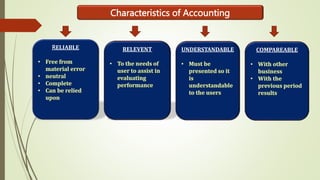
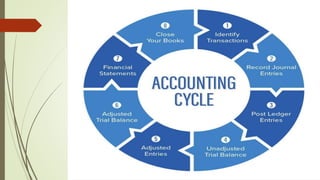
This document provides an overview of basic accounting principles, concepts, and types of accounts. It defines accounting as keeping records of financial transactions according to certain rules. The key differences between accounting and accountancy are explained. The main aspects of accounting are described as record keeping, tracking transactions, and financial reporting. Characteristics of accounting like being reliable, relevant, understandable and comparable are outlined. The three main types of accounts - personal, real, and nominal - are defined along with rules for debiting and crediting each type. Important accounting concepts like separate entity, going concern, money measurement, cost, dual aspect, accounting period, realization and accrual are explained. Finally, the document discusses accounting conventions like consistency, full disclosure, material