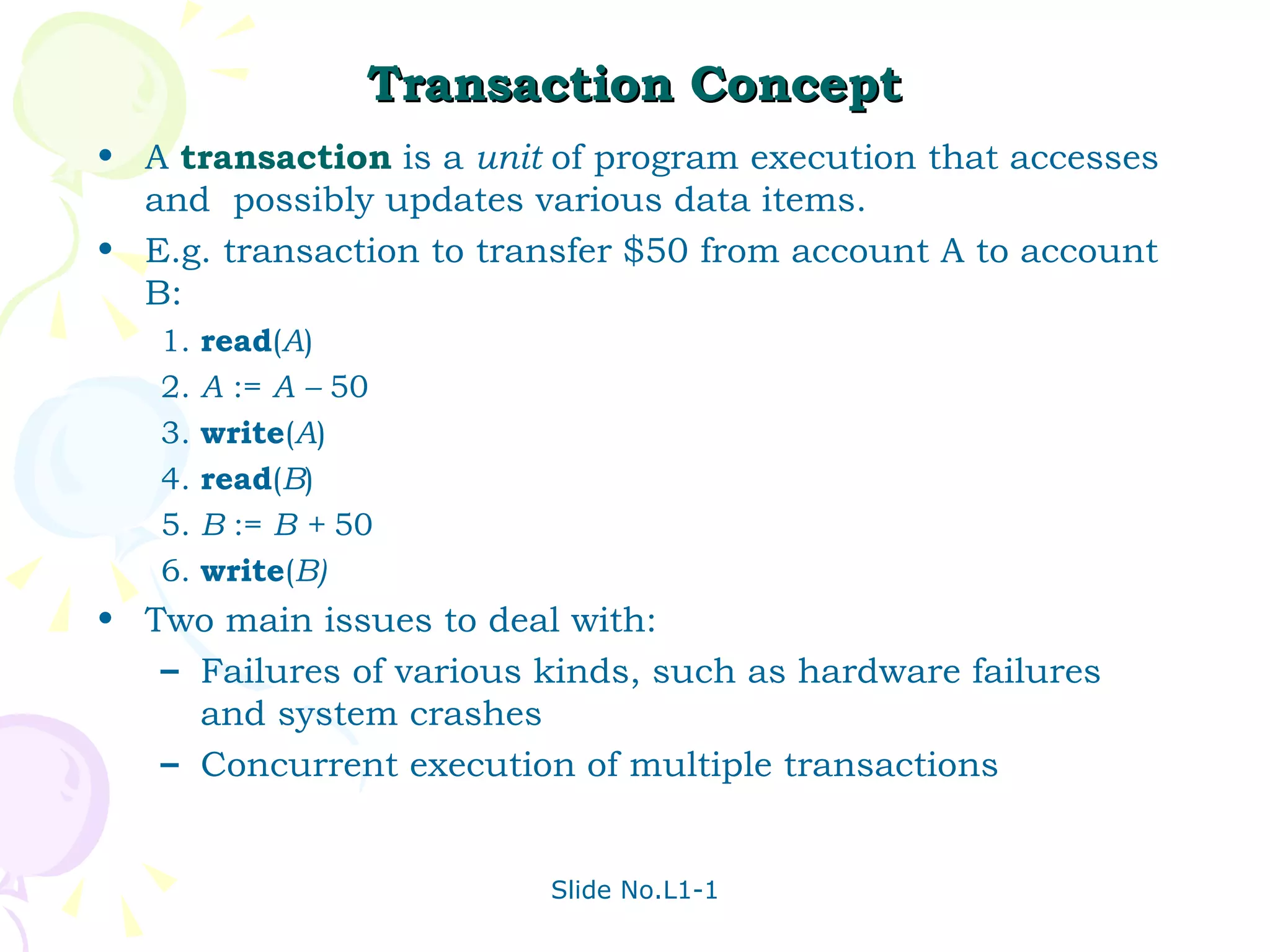
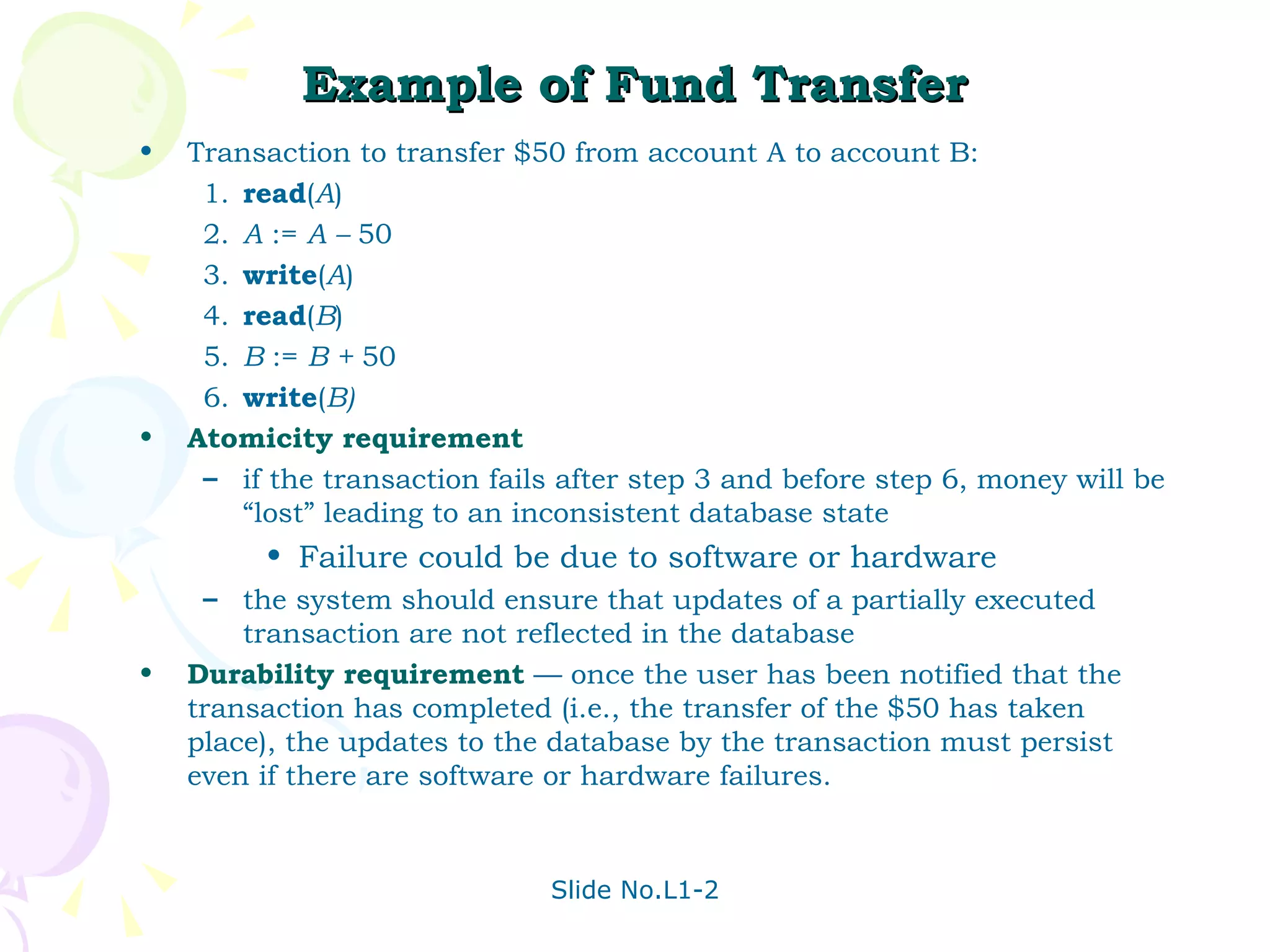
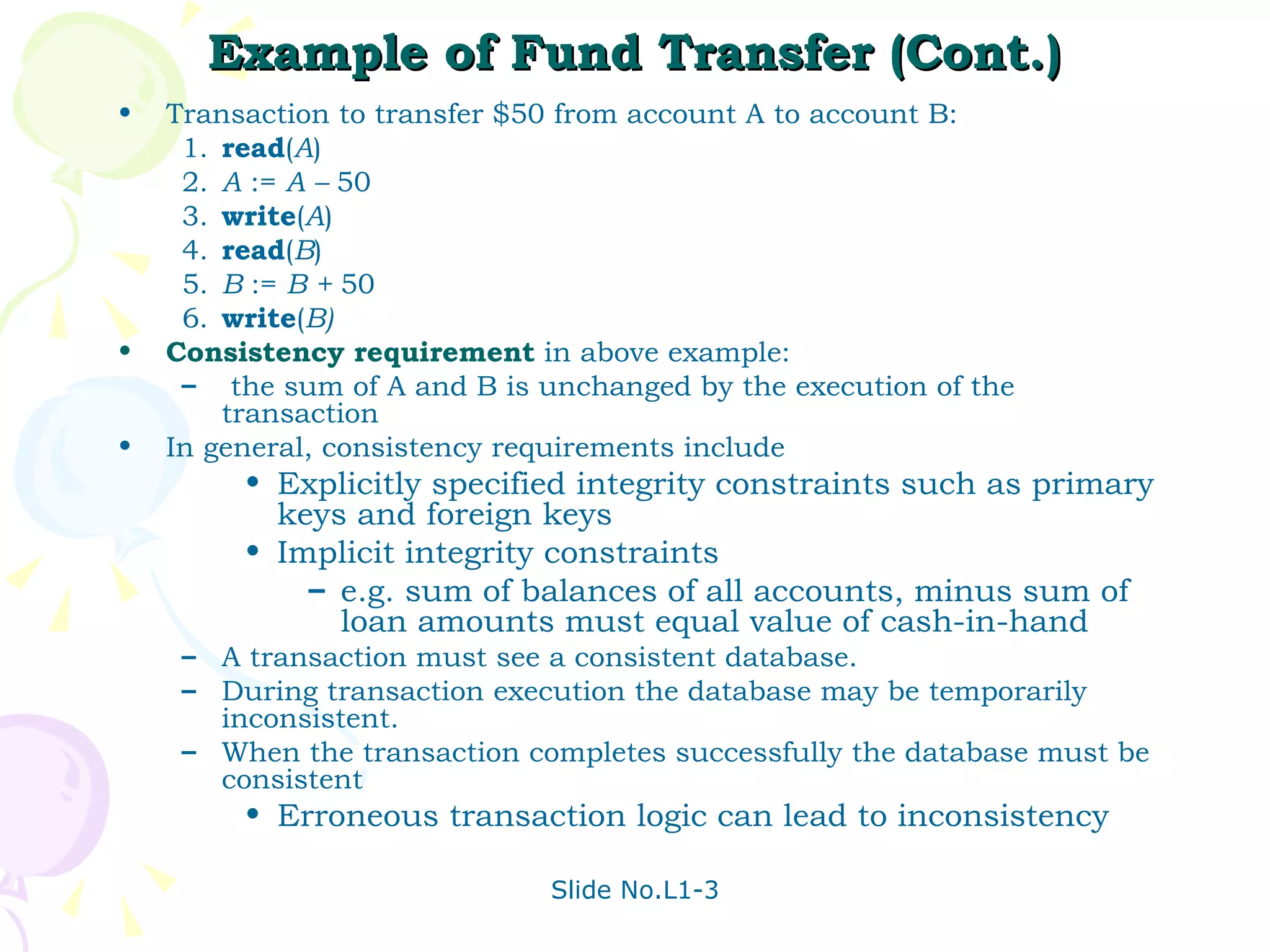
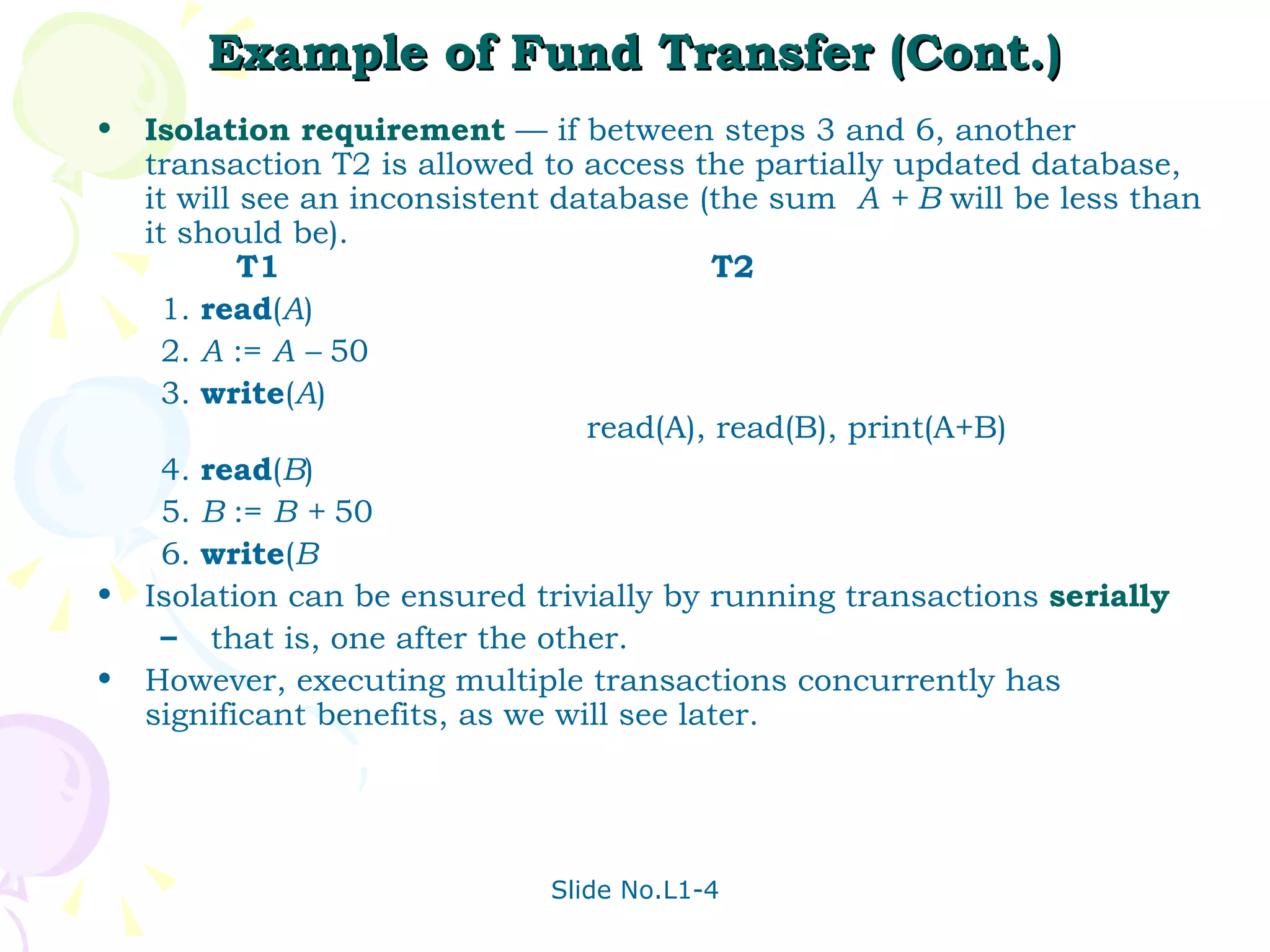
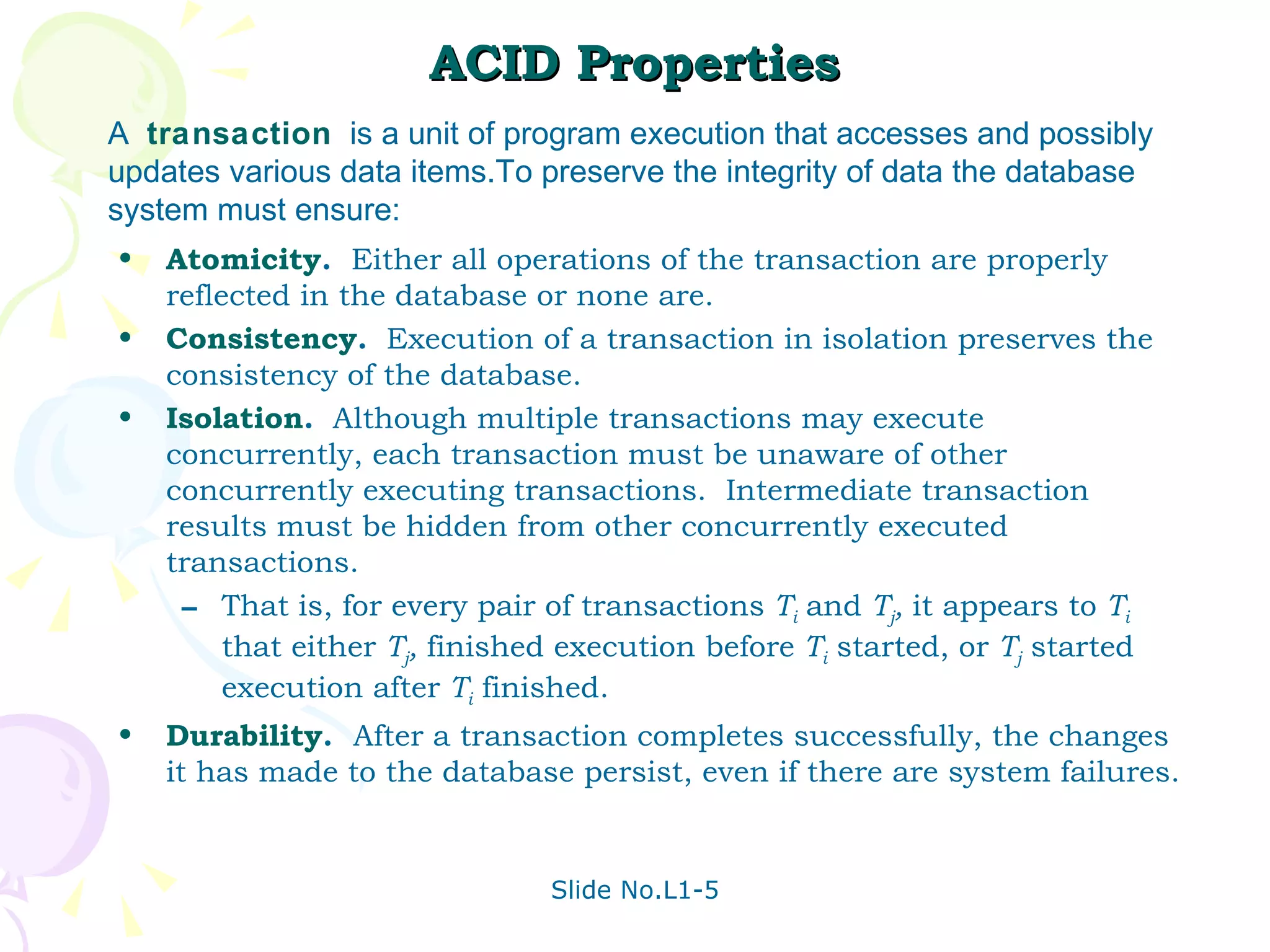
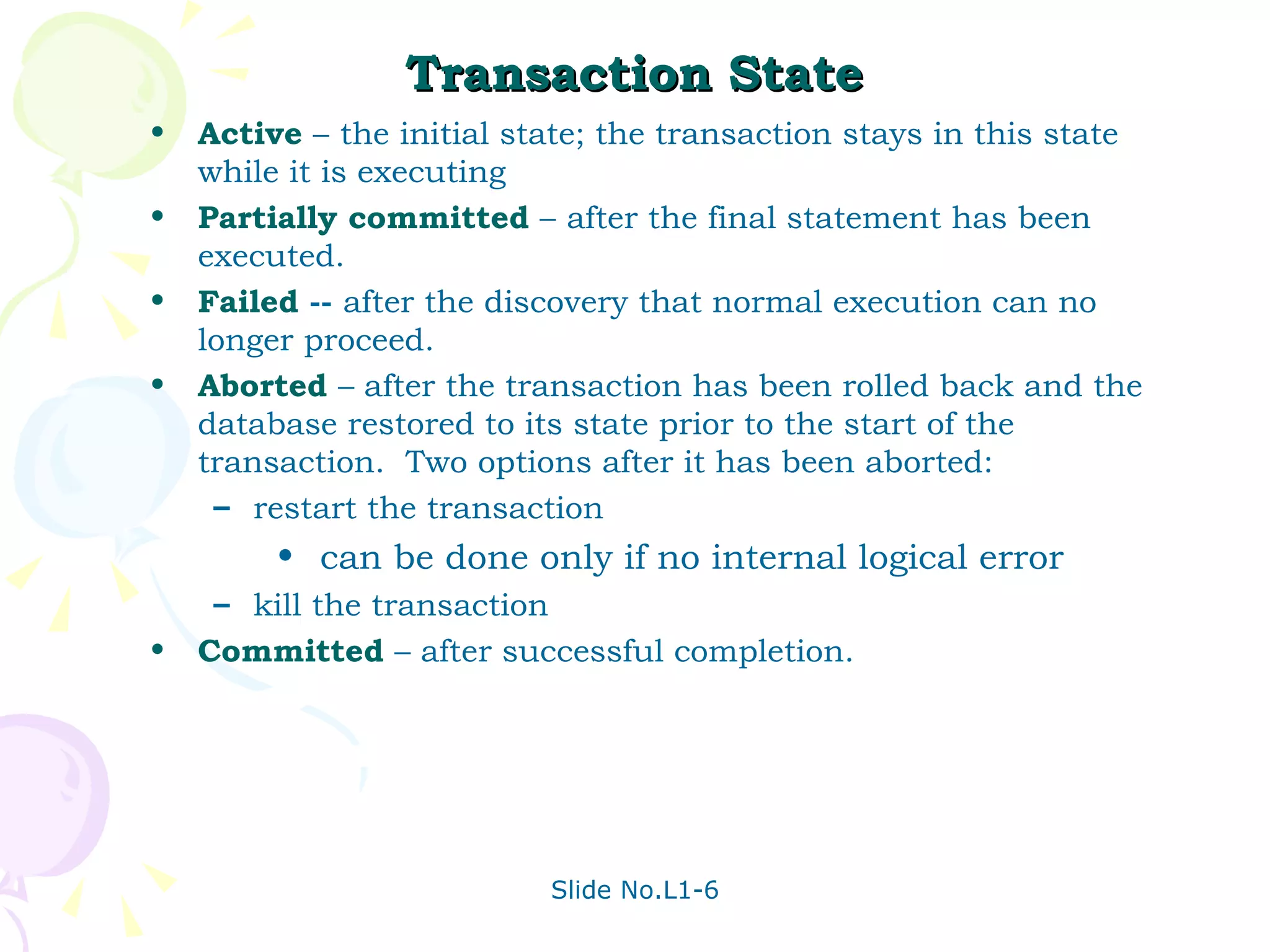
