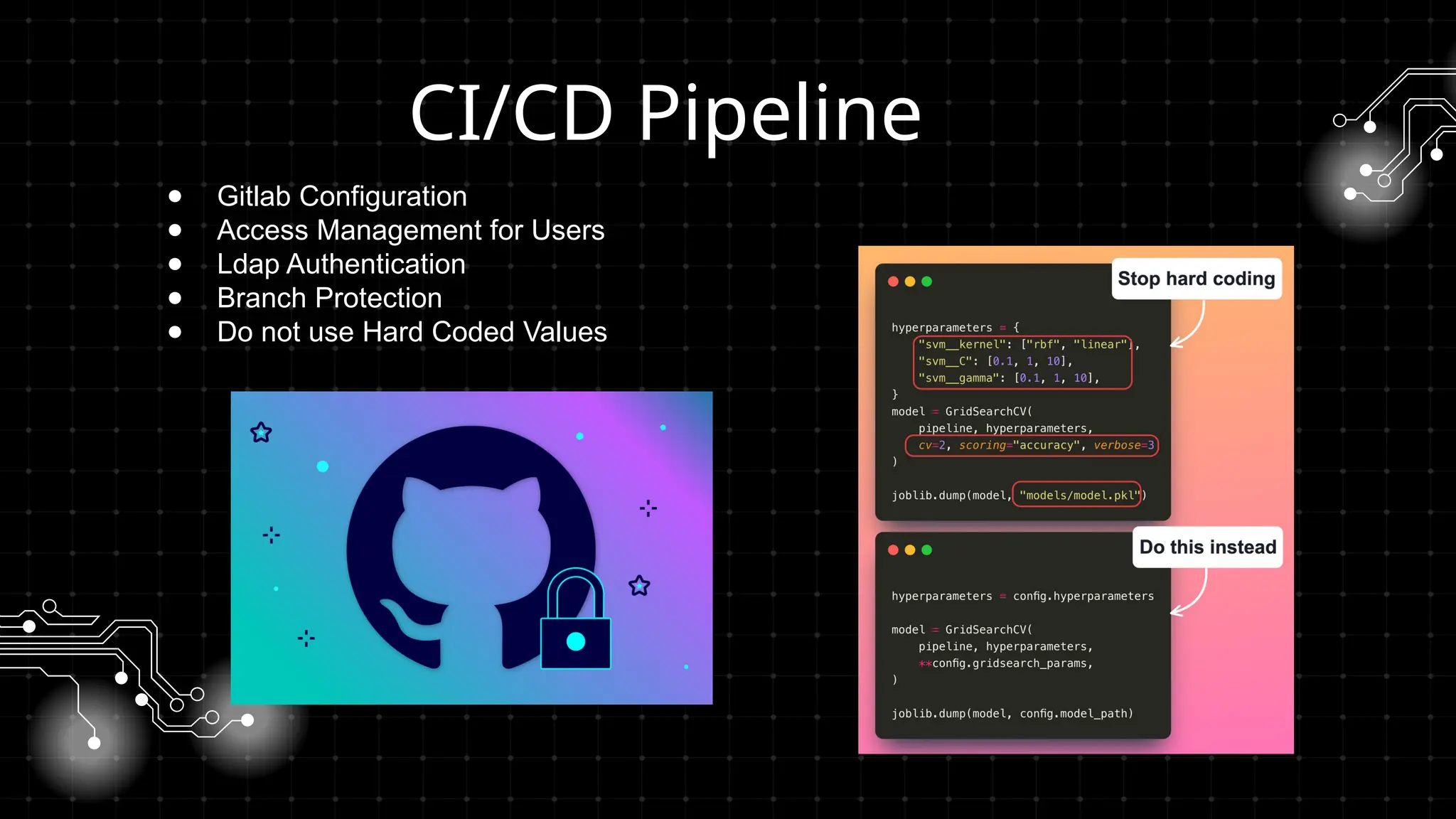
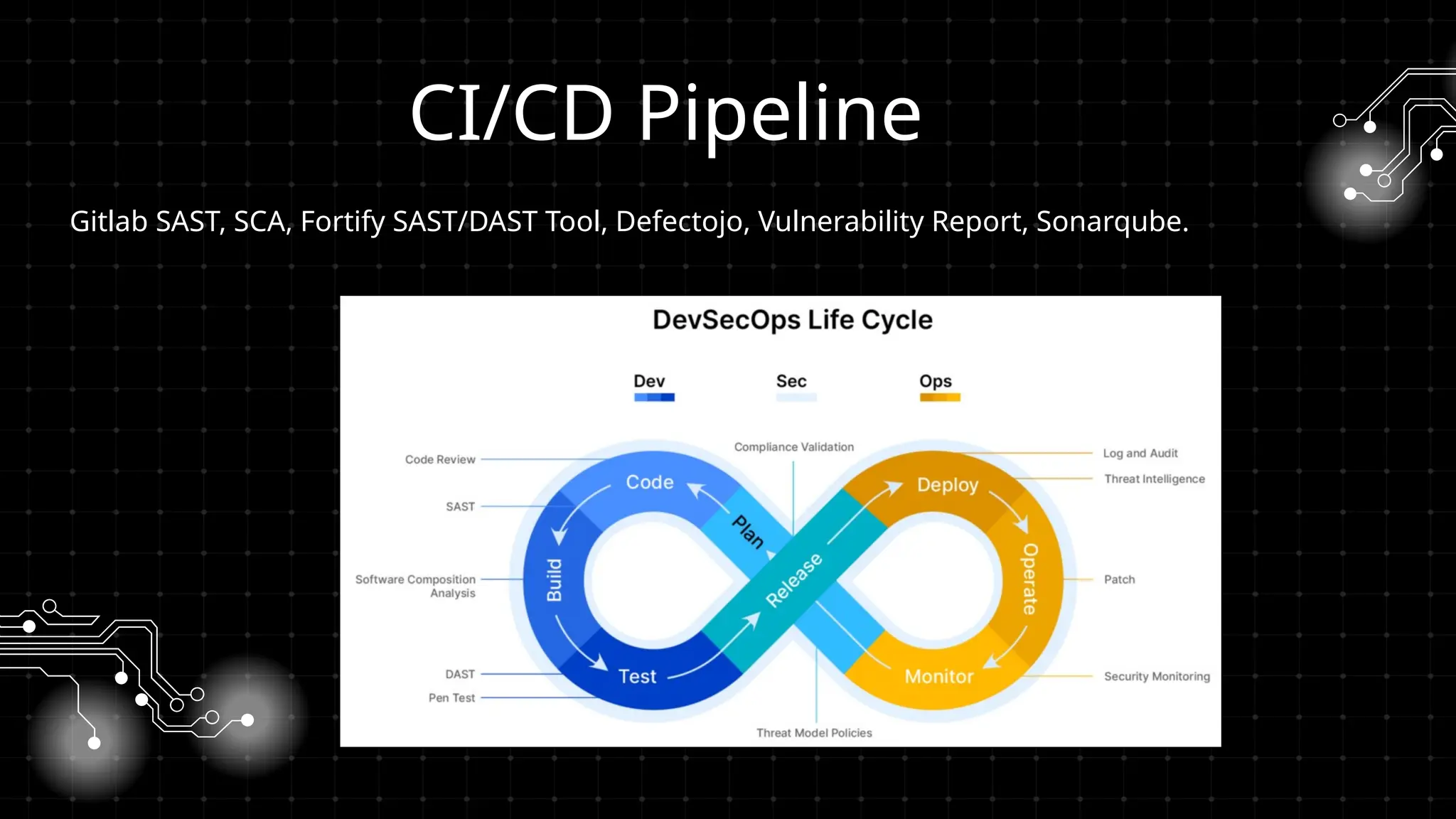
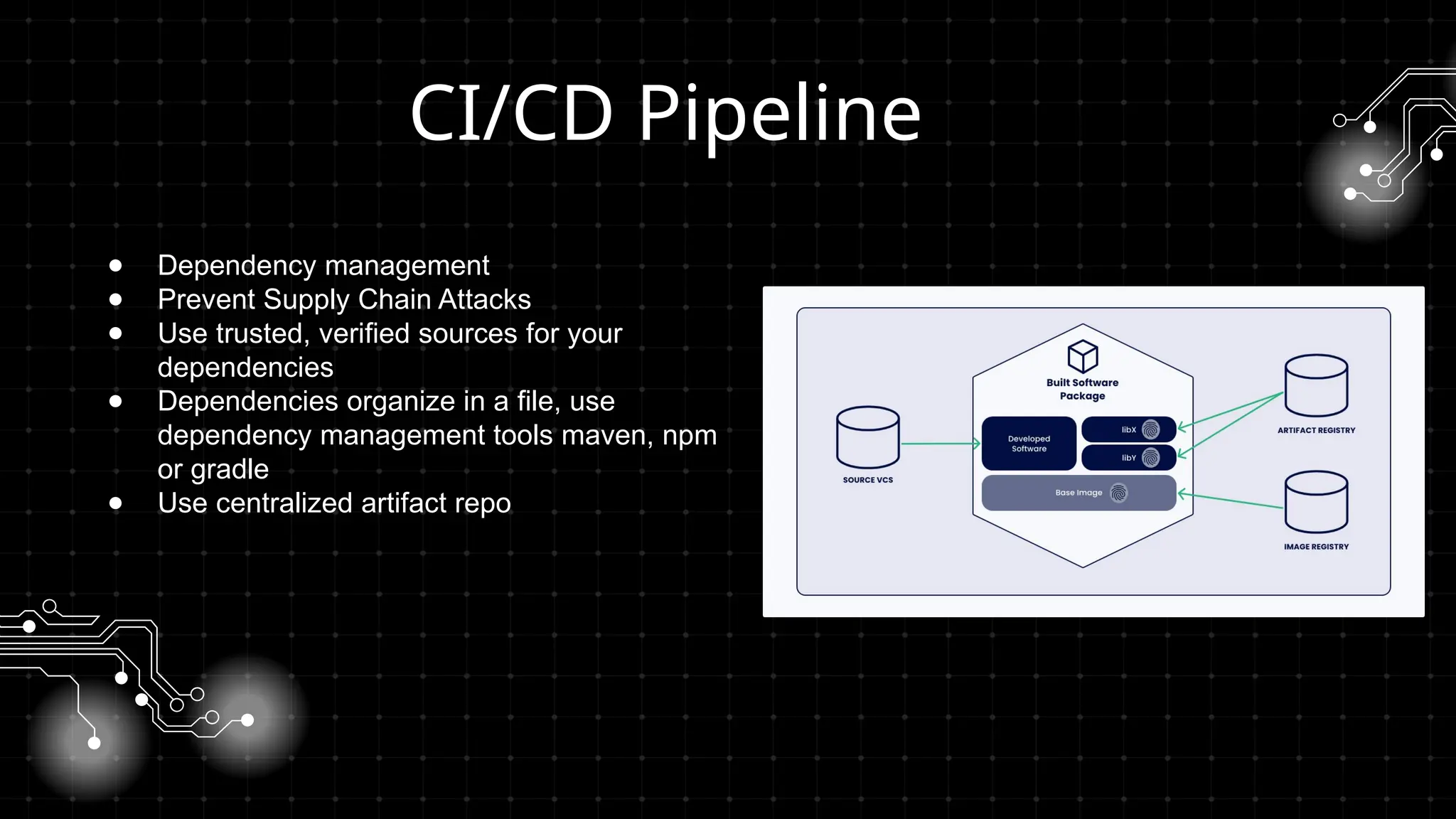
