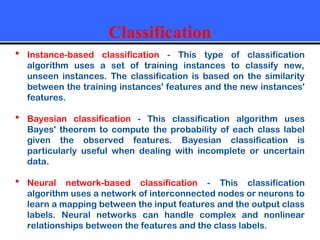
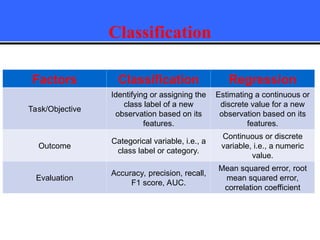
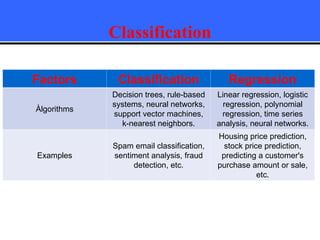
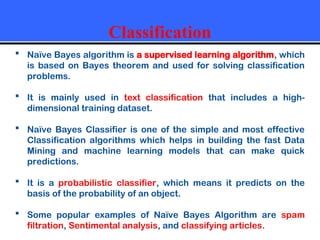
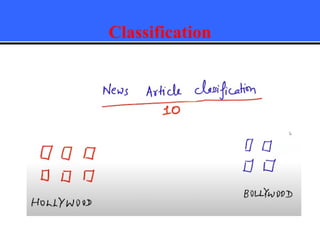
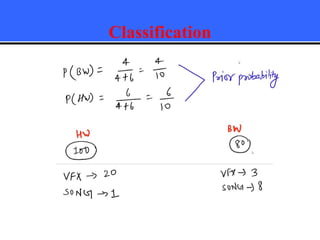
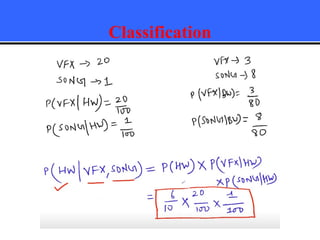
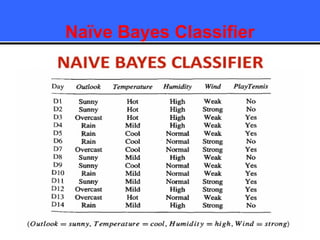
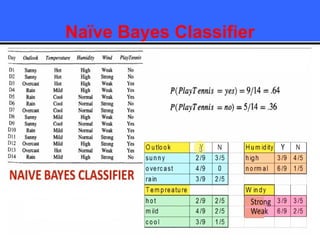
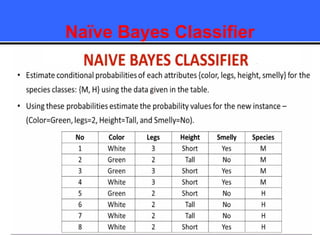
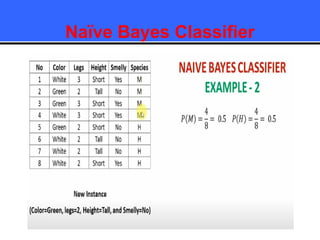
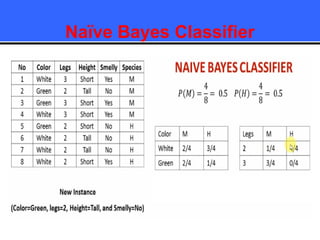
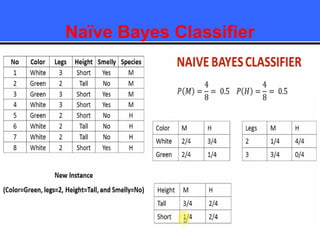
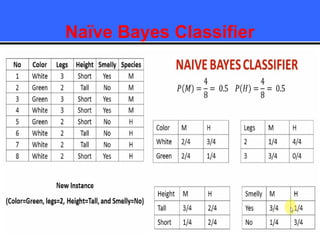
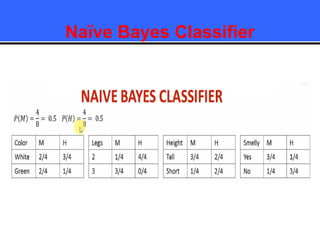
