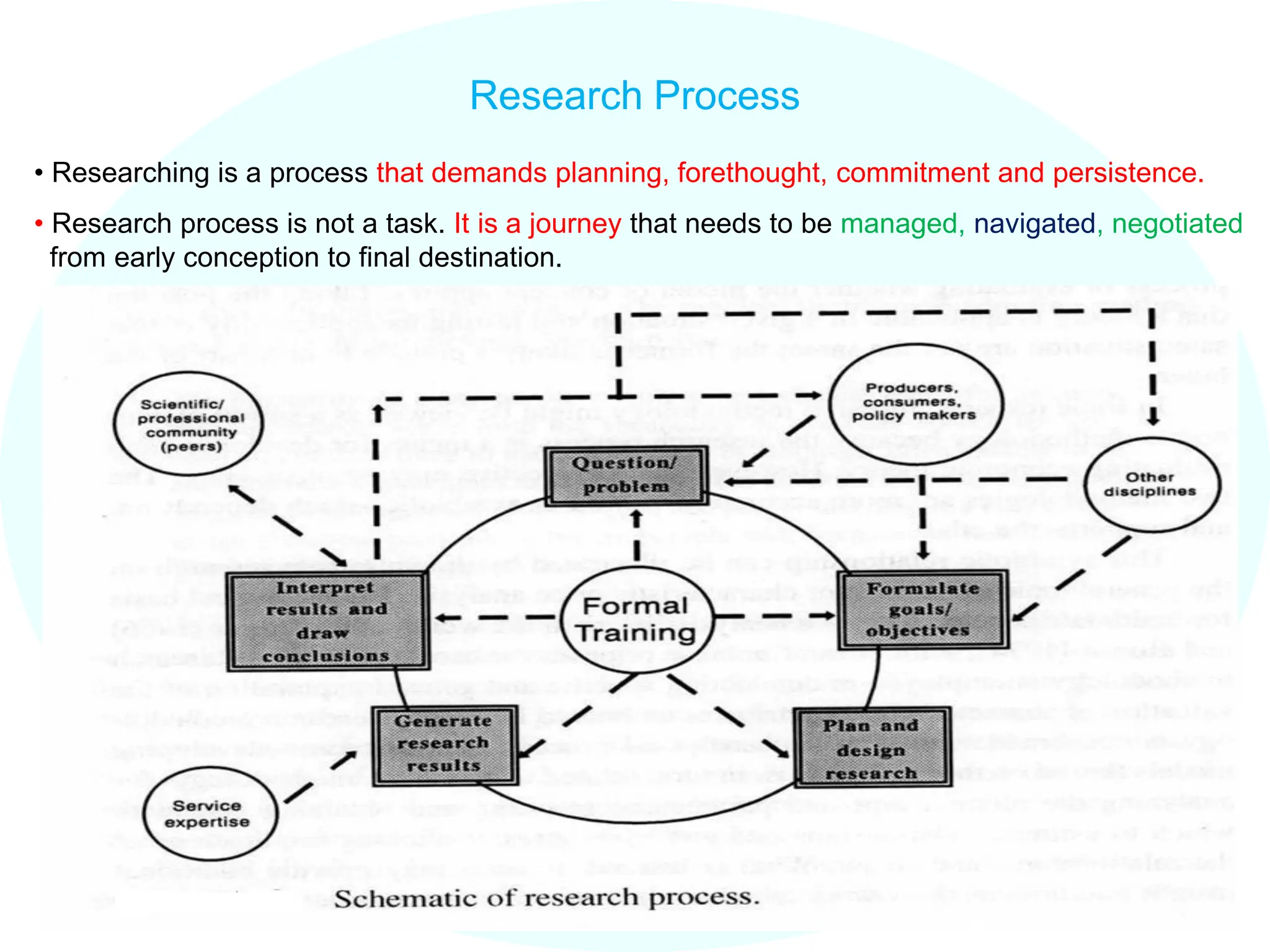
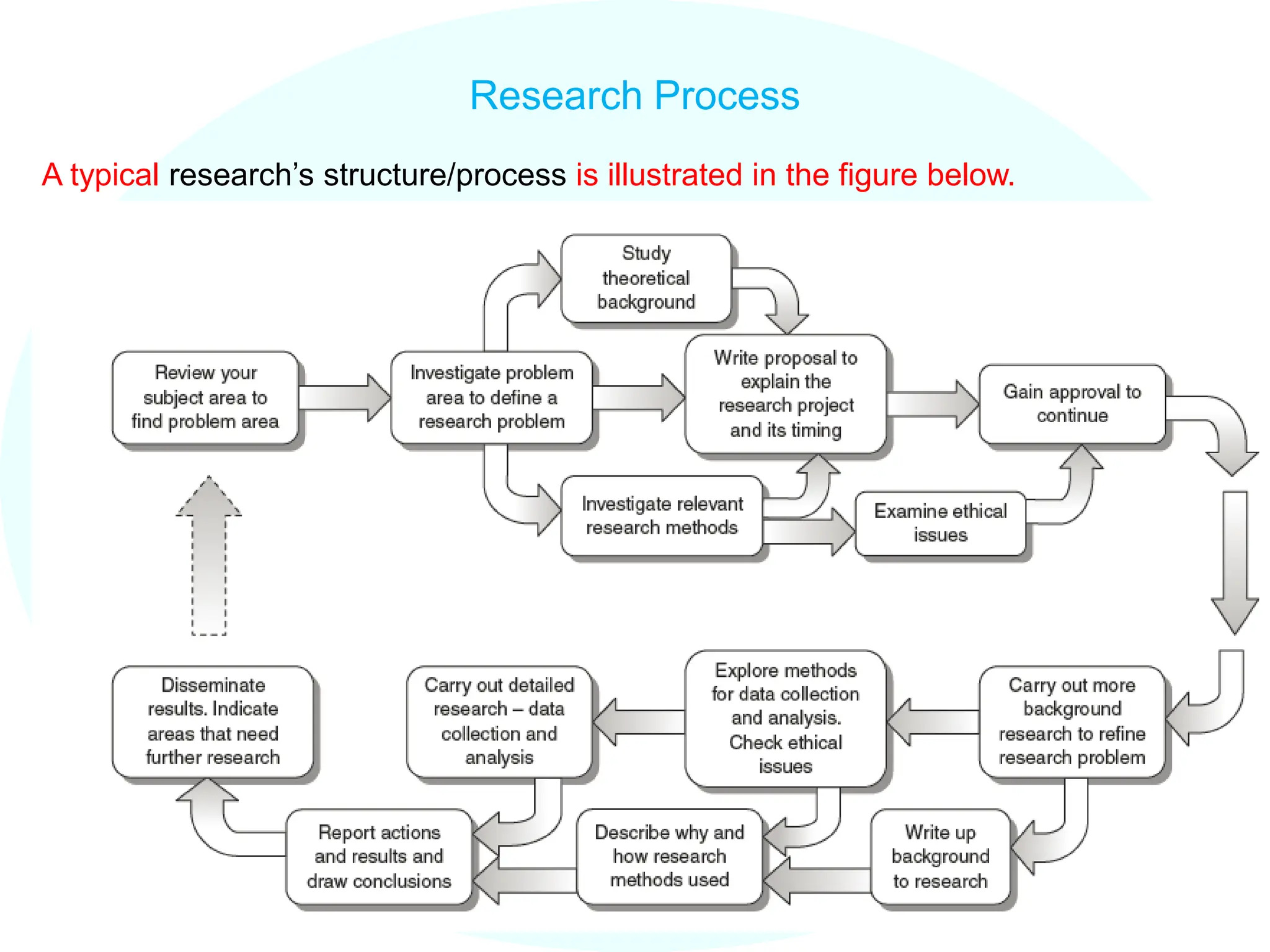
The document discusses research methodology and process. It describes two categories of learners - analytic/organized and intuitive/holistic. It outlines different learning styles - visual, auditory, kinesthetic. It also discusses researcher motivations such as solving problems, generating knowledge. Finally, it provides the typical structure of a research proposal and project framework including what, why, how, and when components.