DevOps iş təhlükəsizliyi sizi maraqlandırır? İstər developer, istər təhlükəsizlik mühəndisi, istərsə də DevOps həvəskarı olun, bu tədbir şəbəkələşmək, biliklərinizi bölüşmək və DevSecOps sahəsində ən son təcrübələri öyrənmək üçün mükəmməl fürsətdir!
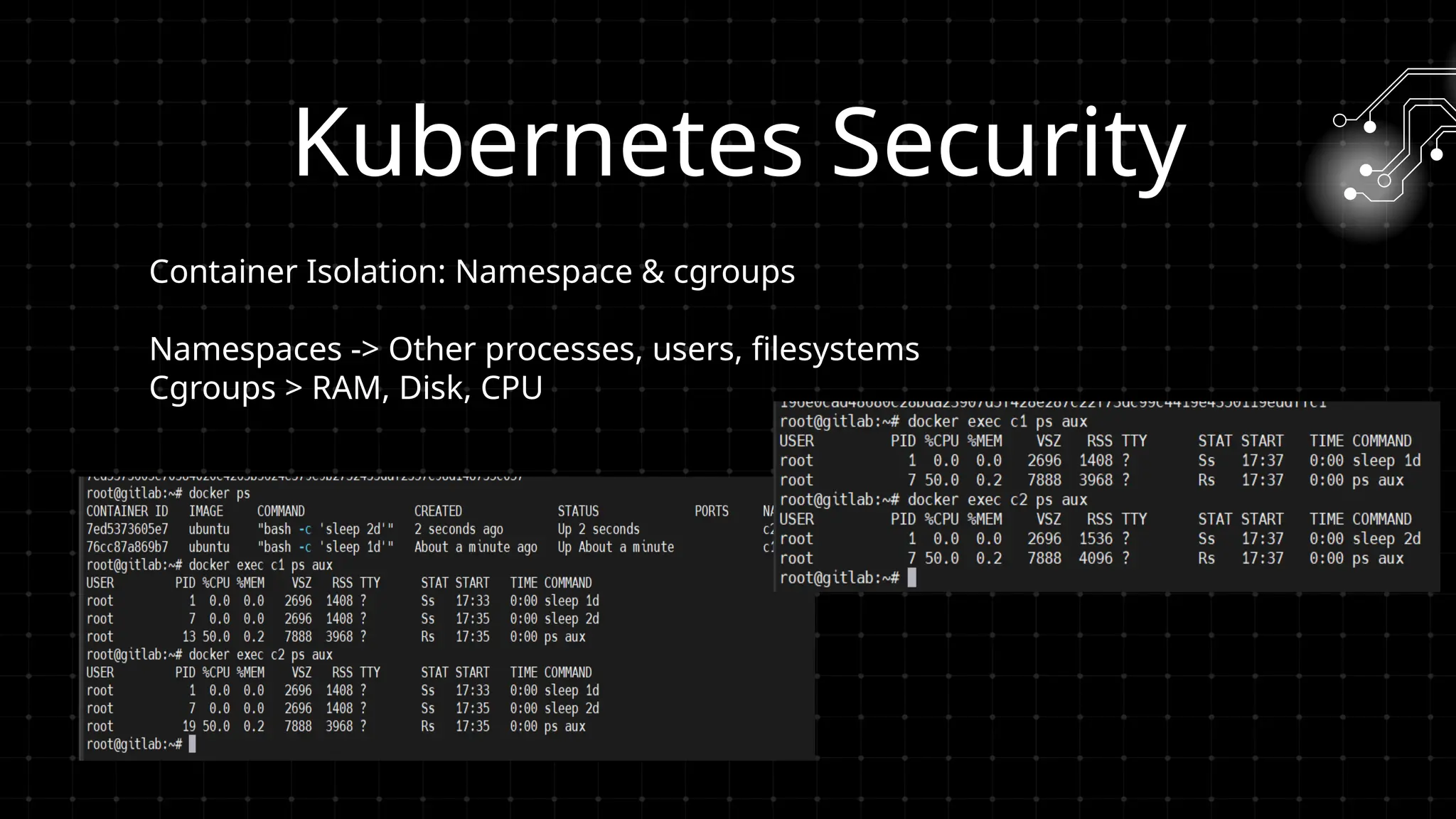
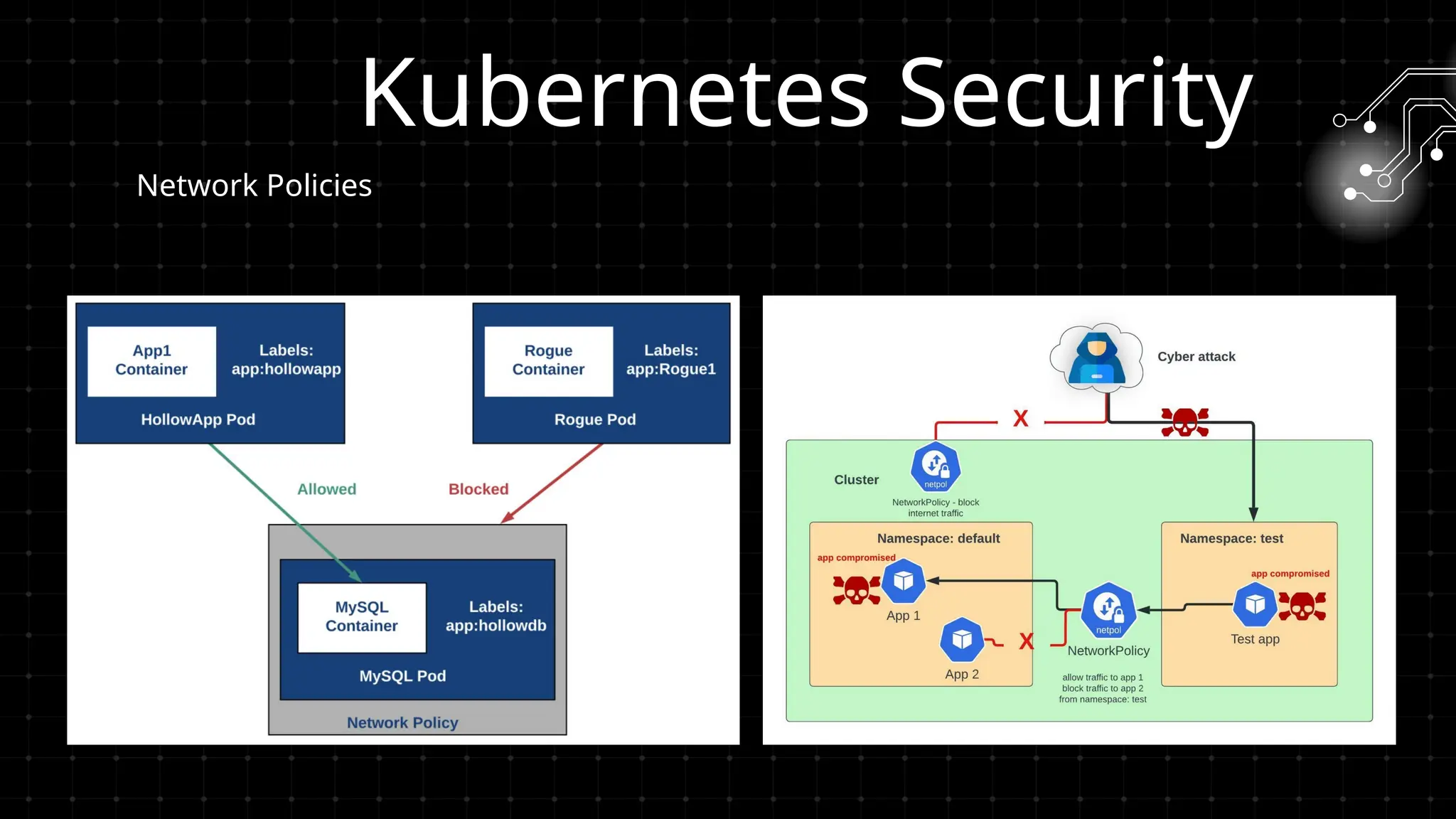
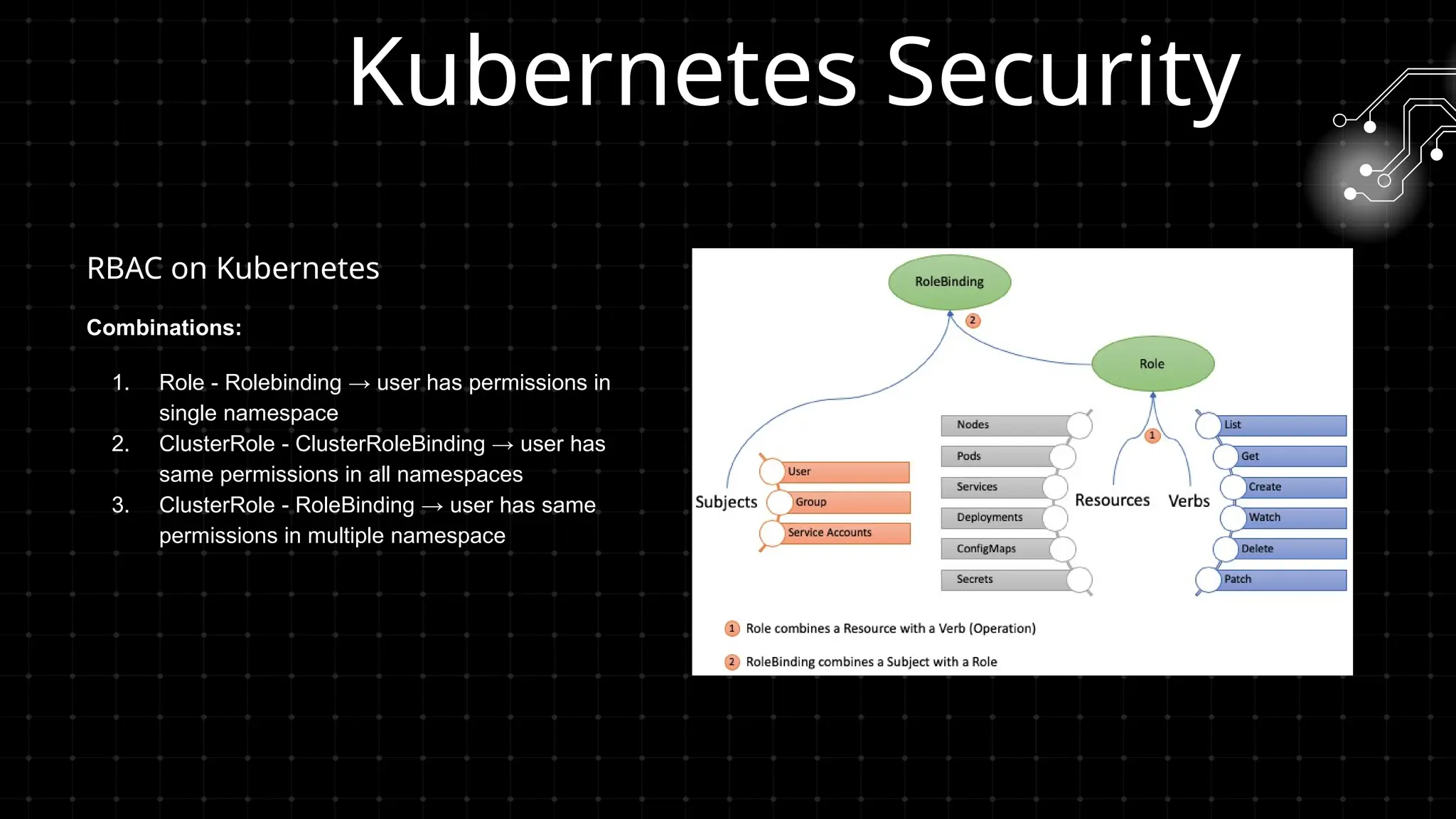
