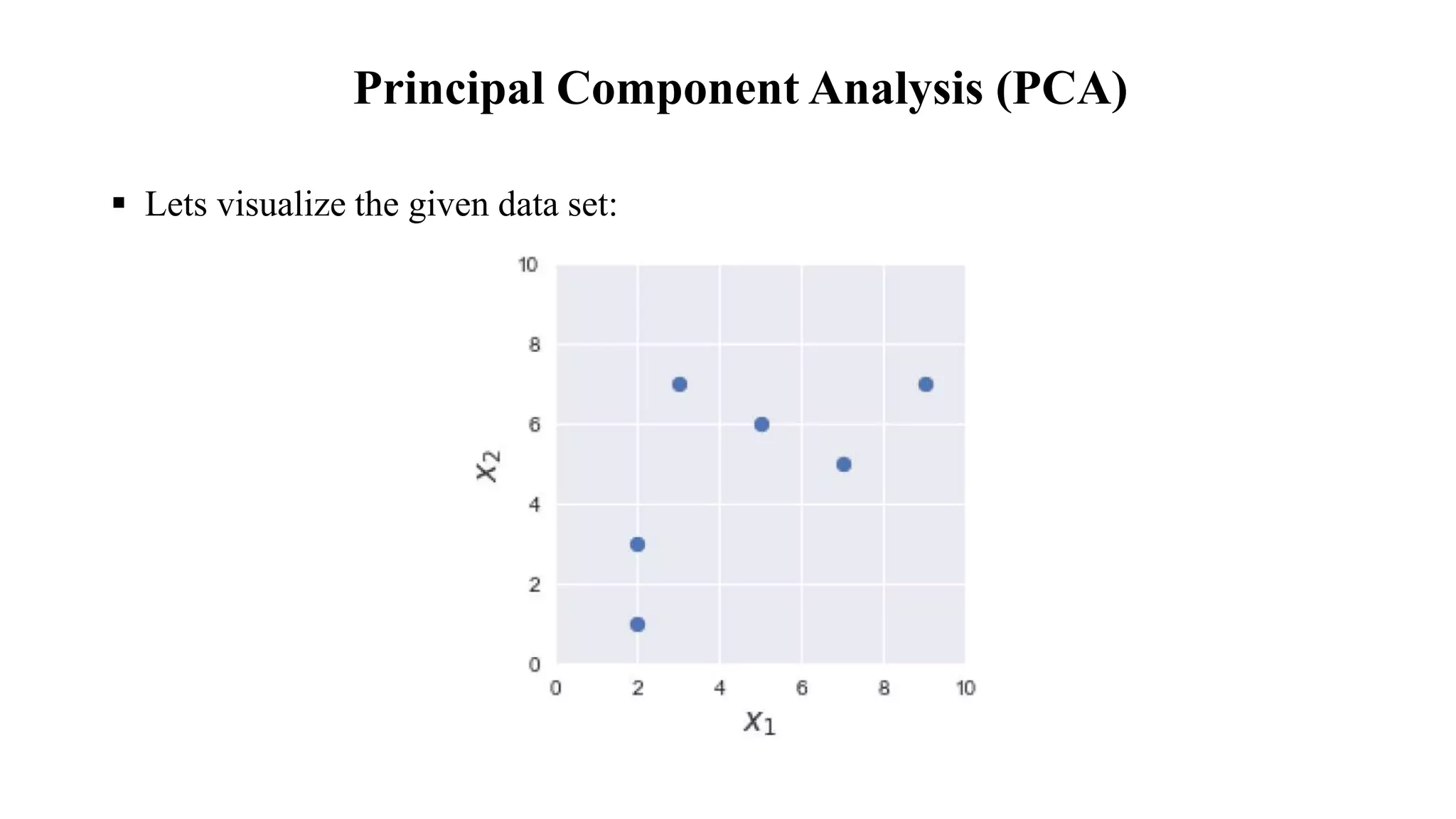
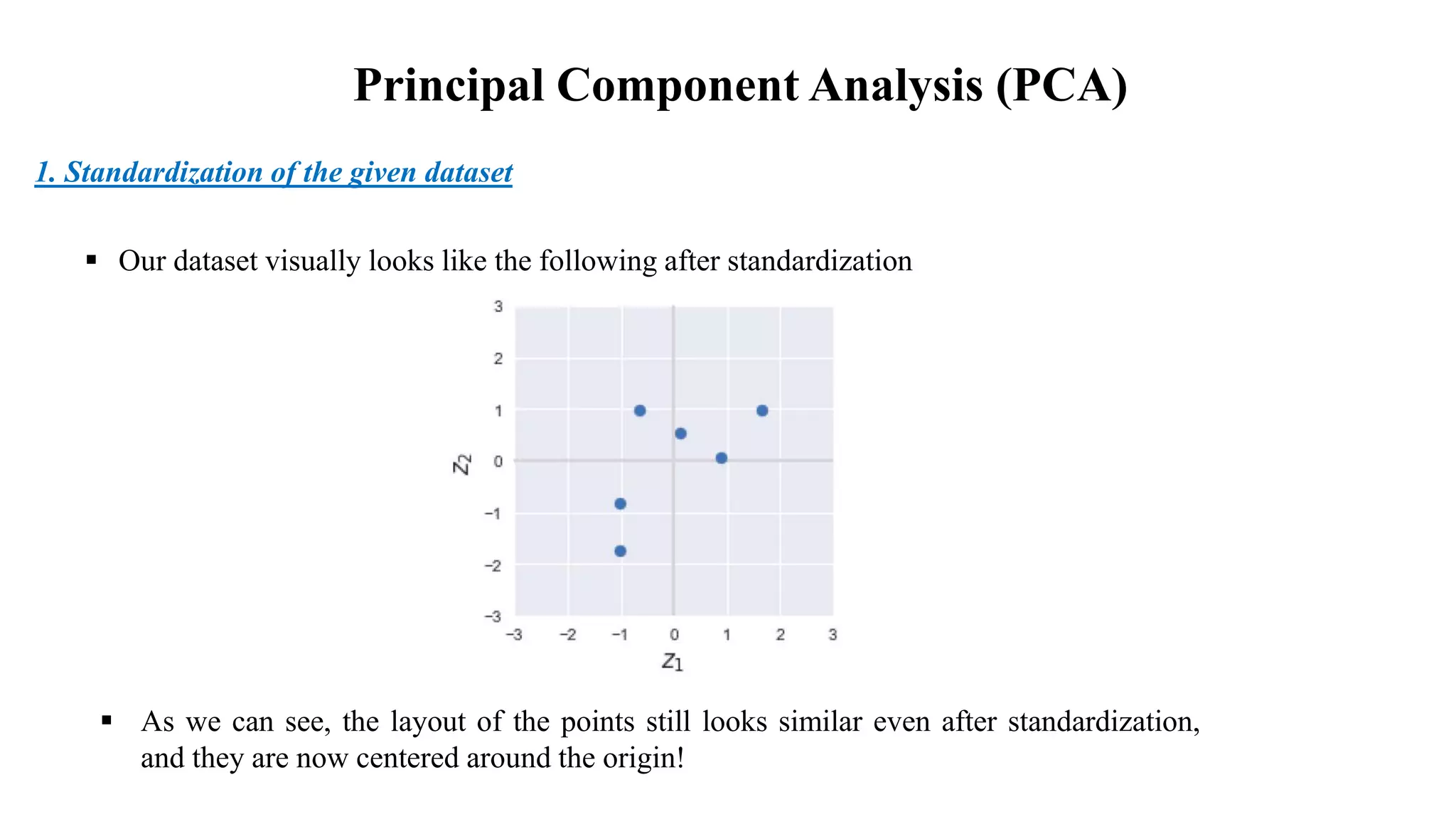
PCA is a technique used to reduce the dimensionality of large datasets while retaining most of the variation in the data. It works by transforming the data to a new set of variables called principal components, which are uncorrelated and ordered so that the first few retain most of the variation in the original dataset. The key steps are: 1) standardizing the data, 2) computing the covariance matrix, 3) calculating its eigenvalues and eigenvectors, 4) selecting the top few eigenvectors which explain most of the variance as the principal components, and 5) projecting the standardized data onto this lower-dimensional space.