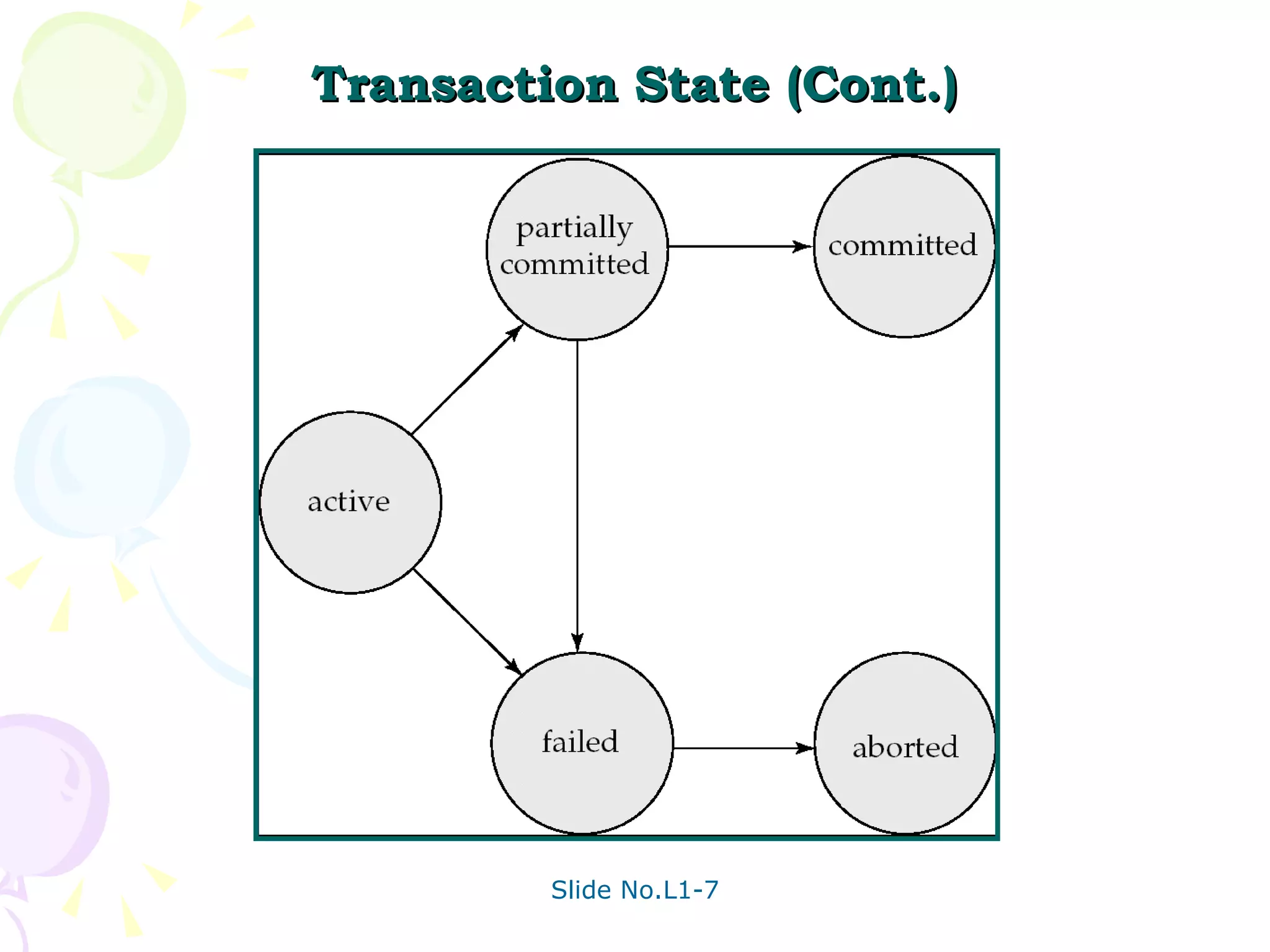
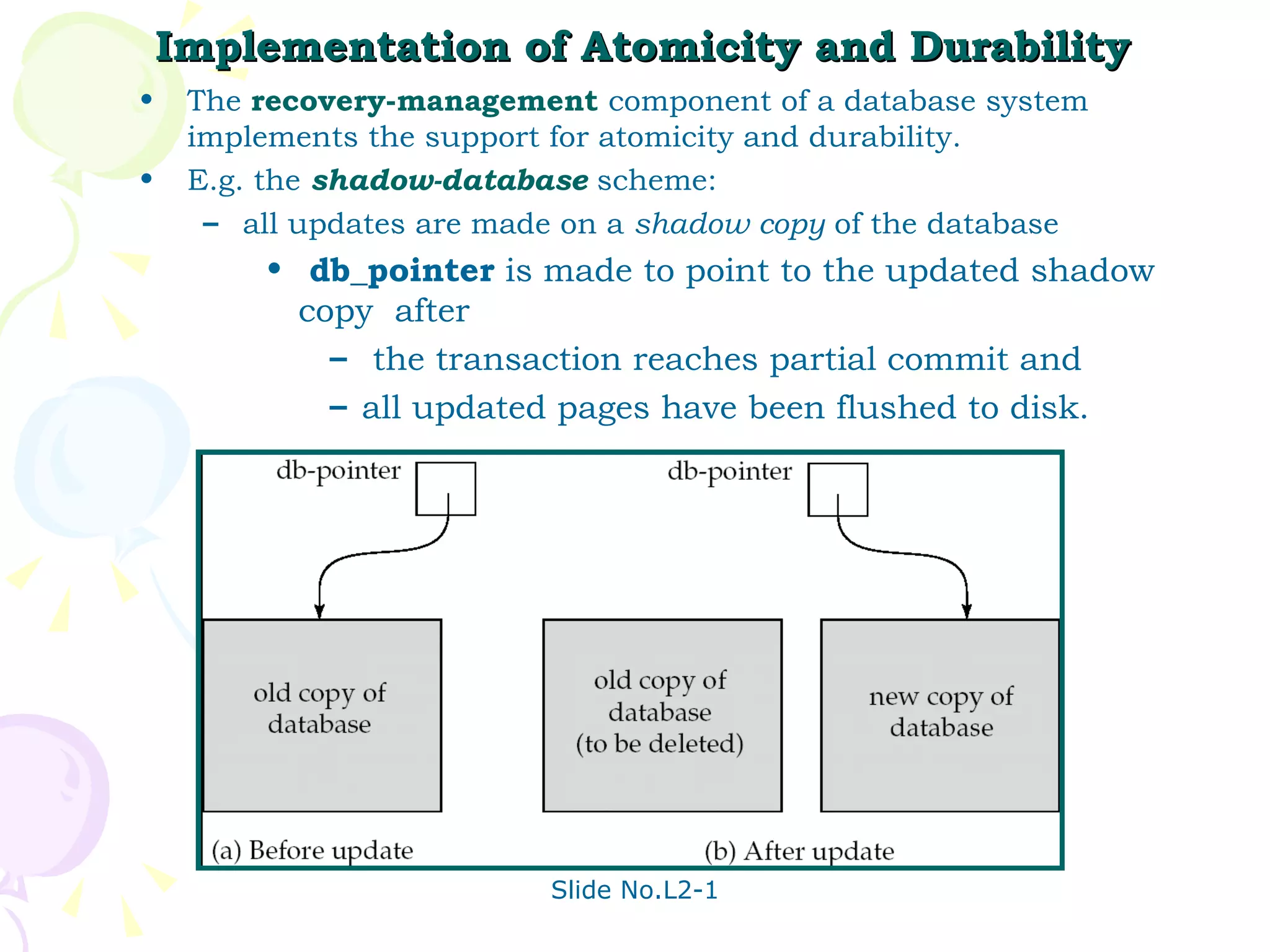
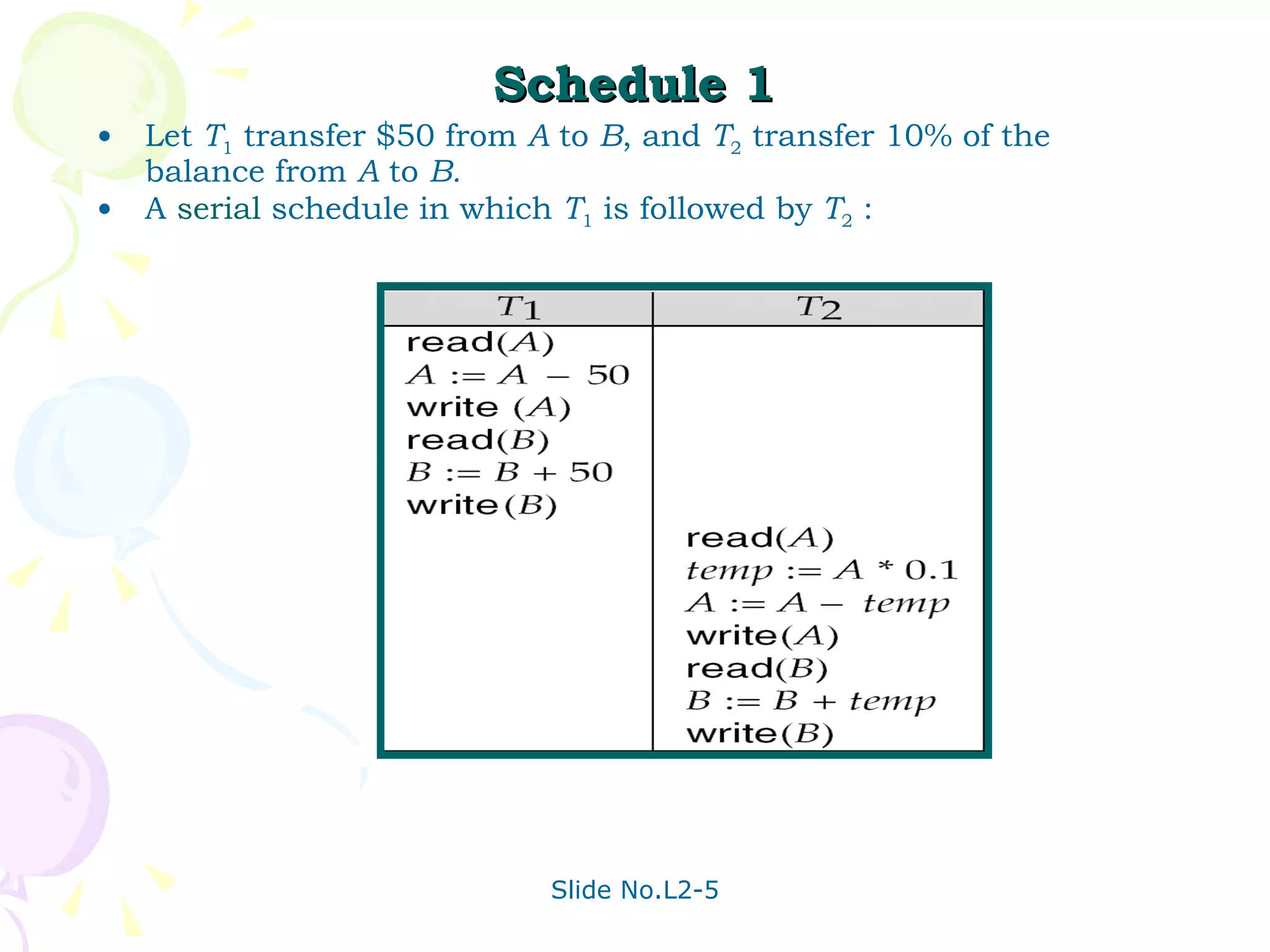
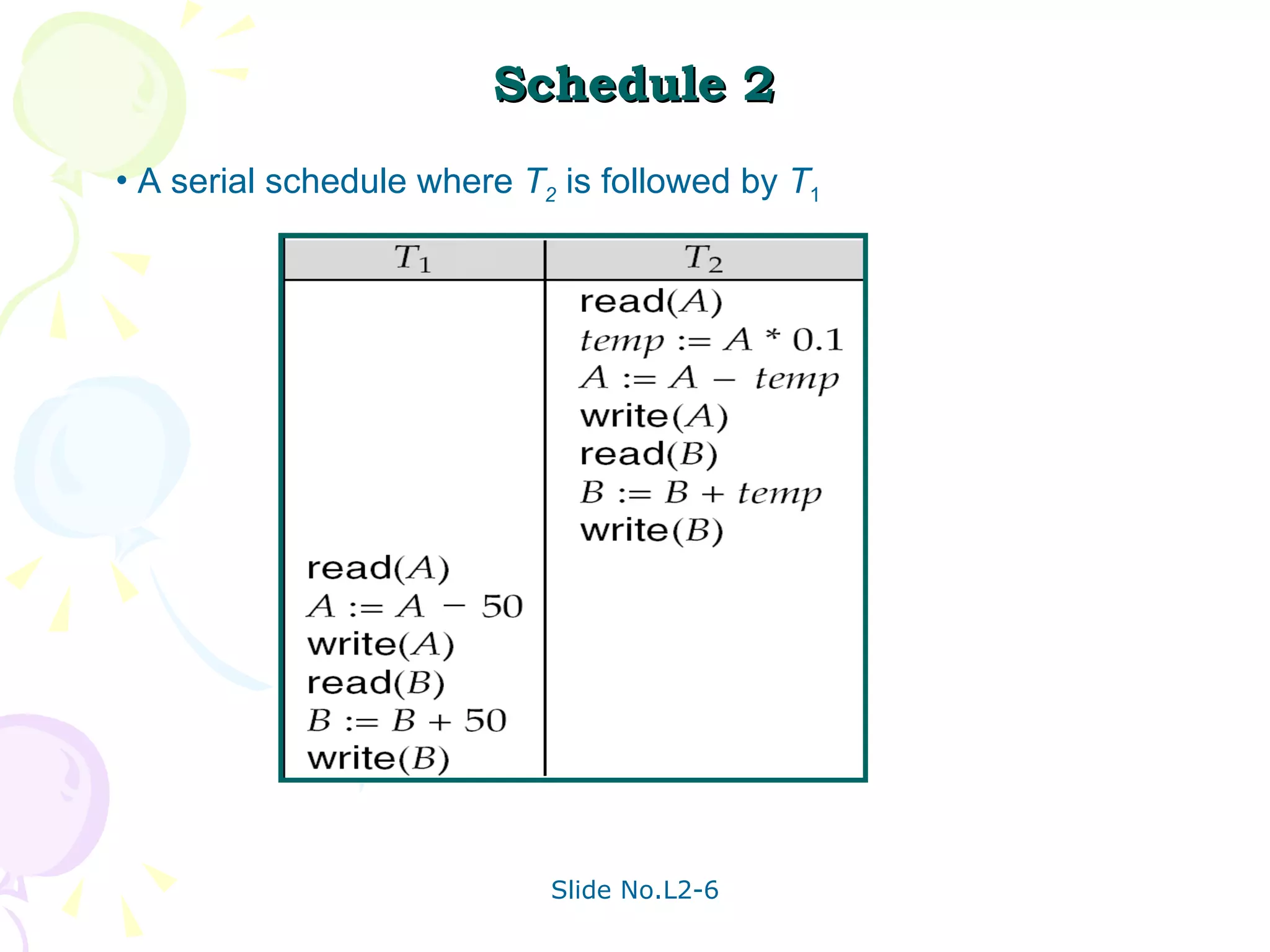
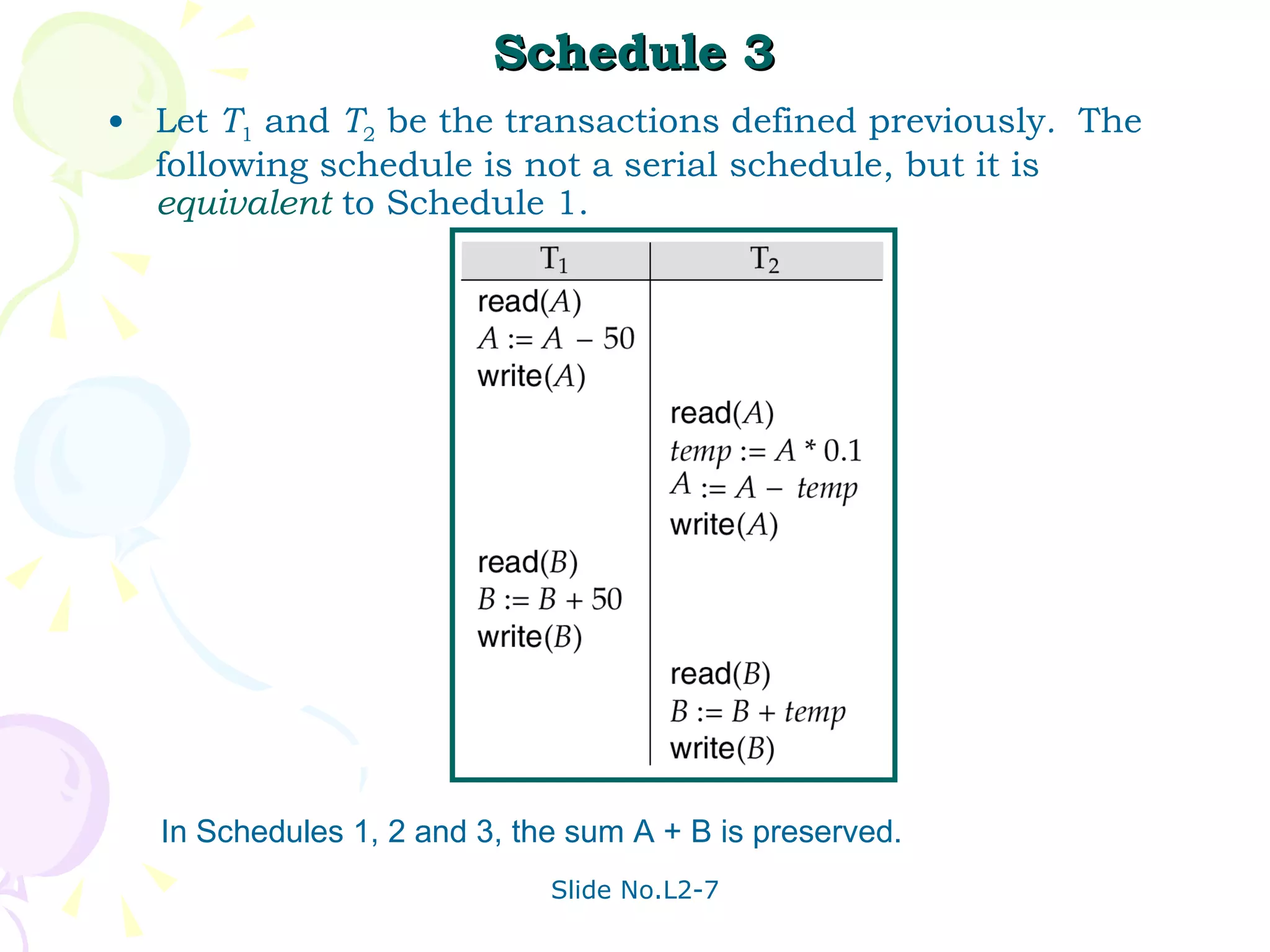
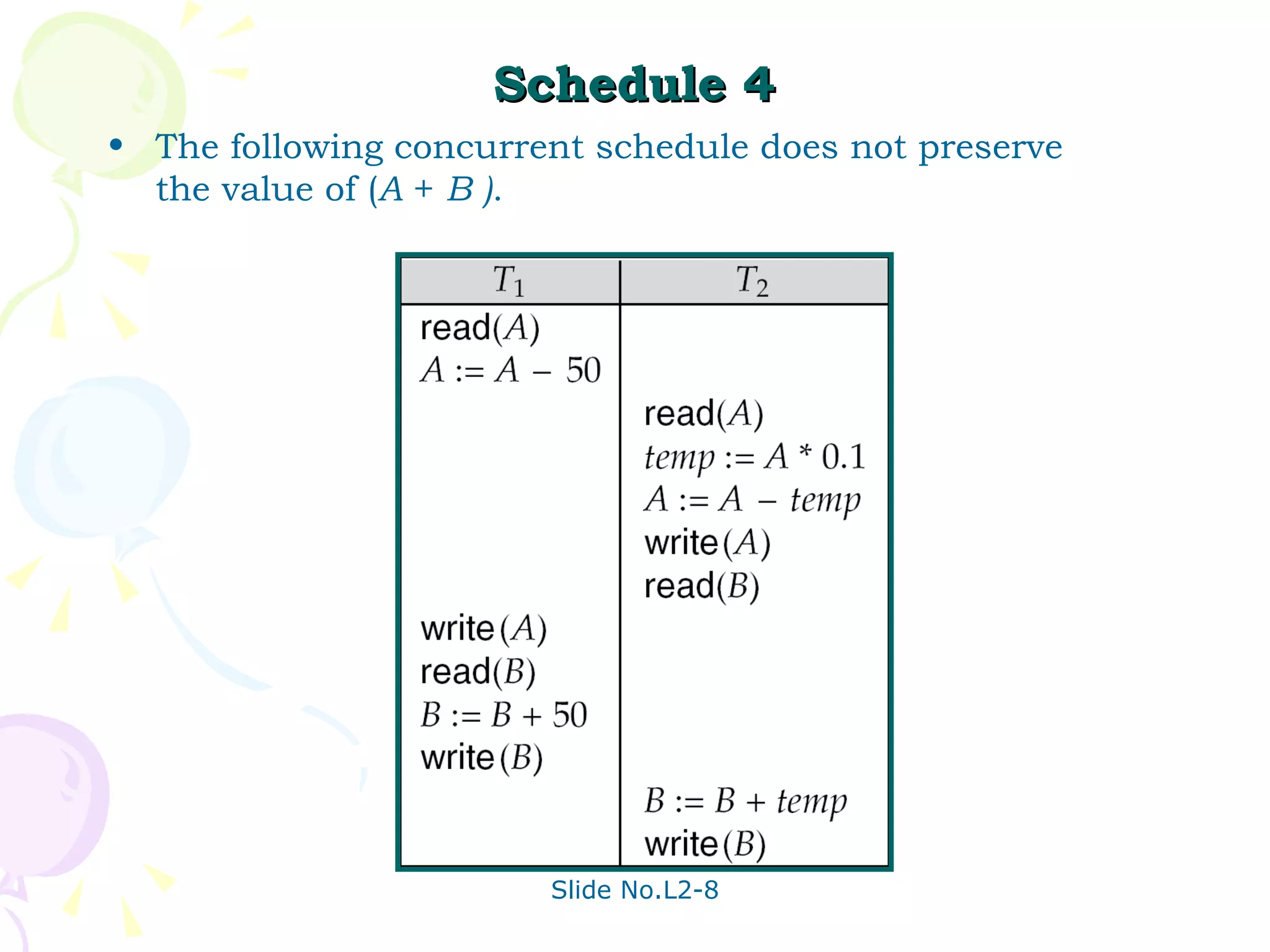
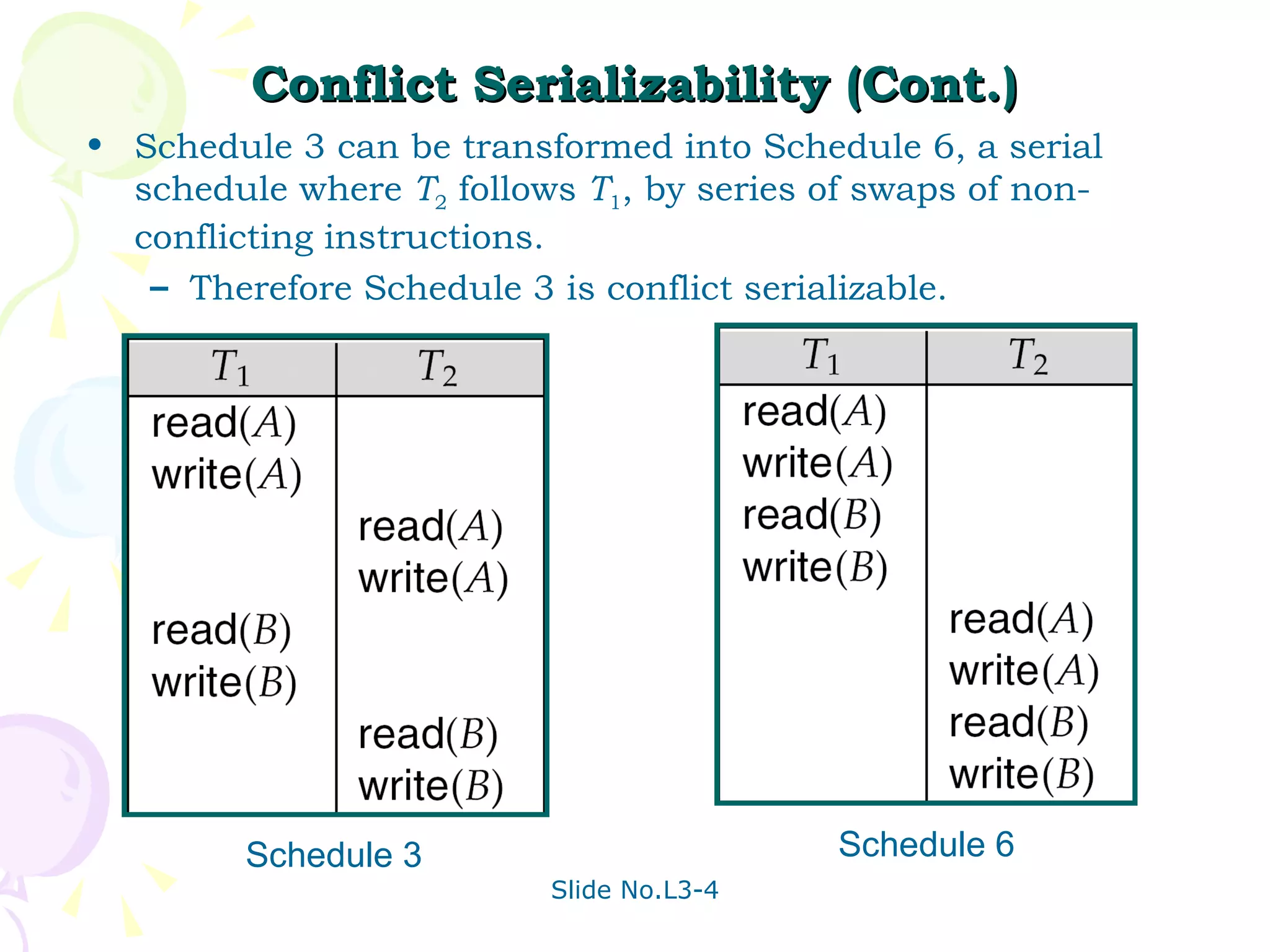