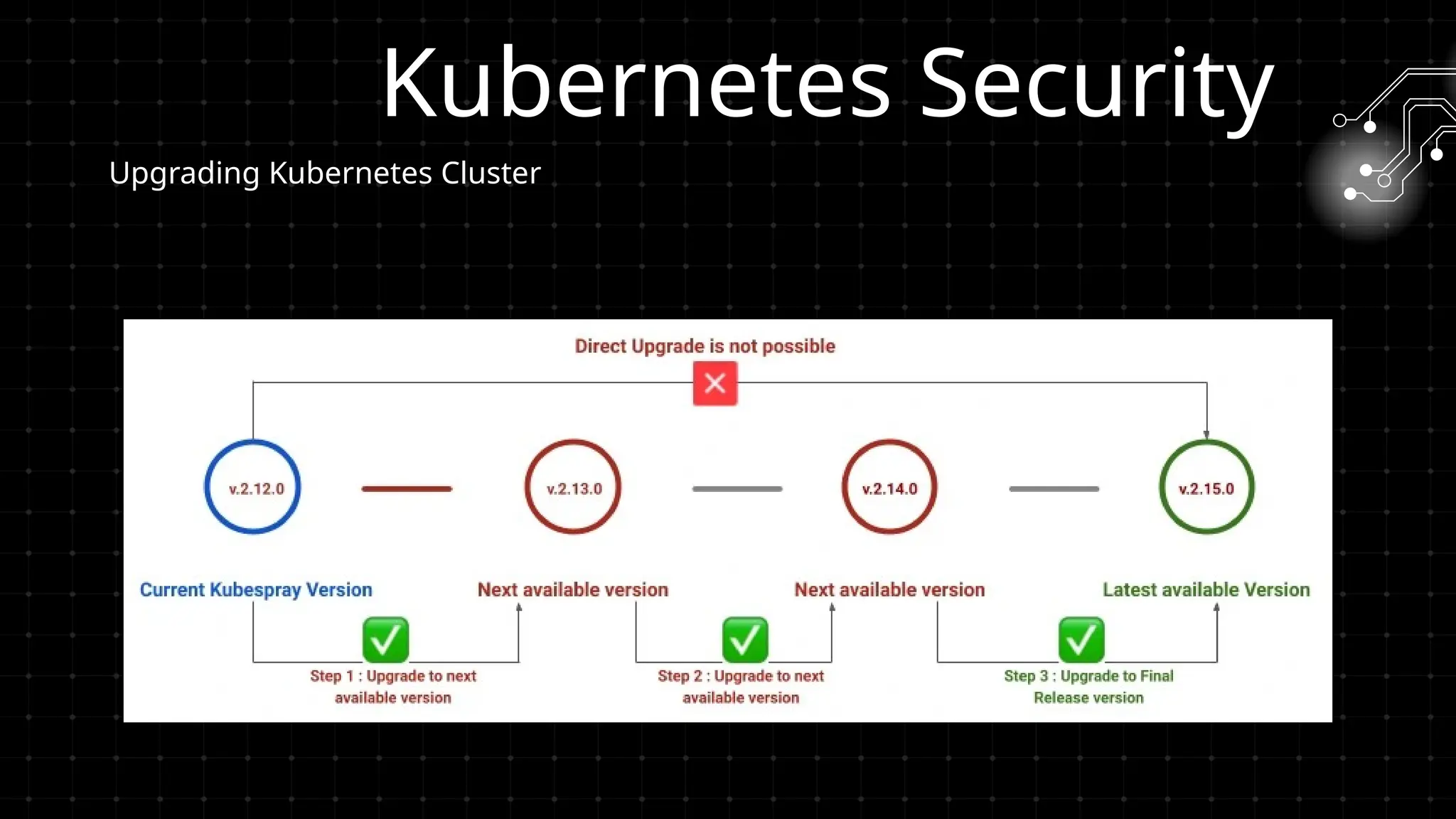
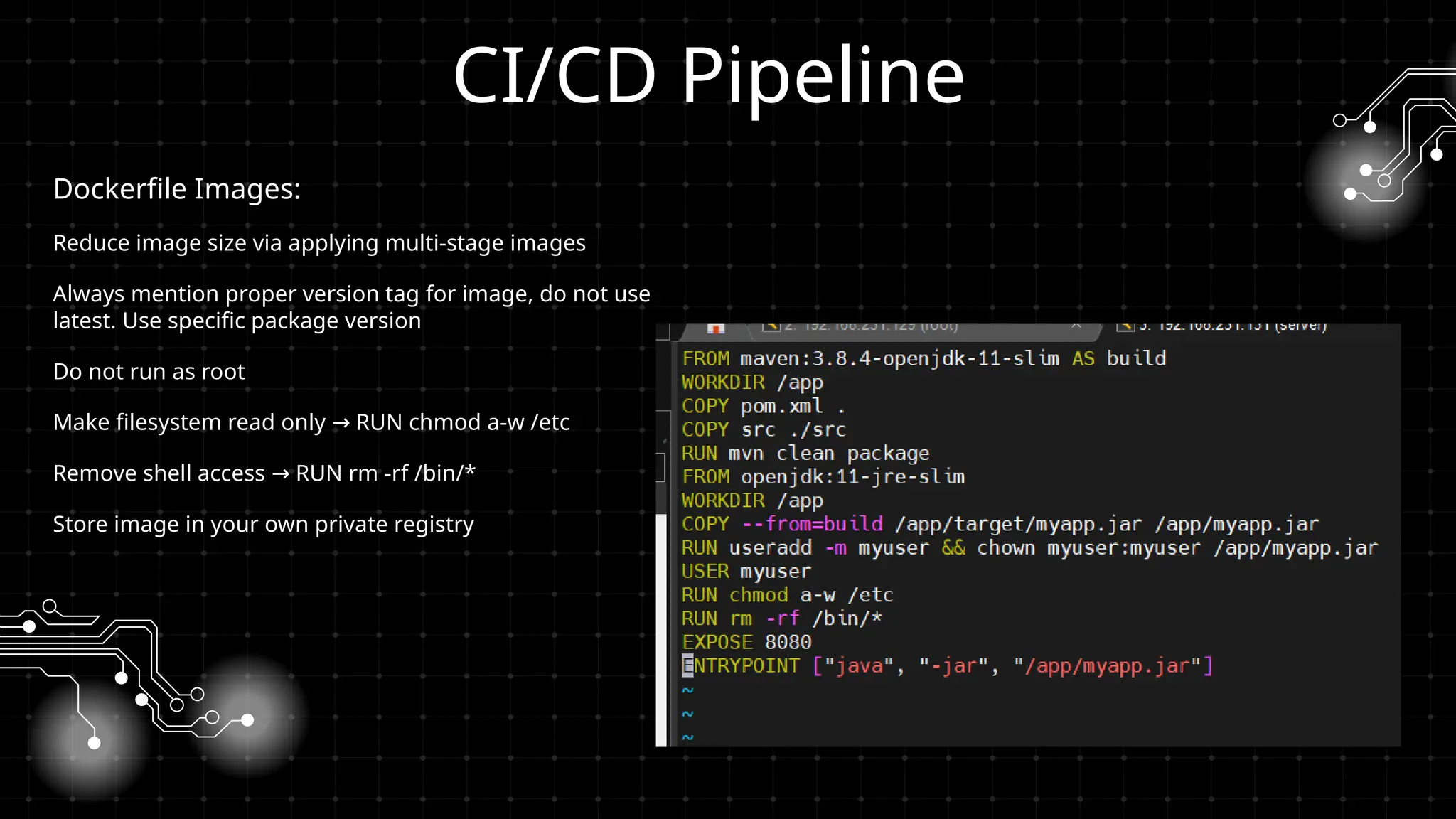
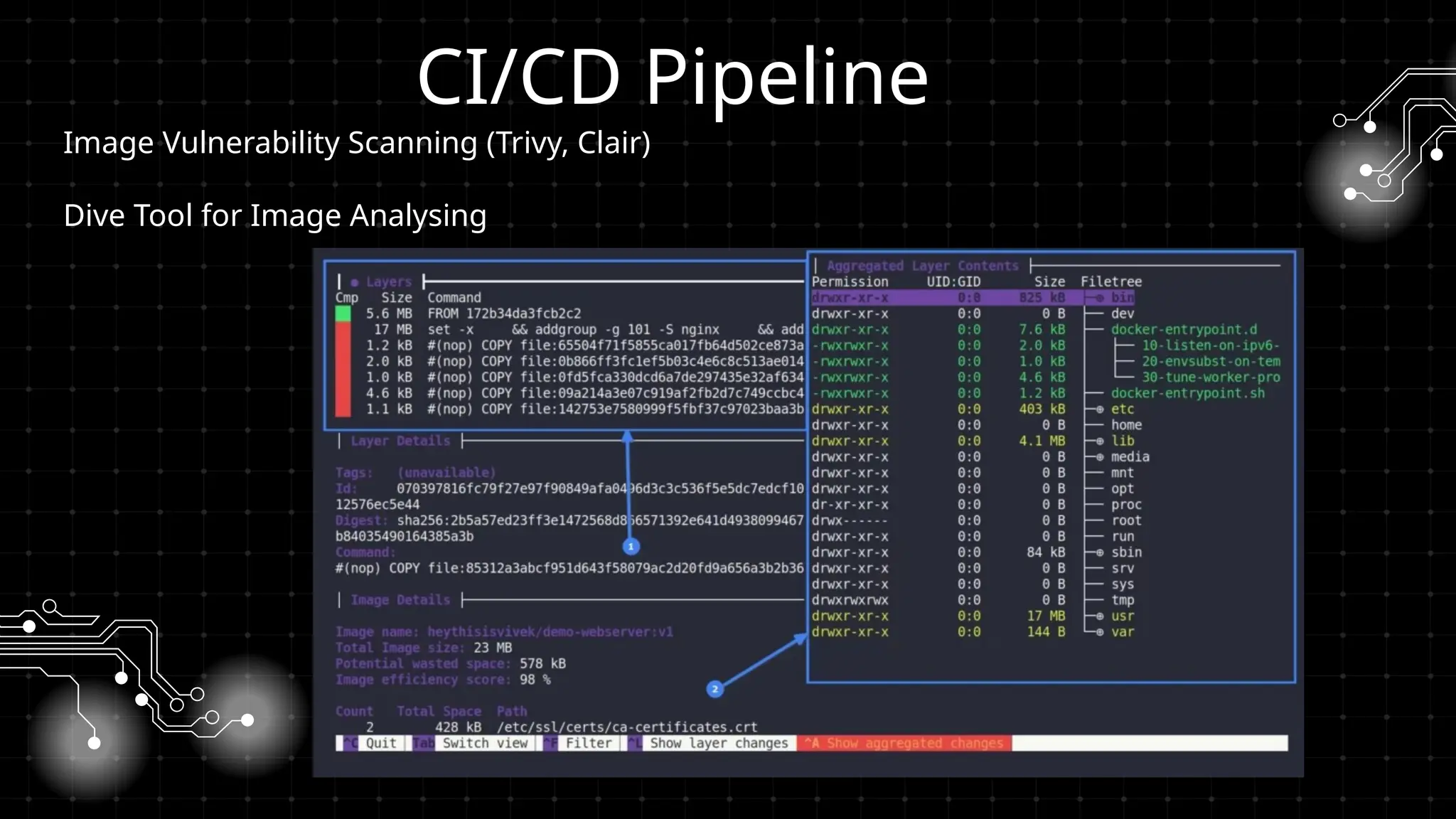
