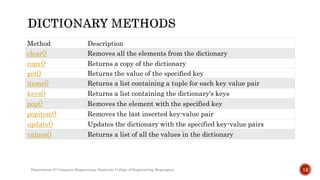
The document provides a comprehensive overview of dictionaries in Python, detailing their structure as key-value pairs, how to access and manipulate them, and various built-in methods available for dictionary operations. Key concepts include creating dictionaries, adding, modifying, deleting items, and using methods like clear(), copy(), get(), items(), keys(), pop(), and update(). Examples illustrate syntax and expected outputs for each operation.






![stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
print(stud['rollno']) #Display rollno value
print(stud['name']) #Display name value
print(stud['class']) #Display class value
print(f'Name of Student is {stud['name']}')# display value with message
Output:
1
Soham
FY
Name of Student is Soham
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-7-320.jpg)
![stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
print(f'Dictionary {stud}')
stud['Div']='G' #add new key and value
print(f'Dictionary after adding new item {stud}’)
[note: new item added at the end]
Output:
Dictionary {'rollno': 1, 'name': 'Soham',
'class': 'FY'}
Dictionary after adding new item
{'rollno': 1, 'name': 'Soham', 'class': 'FY',
'Div': 'G'}
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-8-320.jpg)
![stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
print(f'Dictionary before modification {stud}’)
stud['rollno']=2 #modify rollno key’s value
print(f'Dictionary after modification {stud}')
Output:
Dictionary before modification
{'rollno': 1, 'name': 'Soham', 'class':
'FY'}
Dictionary after modification
{'rollno': 2, 'name': 'Soham', 'class':
'FY'}
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-9-320.jpg)
![ del statement use to delete item or delete dictionary in python.
stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
print(f'Dictionary {stud}’)
del stud['name'] # deleting key name and its value
print(f'Dictionary after delete operation {stud}’)
Output:
Dictionary {'rollno': 1, 'name':
'Soham', 'class': 'FY'}
Dictionary after delete operation
{'rollno': 1, 'class': 'FY'}
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-10-320.jpg)




![ The items() method is used to return the list with all dictionary keys with values.
Syntax
dict.items()
Example 1:
stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
print(stud.items())
Output:
dict_items([('rollno', 1), ('name', 'Soham'), ('class', 'FY')])
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-16-320.jpg)
![ Example 2:
stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
item=stud.items() # item variable to stored items in stud dict
print('origional dictionary items')
print(item) #display item
del stud['class'] #deleting class key and its value
print('updated dictionary items')
print(item) #updated items in stud dictionary
Output:
origional dictionary items
dict_items([('rollno', 1), ('name', 'Soham'), ('class', 'FY')])
updated dictionary items
dict_items([('rollno', 1), ('name', 'Soham')])
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-17-320.jpg)
![ The keys() method returns a view object.
The view object contains the keys of the dictionary, as a list.
Syntax:
dict.keys()
Example:
stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
print(stud.keys()) # display keys of stud dictionary as a list
Output:
dict_keys(['rollno', 'name', 'class'])
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-18-320.jpg)
![ Example 2:
When an item is added in the dictionary, the view object also gets updated:
stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
key=stud.keys() # key variable to stored keys in stud dict
print('origional dictionary keys')
print(key) #display keys
stud['branch']='Comp' #inserting new branch key
print('updated dictionary keys')
print(key) #updated keys in stud dictionary
Output:
origional dictionary keys
dict_keys(['rollno', 'name', 'class'])
updated dictionary keys
dict_keys(['rollno', 'name', 'class',
'branch'])
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-19-320.jpg)



![ The values() method returns a view object.
The view object contains the values of the dictionary, as a list.
Syntax:
dict.values()
Example:
stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
print(stud.values()) # display keys of stud dictionary as a list
Output:
dict_values([1, 'Soham', 'FY'])
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-23-320.jpg)
![ Example 2:
When an item is added in the dictionary, the view object also gets updated:
stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
val=stud.values() # val variable to stored keys in stud dict
print('origional dictionary values')
print(val) #display values
stud['branch']='Comp' #inserting new branch key
print('updated dictionary values')
print(val) #updated values in stud dictionary
Output:
origional dictionary values
dict_values([1, 'Soham', 'FY'])
updated dictionary values
dict_values([1, 'Soham', 'FY',
'Comp'])
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-24-320.jpg)
![ An Aliasing Dictionary is use to assign a dictionary to another dictionary by updating the
content on both dictionary at a time.
Aliasing is whenever two variables refer to the same dictionary object, changes to one
affect the other
Example:
stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
stud_new={} #another dict
stud_new=stud # aliasing stud dict to stud_new
print(stud_new) # diplay stud_new dict
stud['class']='SY' #updating stud dict
print(f'Original Dict: {stud}')# display stud dict
print(f'Alised Dict: {stud_new}')# display stud_new dict
Output:
{'rollno': 1, 'name': 'Soham', 'class': 'FY'}
Original Dict: {'rollno': 1, 'name': 'Soham', 'class':
'SY'}
Alised Dict: {'rollno': 1, 'name': 'Soham', 'class':
'SY'}
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-25-320.jpg)
![ Copy() used to copy dictionary.
But with this updating one dictionary not reflected on another dictionary.
Example:
stud={'rollno':1,
'name':'Soham',
'class':'FY'}
stud_new={} #another dict
stud_new=stud.copy() # copying stud dict to stud_new
print(stud_new) # diplay stud_new dict
stud['class']='SY' #updating stud dict
print(f'Original Dict: {stud}')# display stud dict
print(f'Copied Dict: {stud_new}')# display stud_new dict
Output:
{'rollno': 1, 'name': 'Soham', 'class': 'FY'}
Original Dict: {'rollno': 1, 'name': 'Soham', 'class':
'SY'}
Alised Dict: {'rollno': 1, 'name': 'Soham', 'class':
‘FY'}
Department of Computer Engineering, Sanjivani College of Engineering, Kopargaon 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-dictionary-240527082648-52c303a0/85/Unit4-Basic-Concepts-and-methods-of-Dictionary-pptx-26-320.jpg)