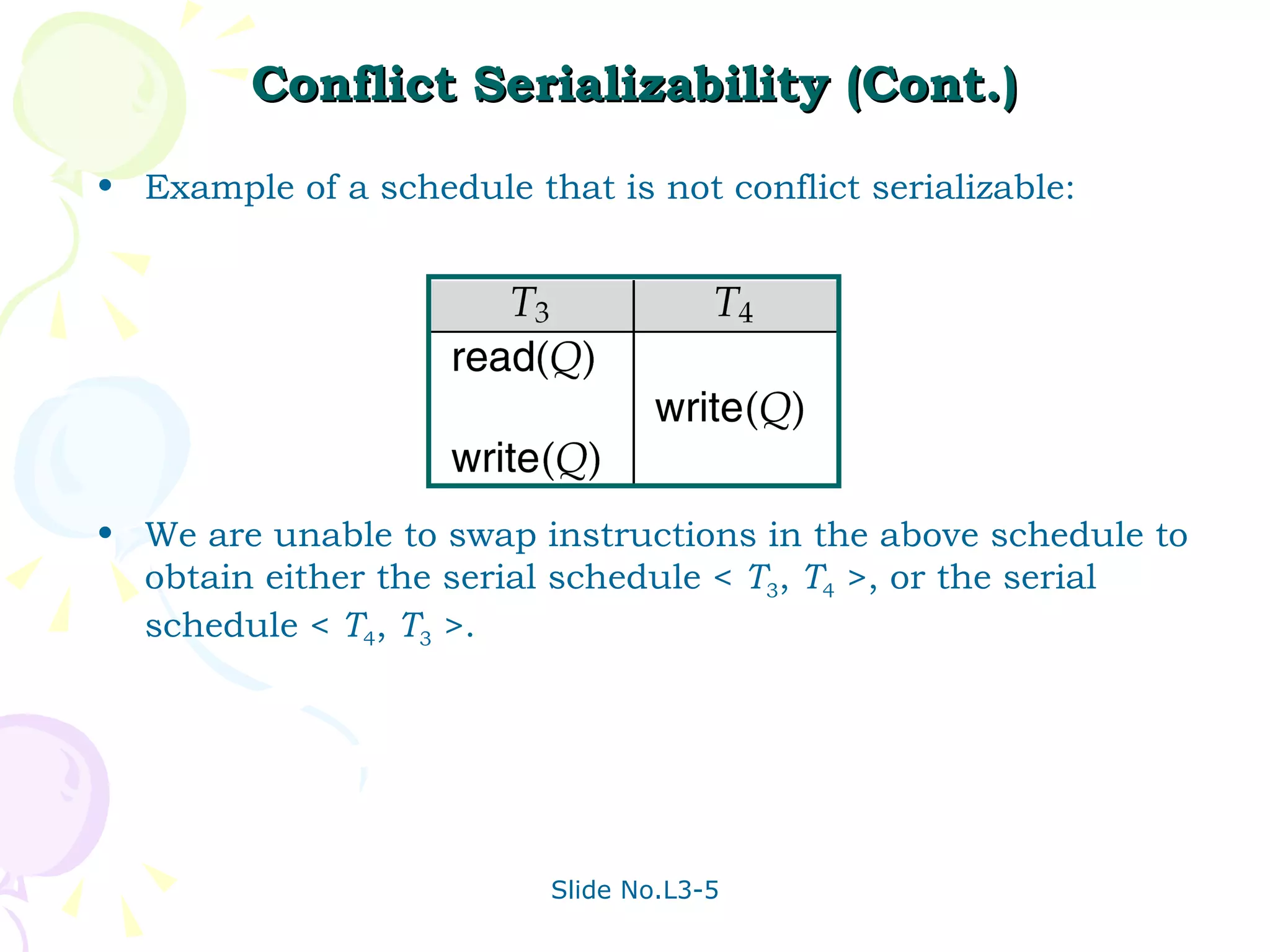
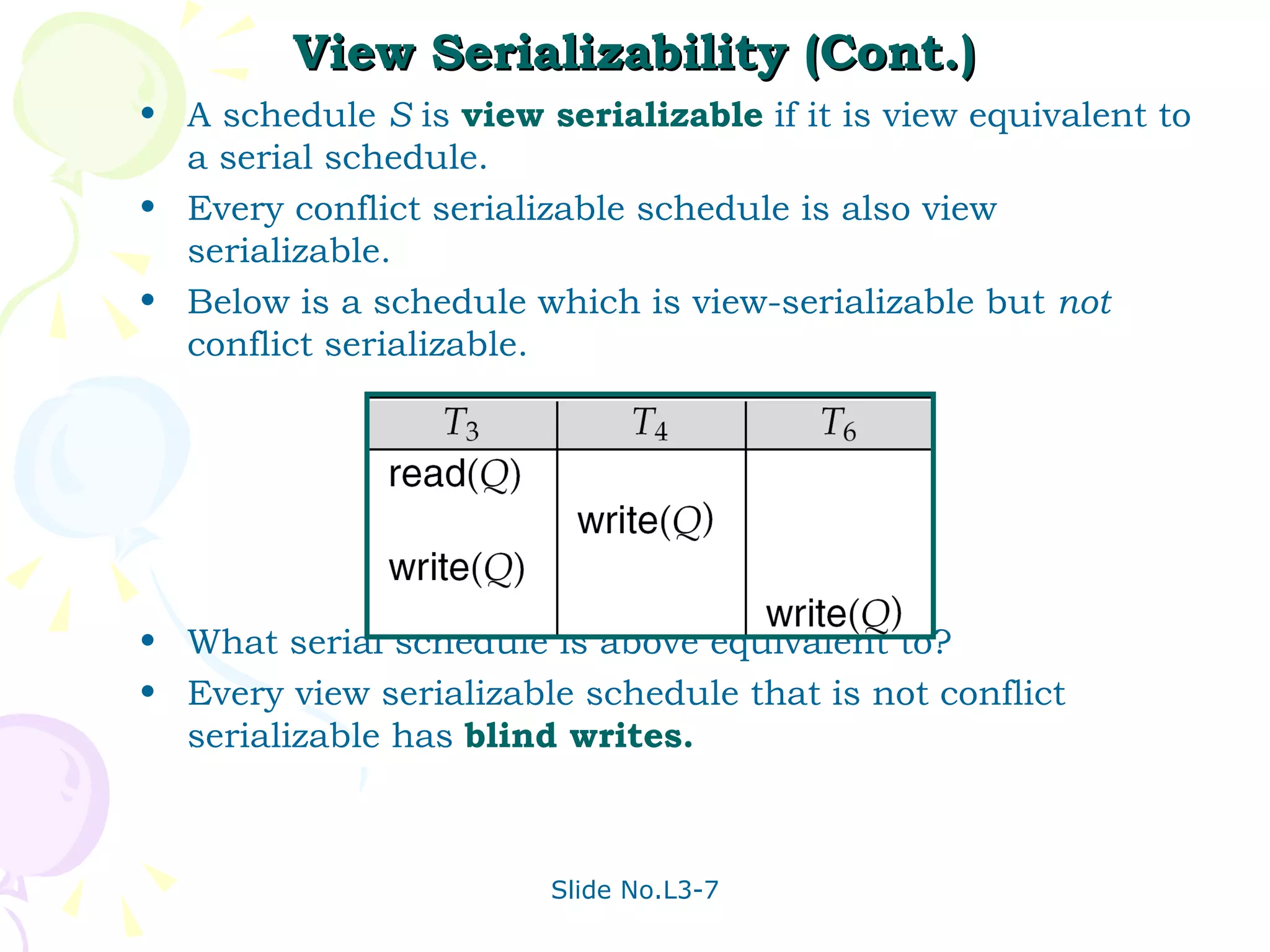
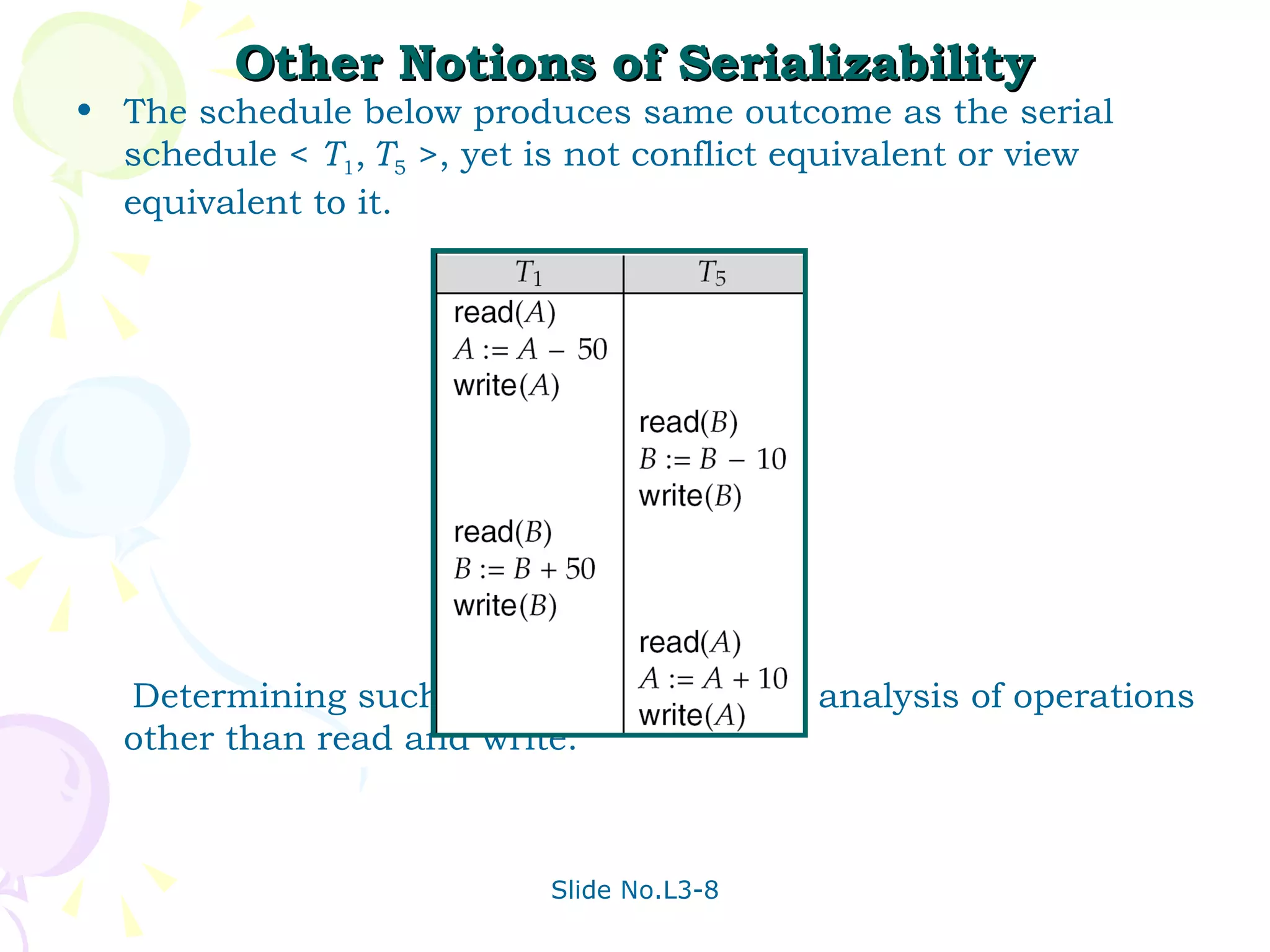
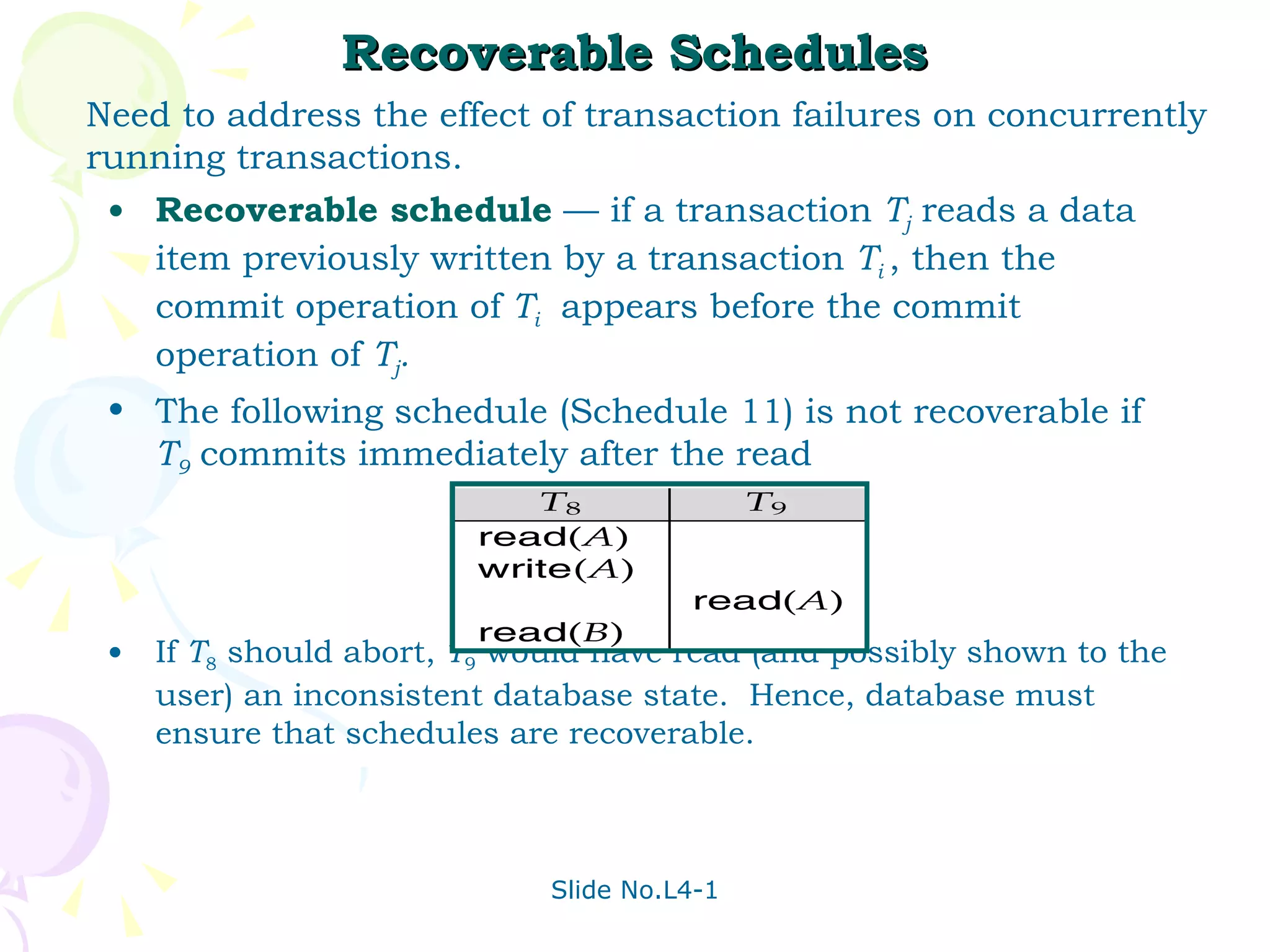
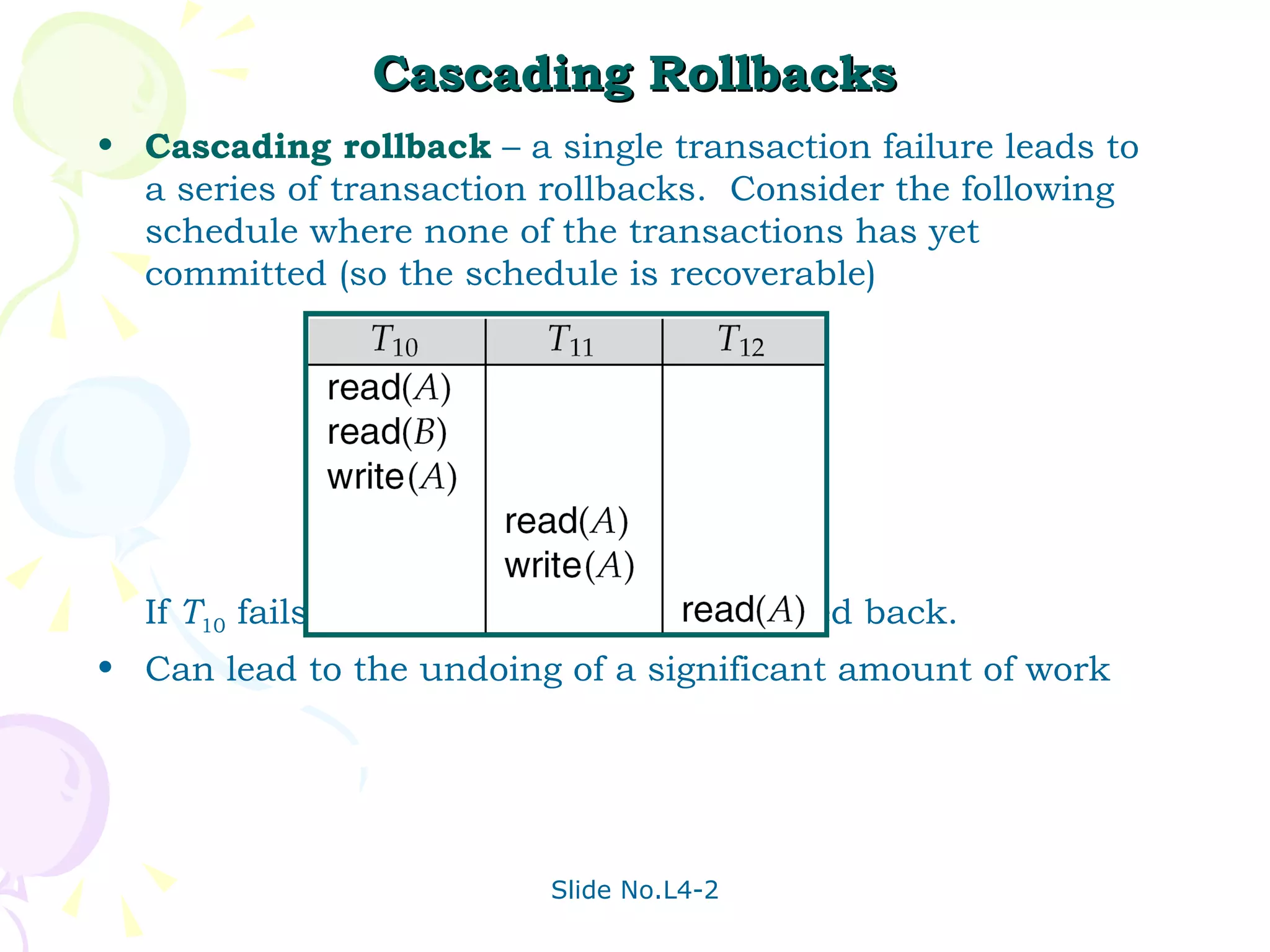
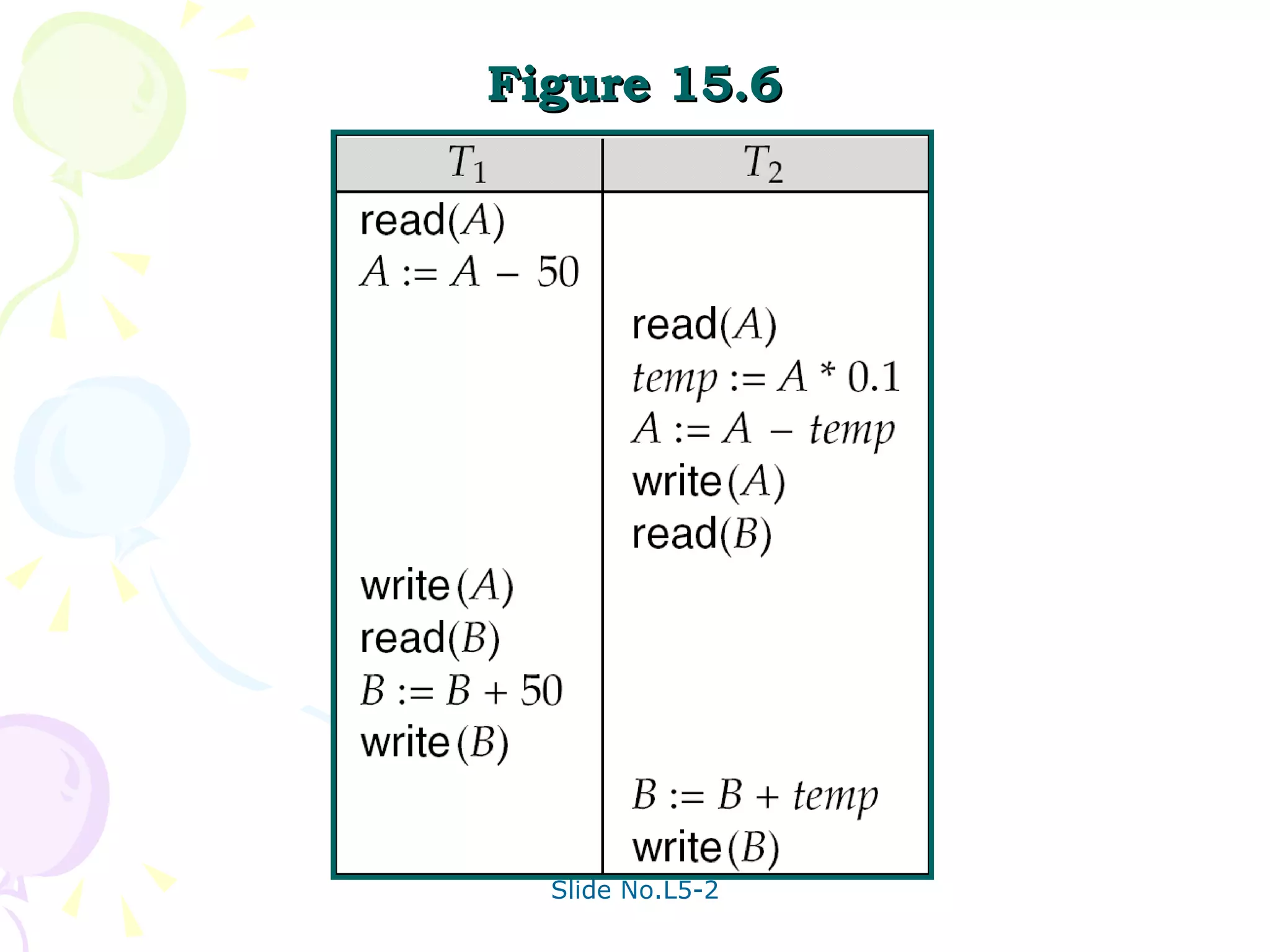