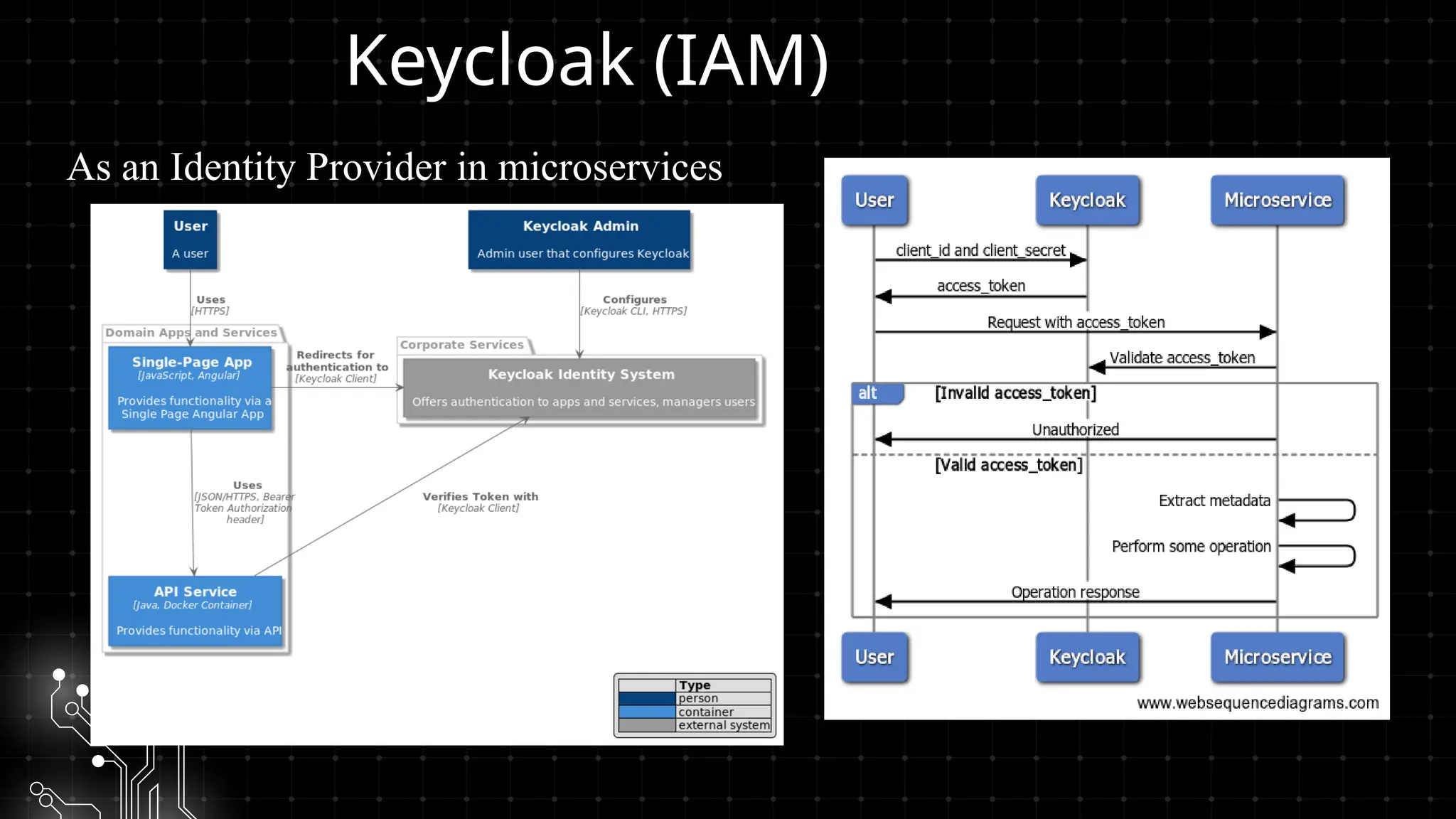
Bu workshopda DevOps infrastrukturlarının təhlükəsizliyini necə artırmaq barədə danışacayıq. DevOps sistemləri qurularkən avtomatlaşdırılmış, yüksək əlçatan və etibarlı olması ilə yanaşı, həm də təhlükəsizlik məsələləri nəzərə alınmalıdır. Bu səbəbdən, DevOps komandolarının təhlükəsizliyə yönəlmiş praktikalara riayət etməsi vacibdir.