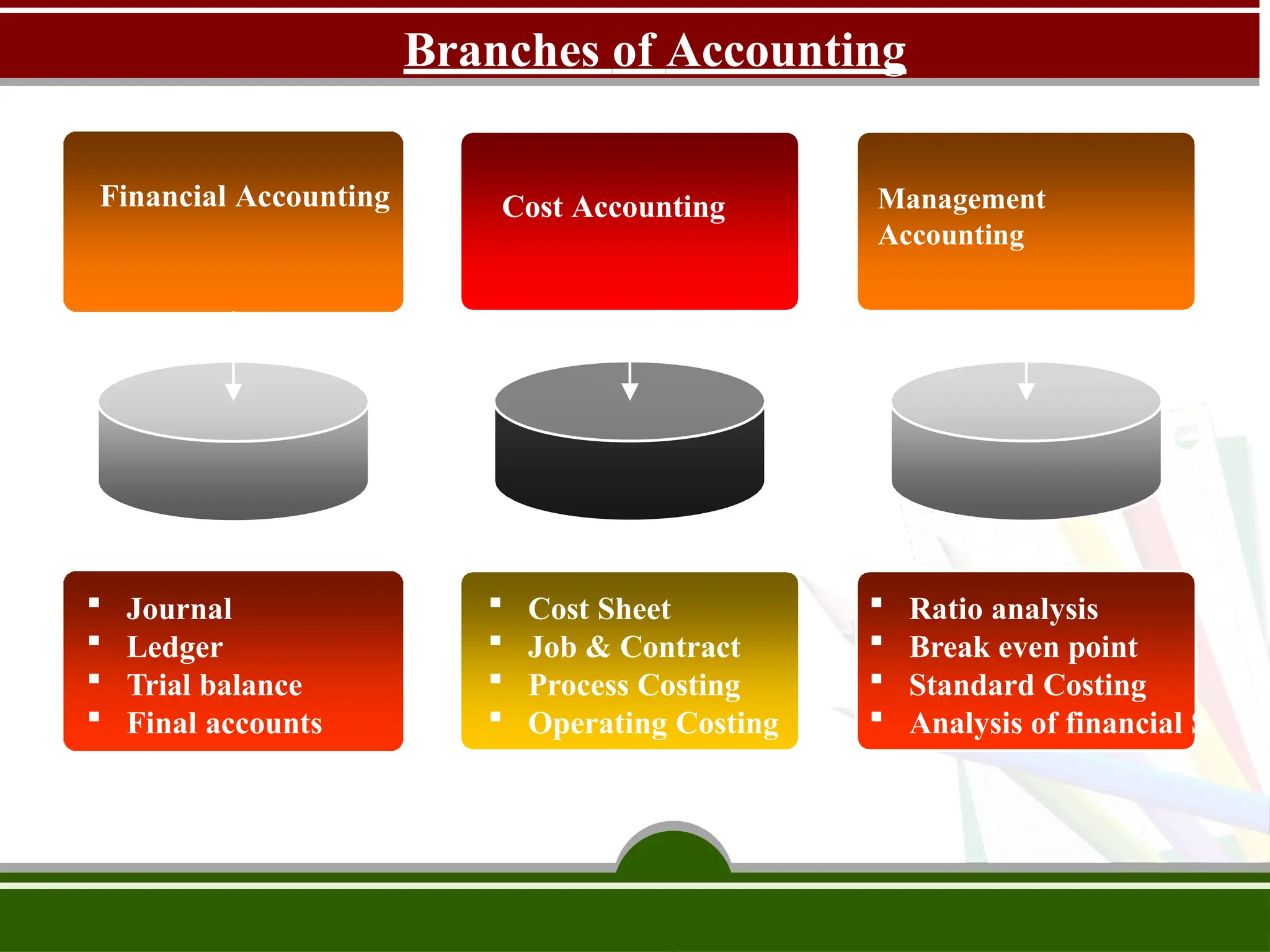
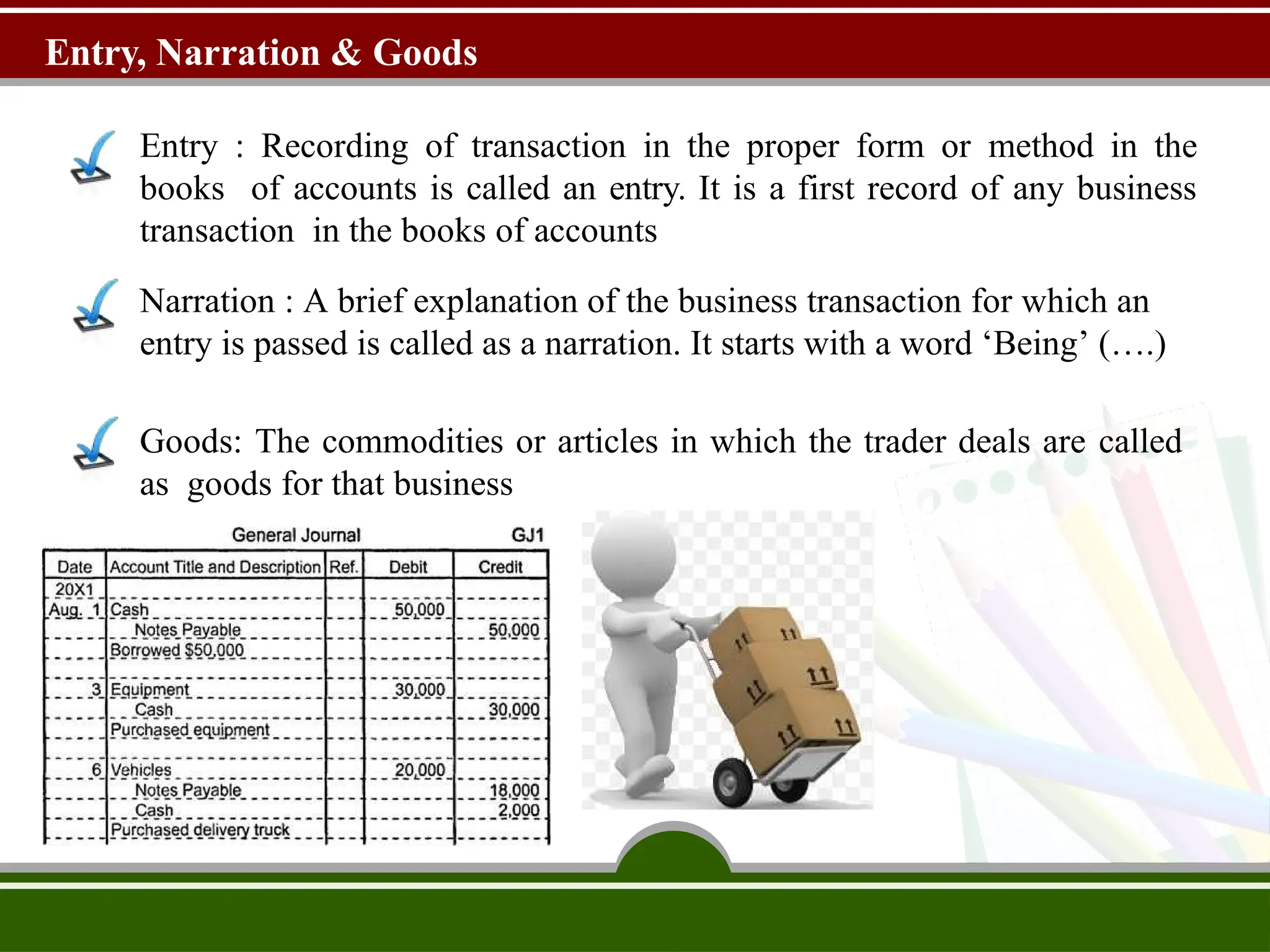
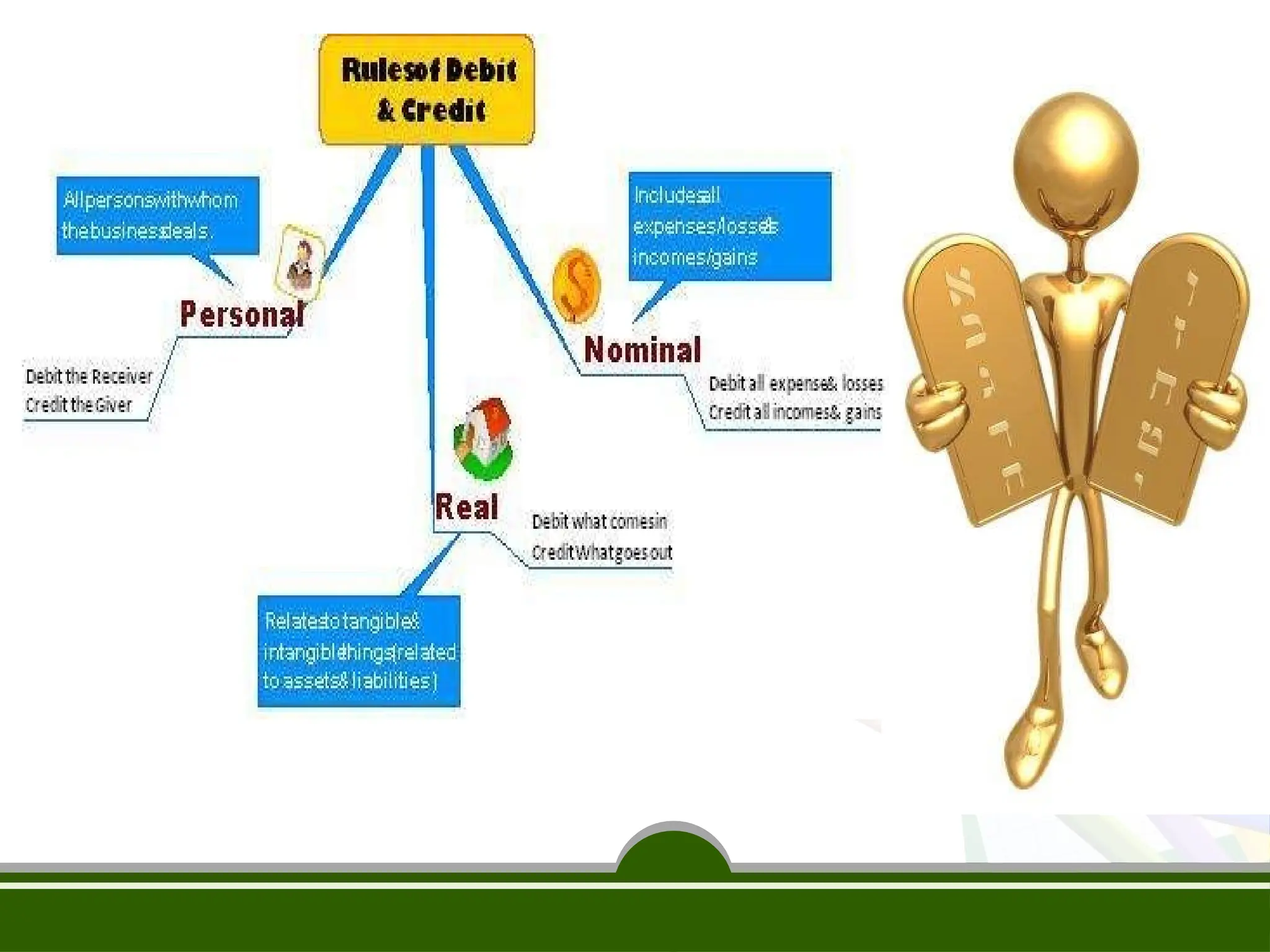
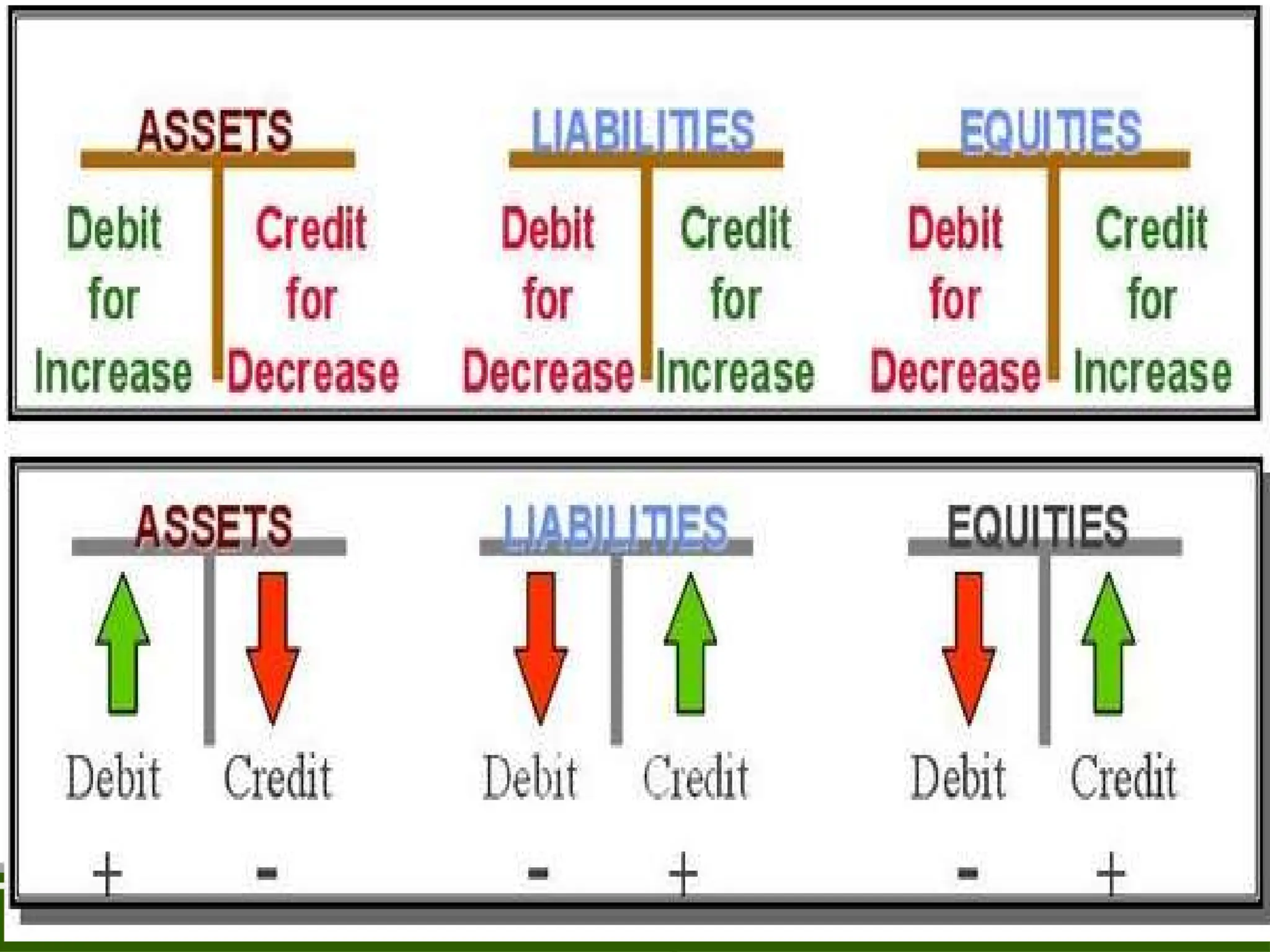
The document discusses the fundamental concepts of bookkeeping and accountancy, highlighting the definitions, objectives, and branches of accounting. It defines bookkeeping as a systematic process for recording monetary transactions to maintain accurate financial records and outlines essential accounting principles and concepts such as the business entity concept, going concern, and dual aspect. Additionally, the document addresses inflation accounting and its relevance to current monetary values in financial reporting.