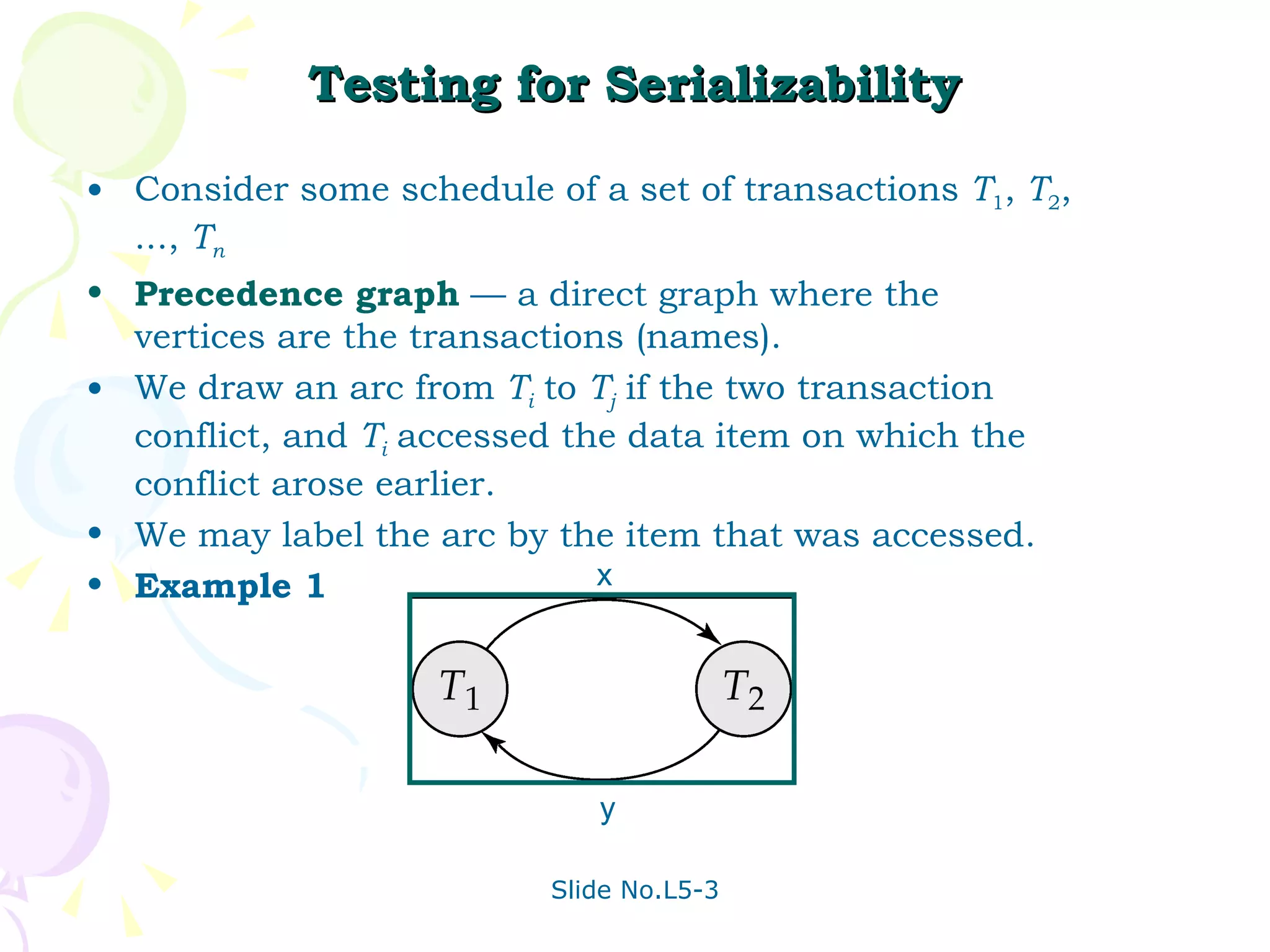
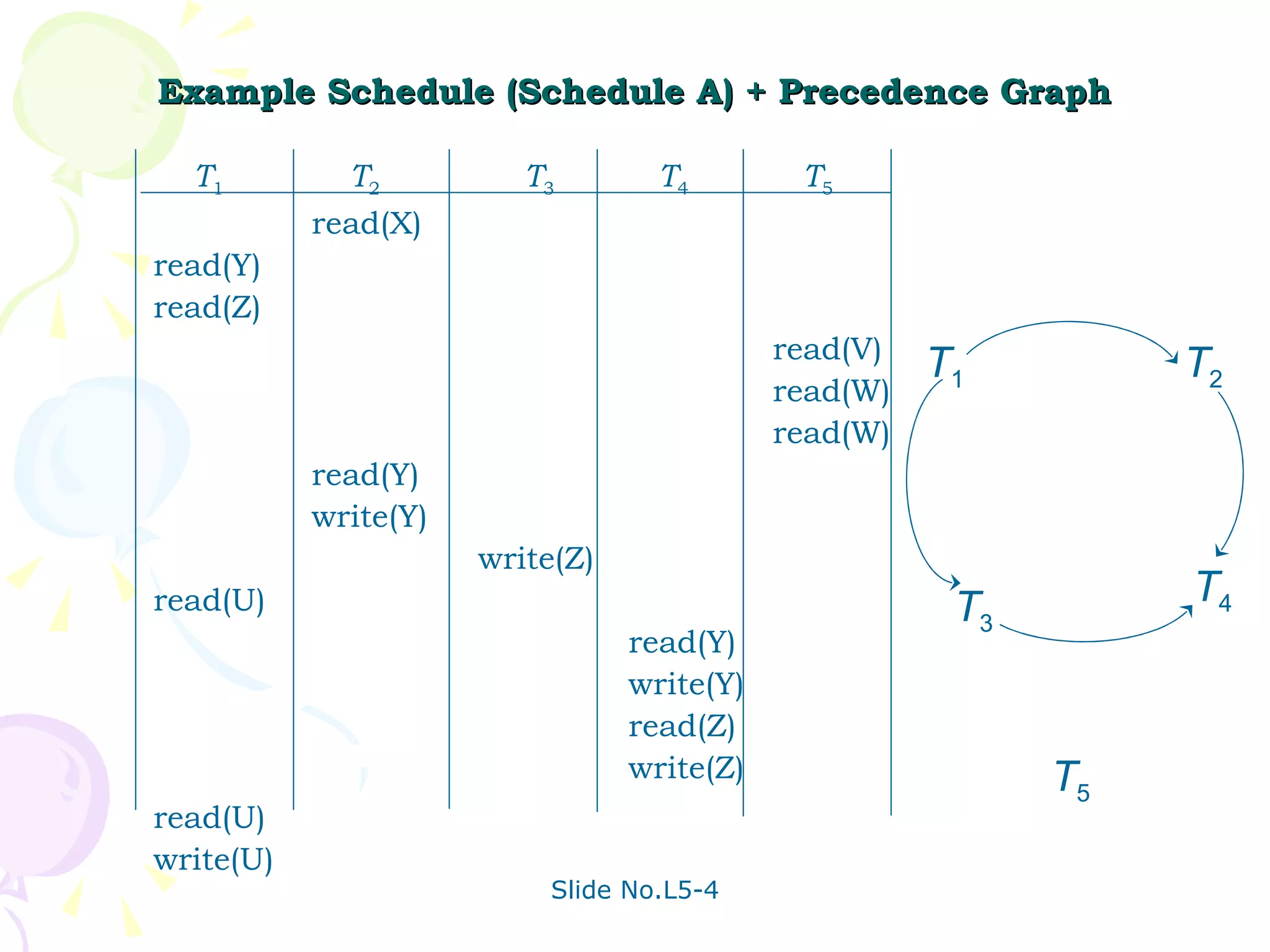
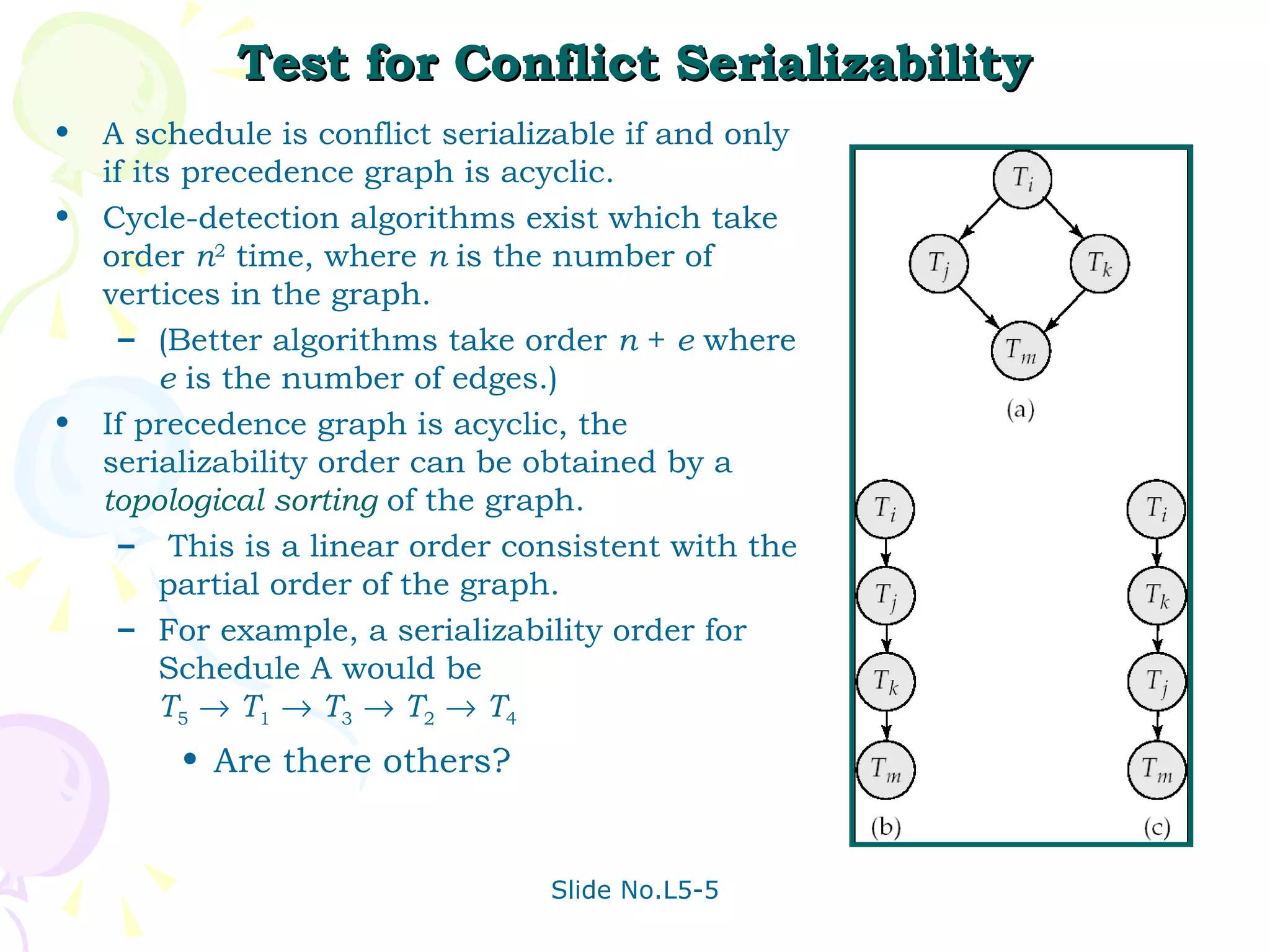
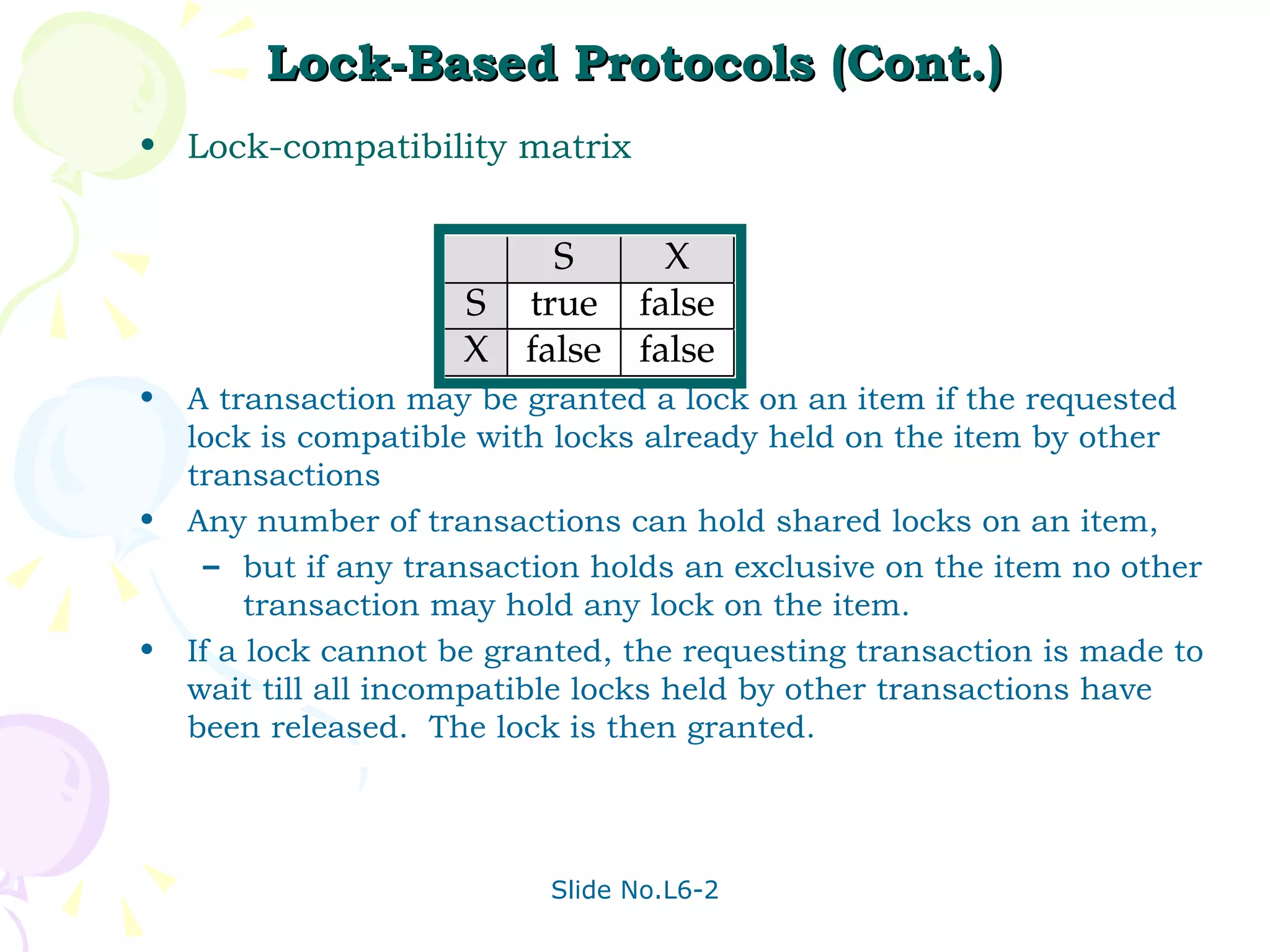
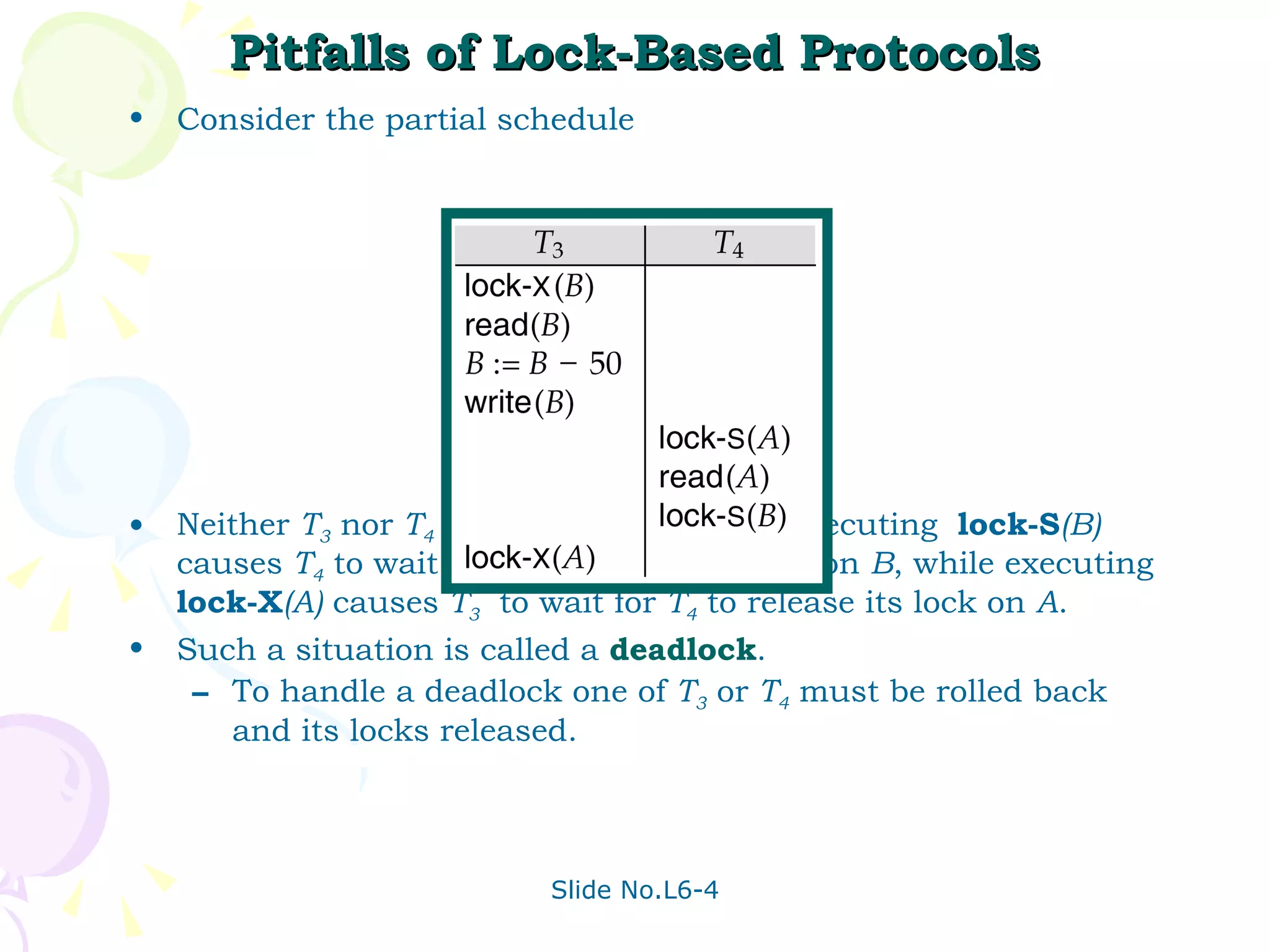
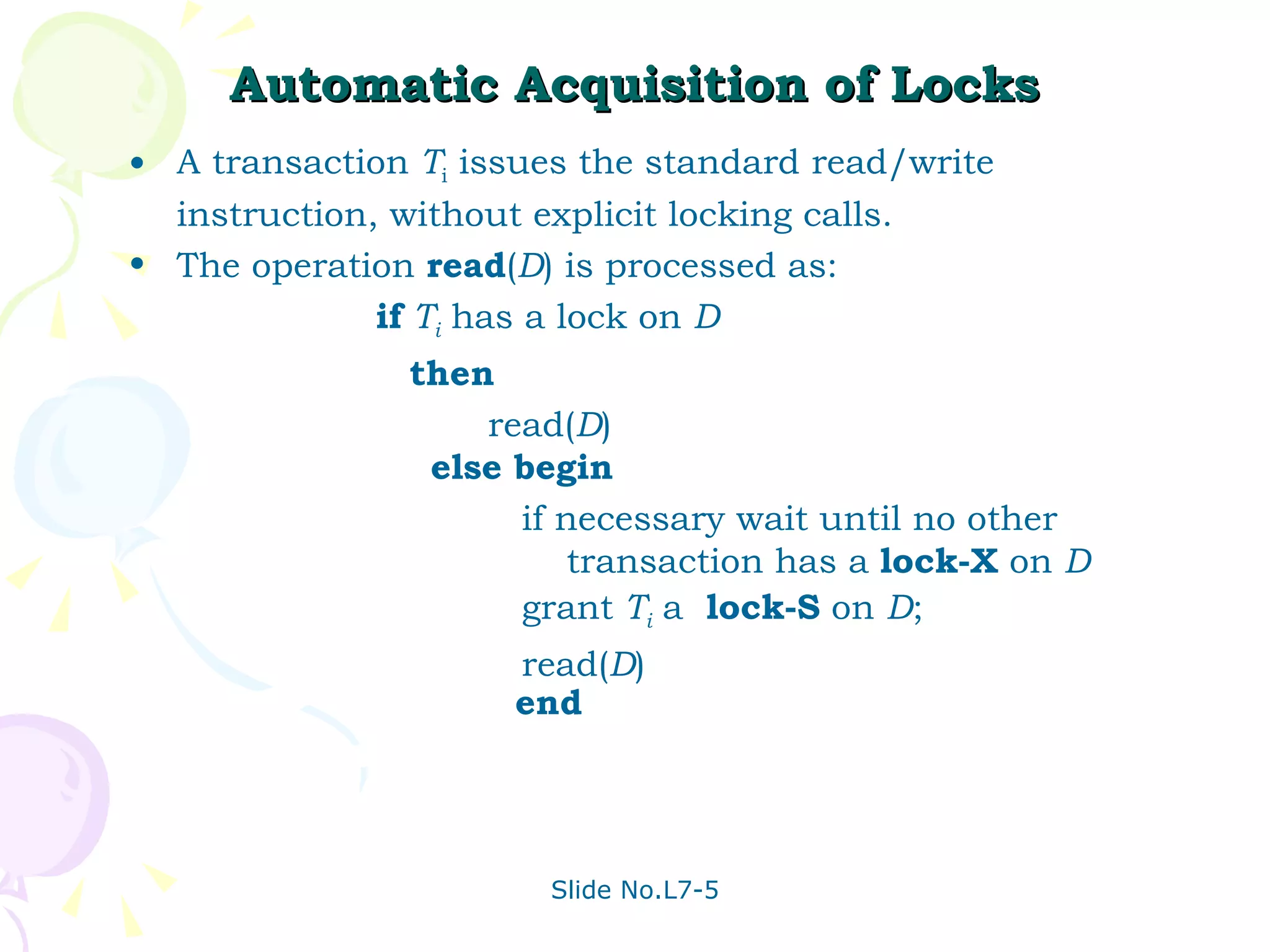
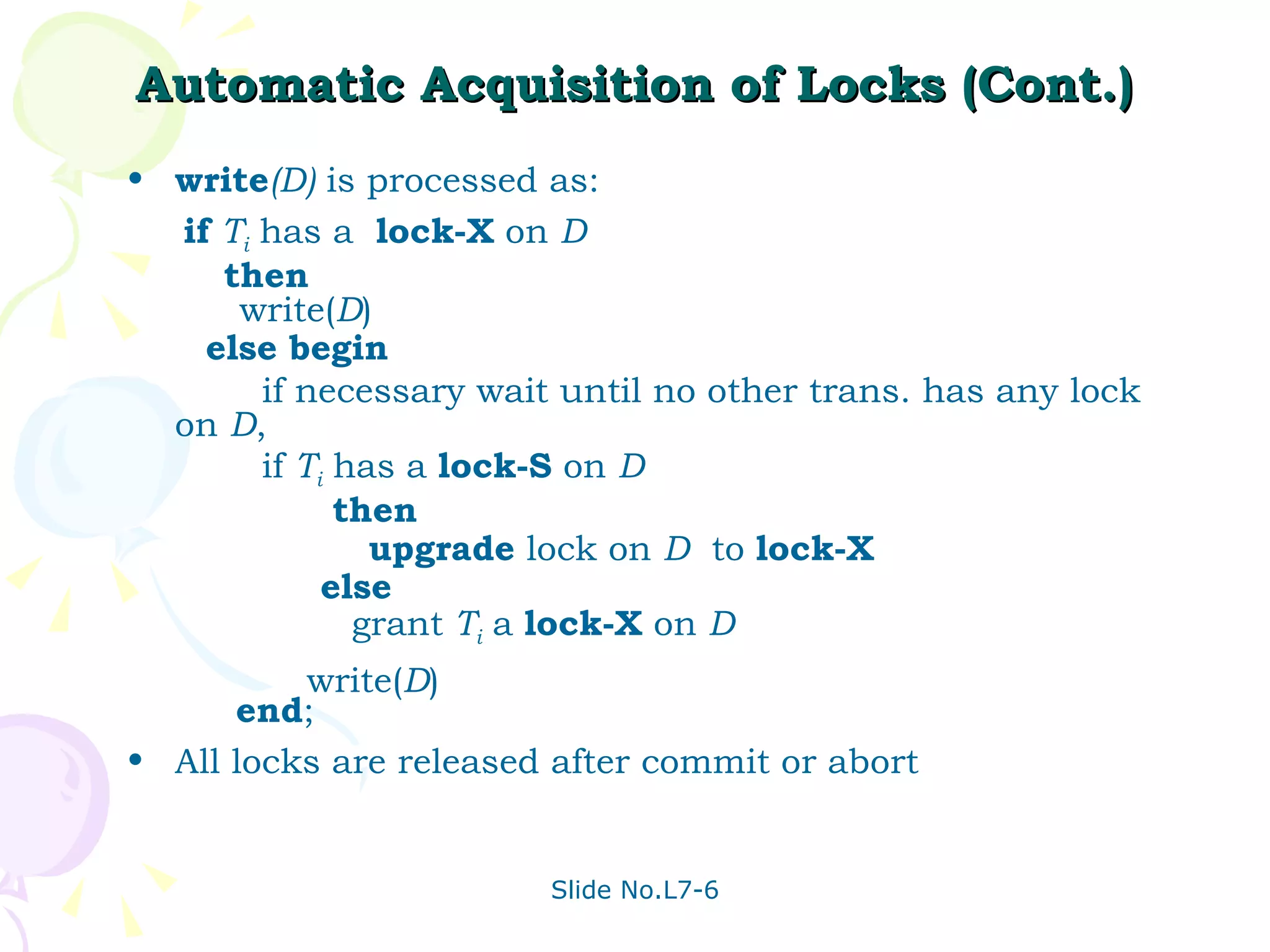
