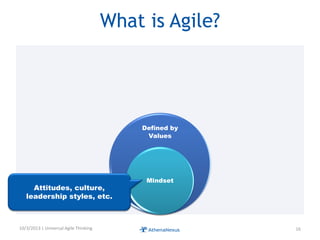
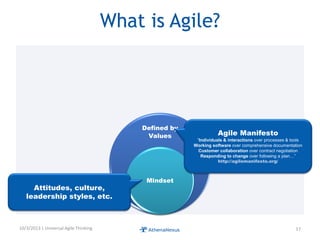
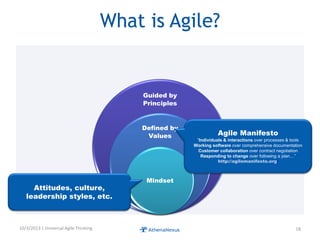
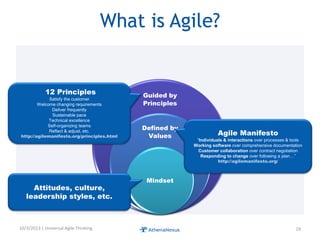
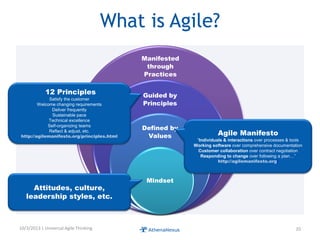
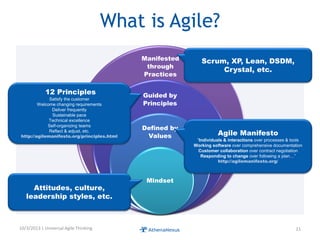
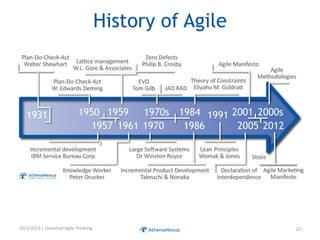
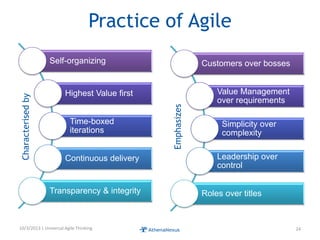
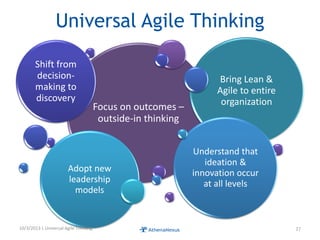
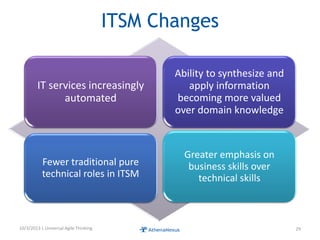
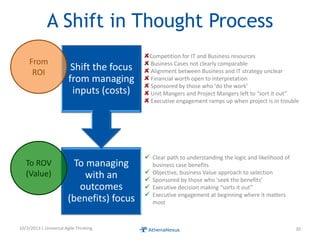
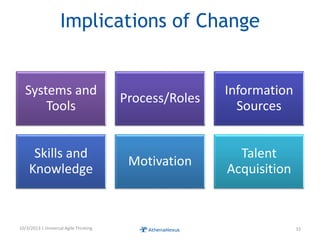
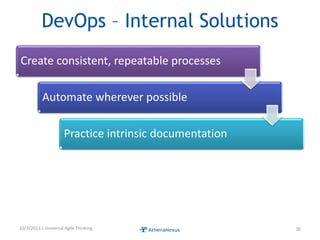
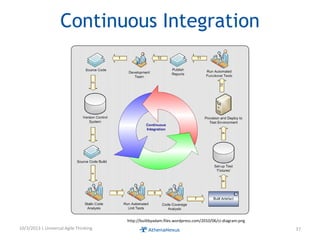
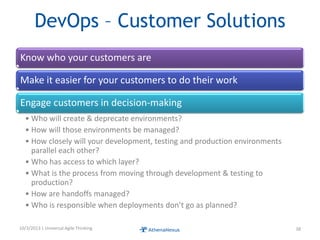
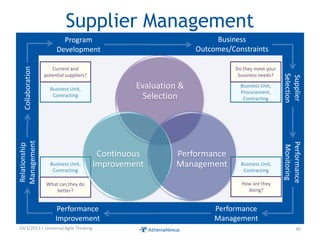
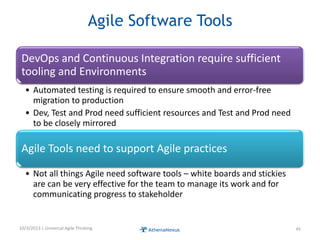
The document discusses challenges faced by organizations in today's rapidly changing digital environment. It proposes adopting agile thinking and practices across entire organizations to better respond to change. Specific solutions discussed for IT service management include focusing on business outcomes rather than costs, defining IT's contribution to value, and adopting DevOps. Procurement is highlighted as an area needing agile approaches to support flexible, collaborative supplier relationships and value-driven selection of solutions.