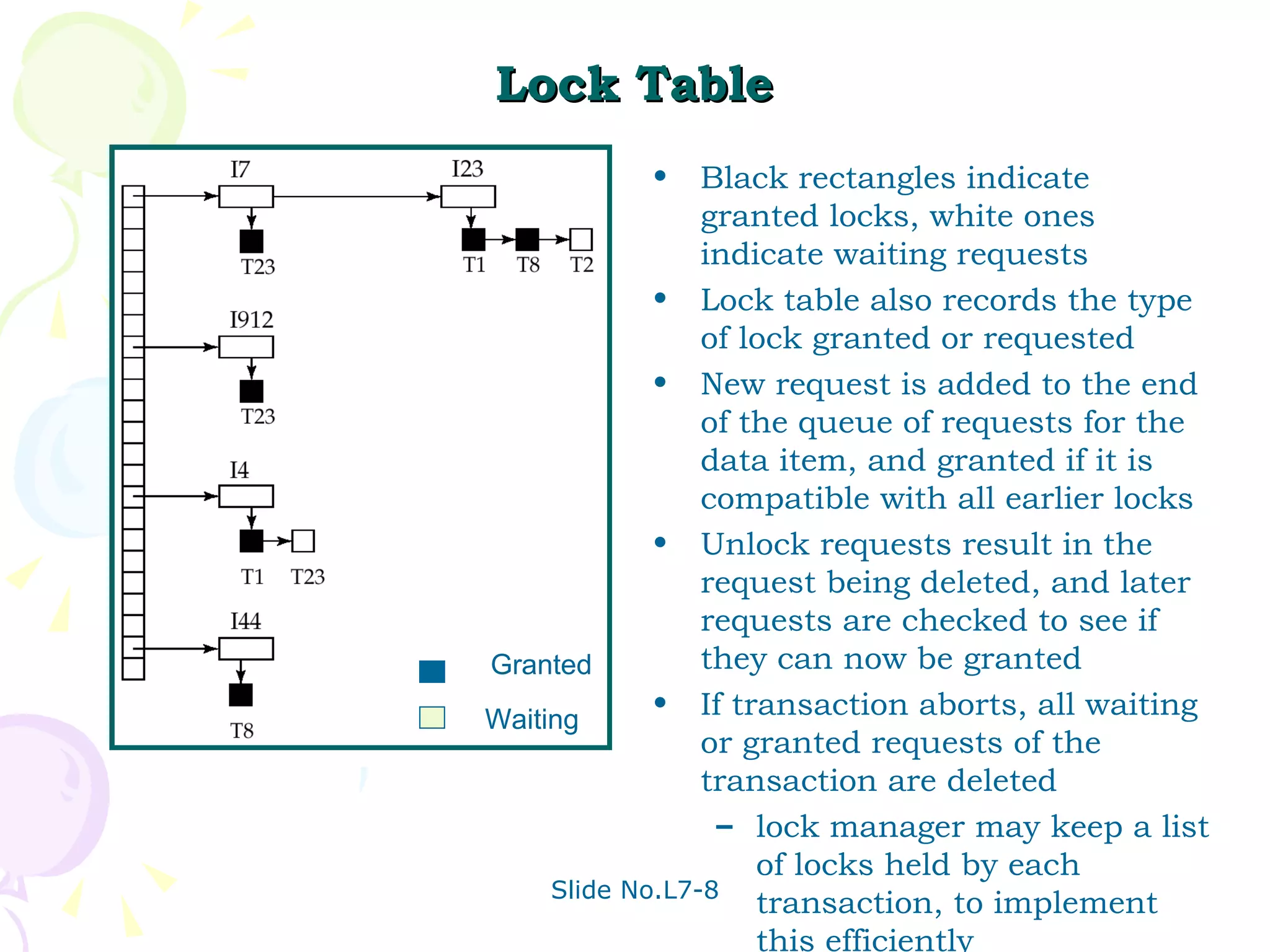
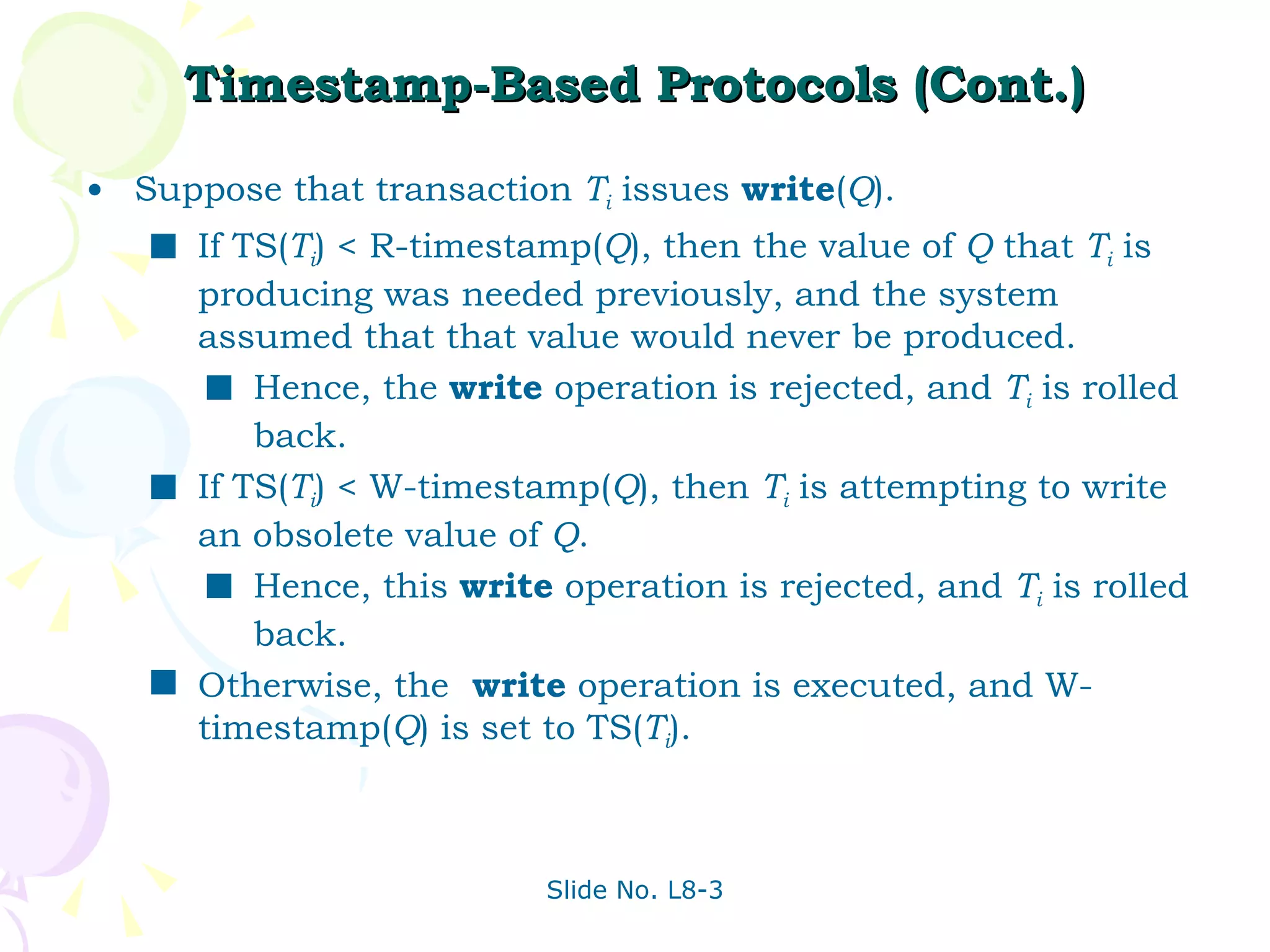
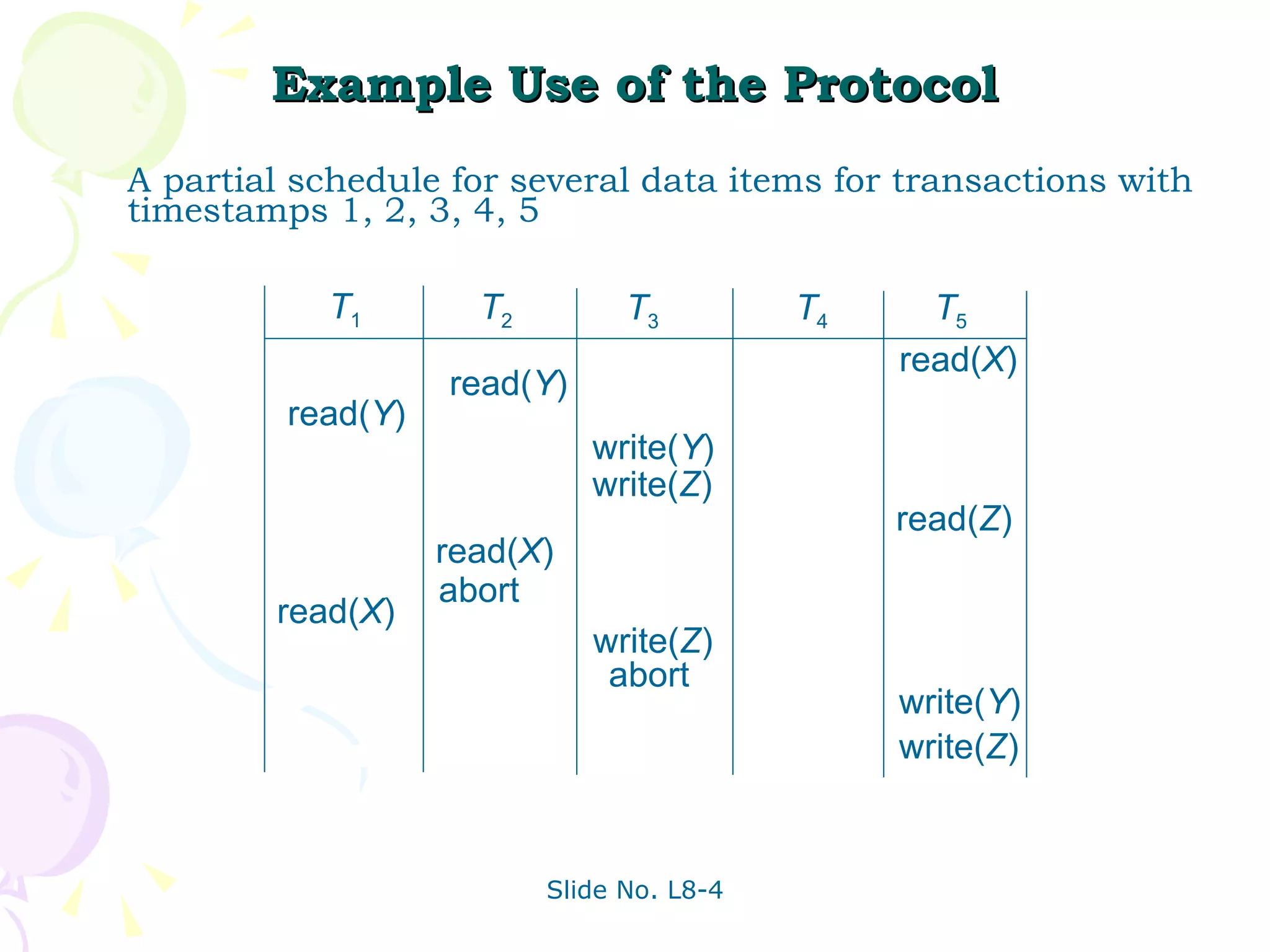
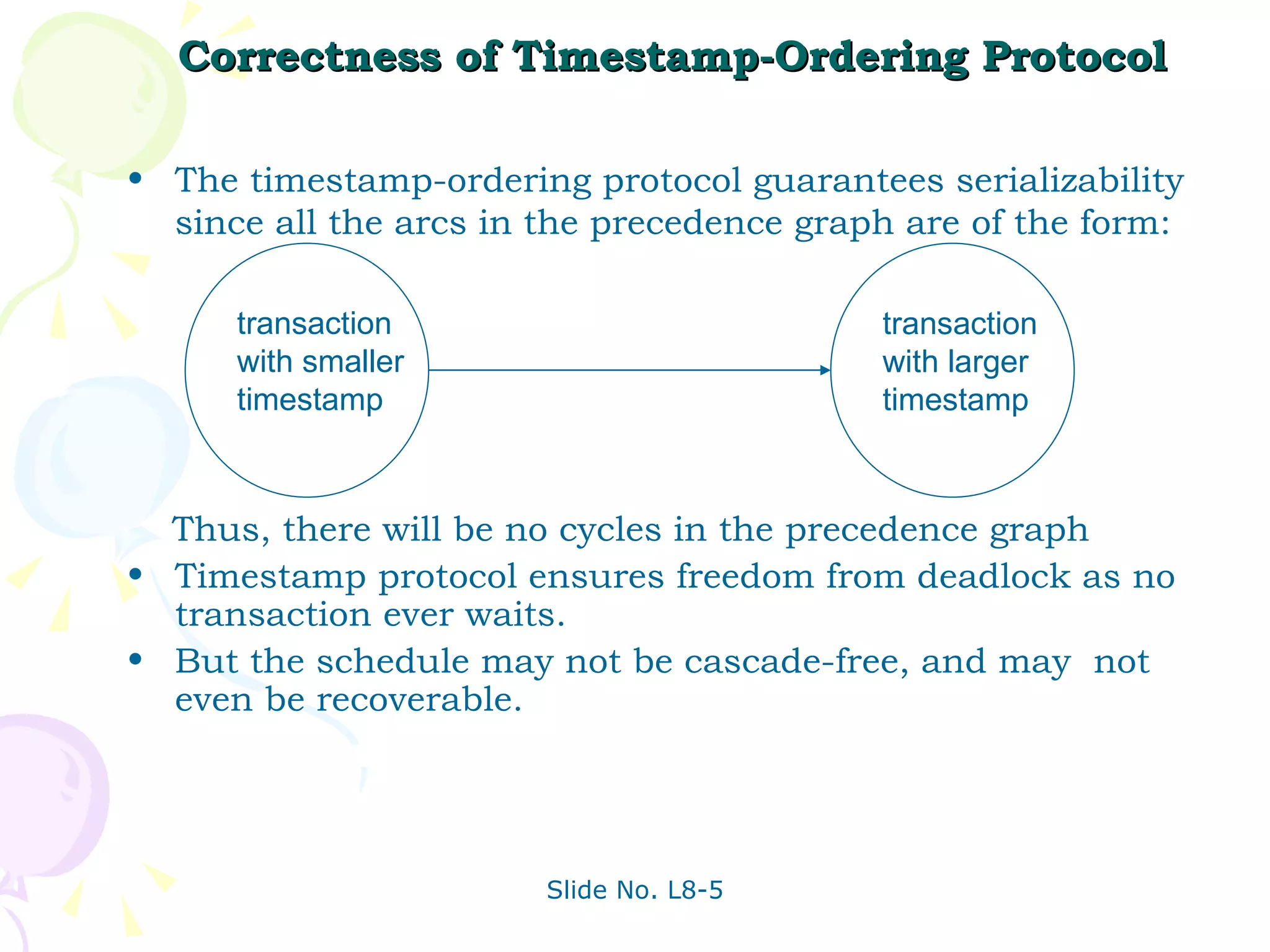
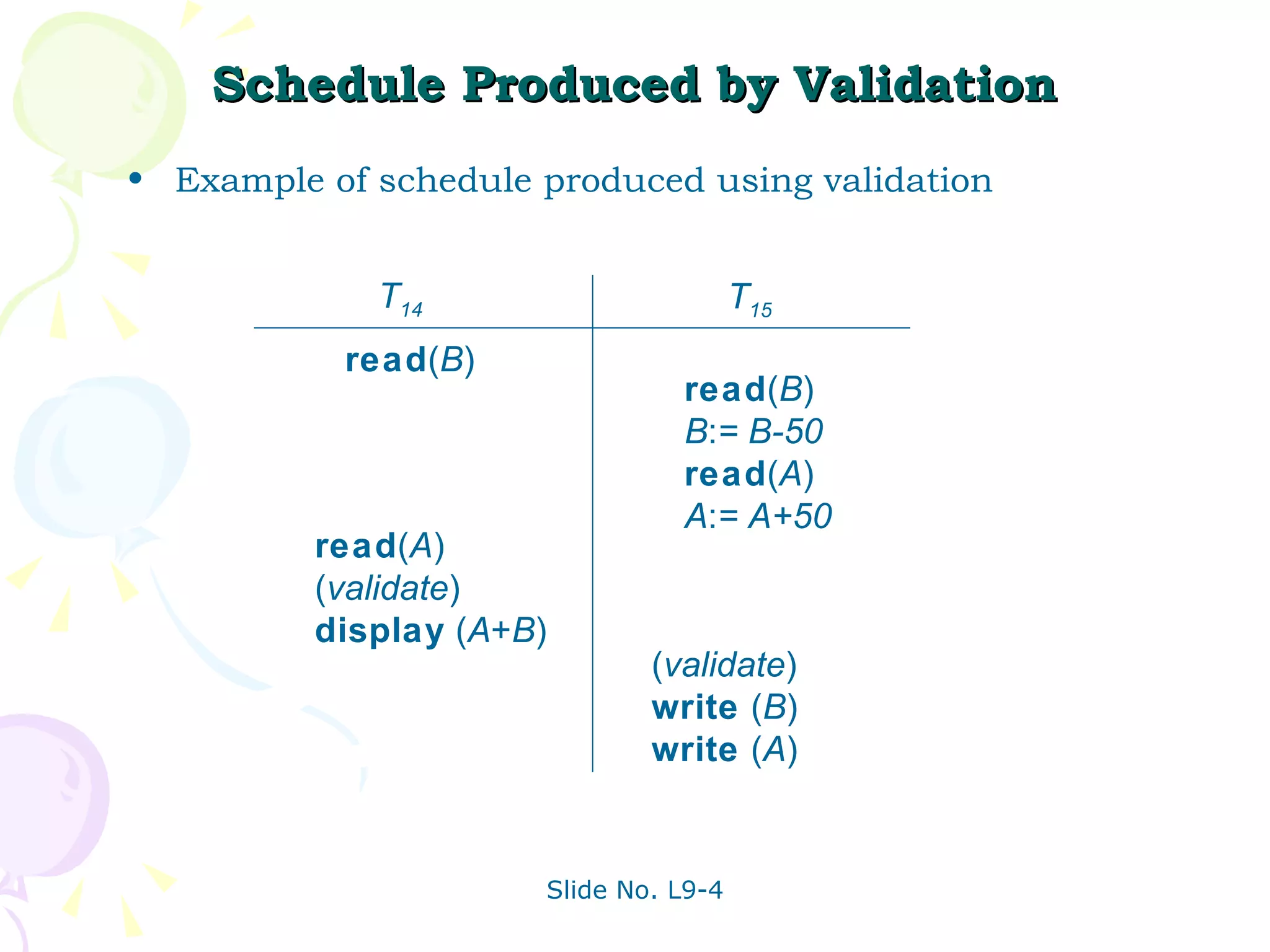
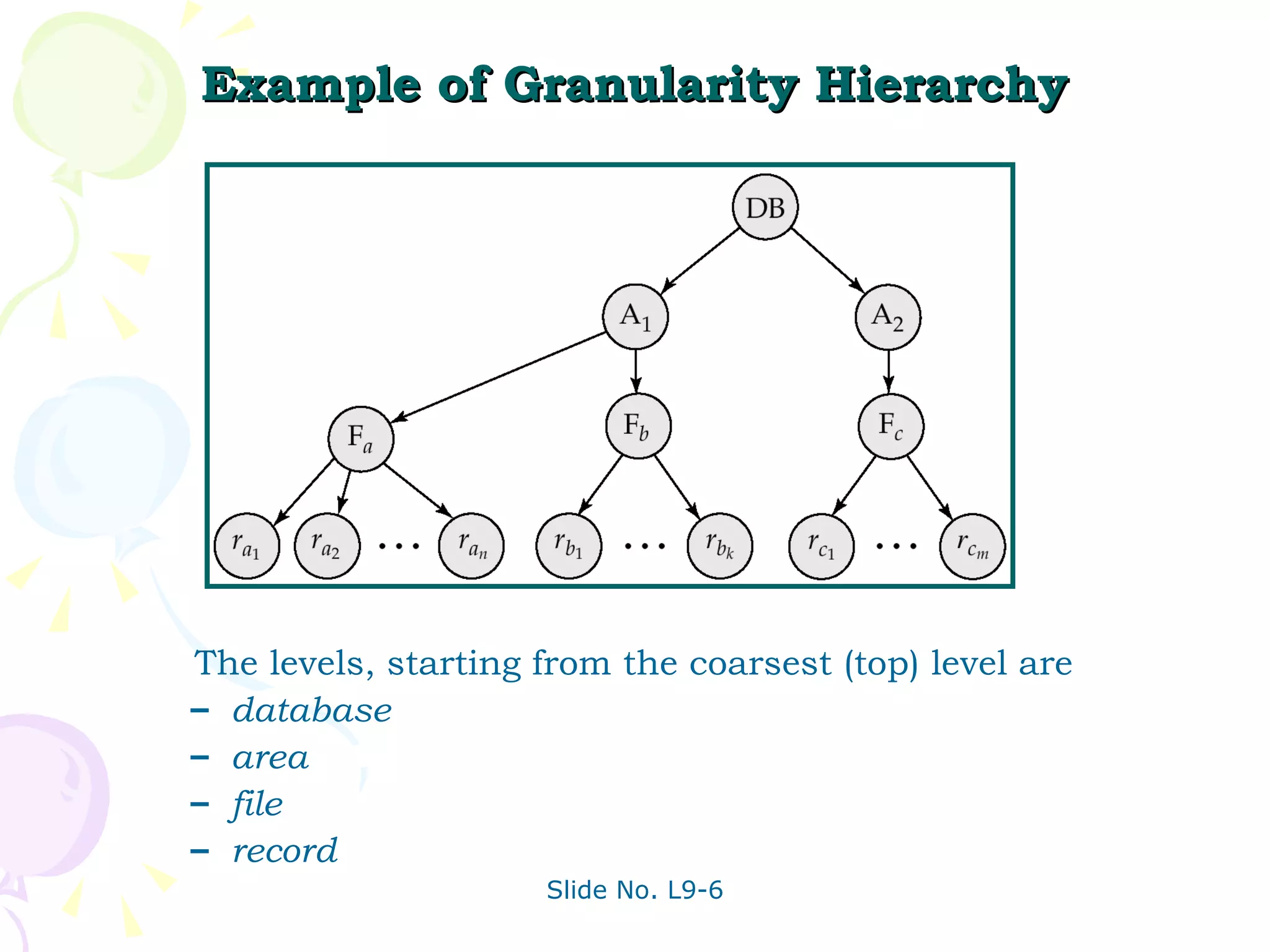
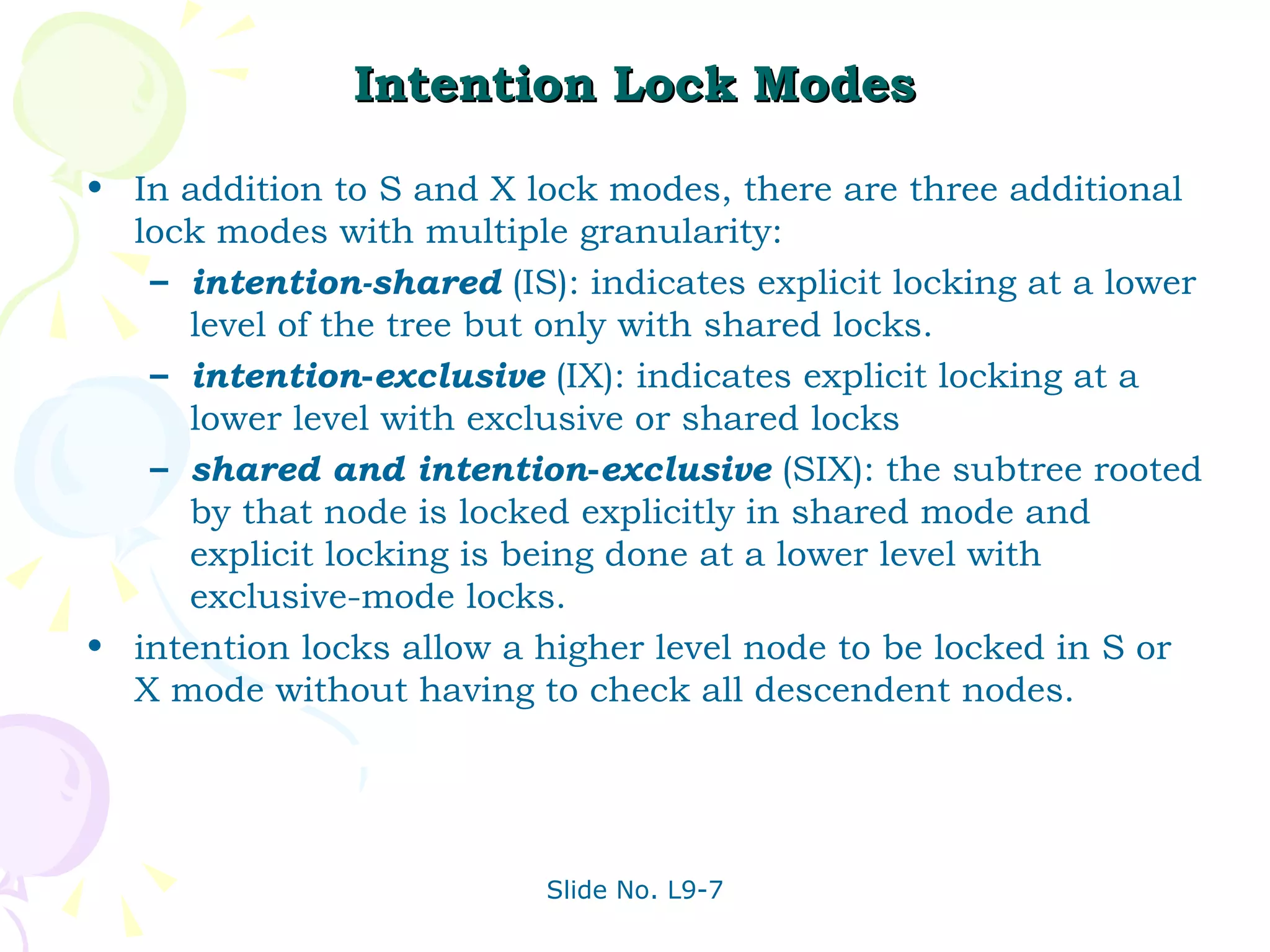
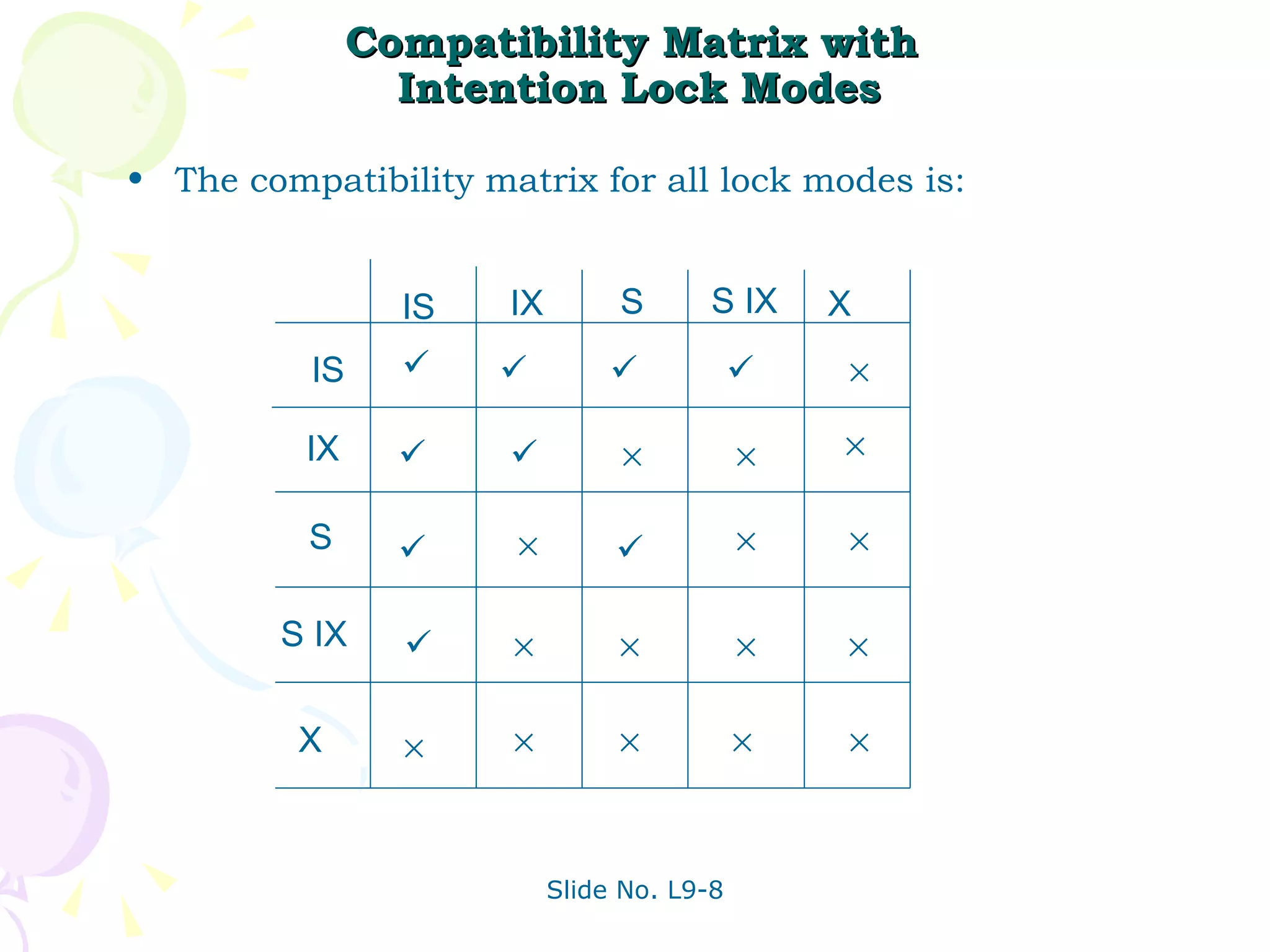
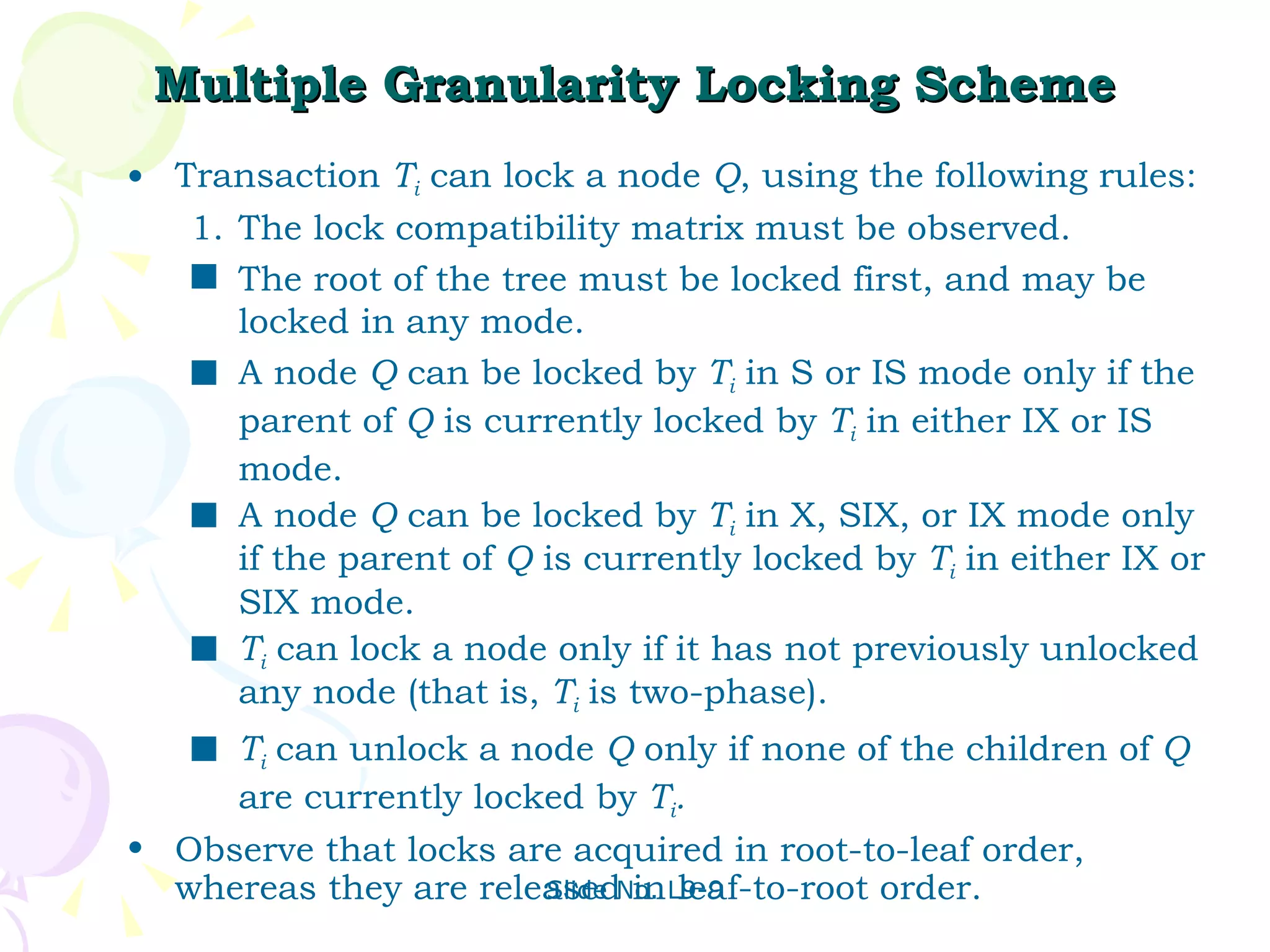
The document discusses transaction management in database systems. It defines a transaction as a unit of program execution that accesses and updates data items. For transactions to preserve data integrity, the database system must ensure atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID properties). Concurrency control schemes are mechanisms that achieve isolation by controlling interactions between concurrent transactions to prevent inconsistent database states. A schedule specifies the order of transaction instructions. For a schedule to be serializable, it must be equivalent to a serial schedule where transactions execute one after another.