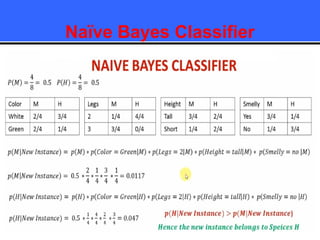
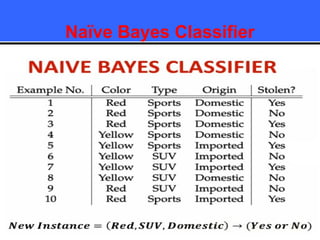
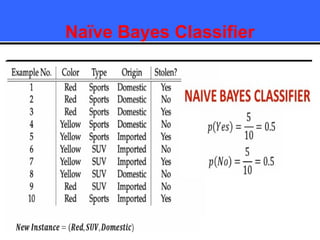
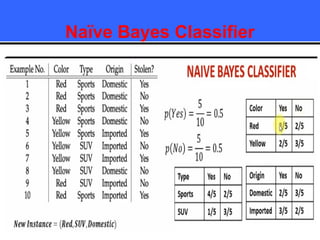
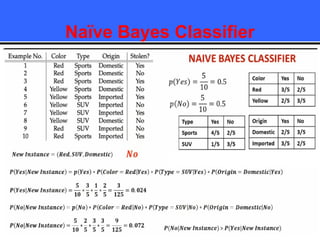
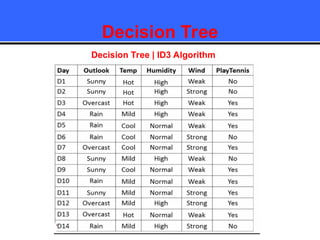
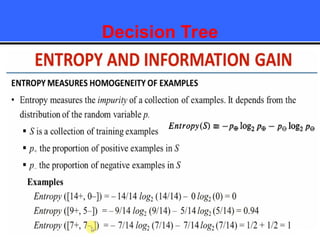
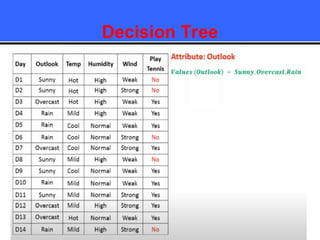
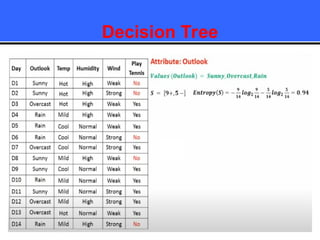
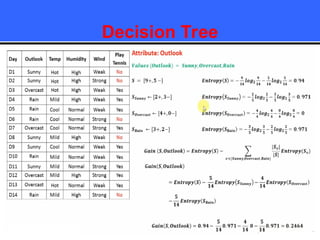
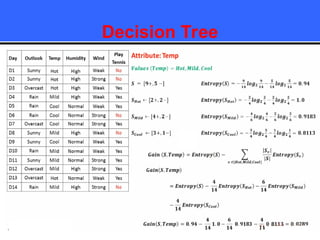
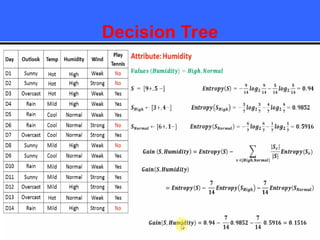
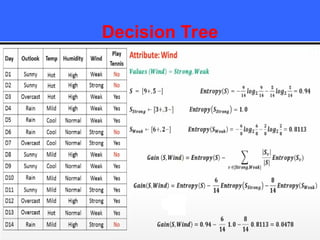
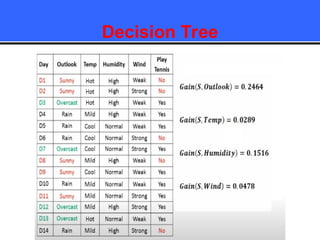
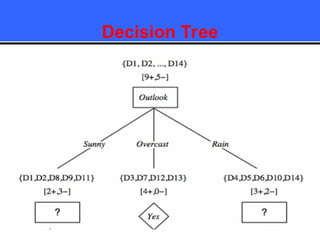
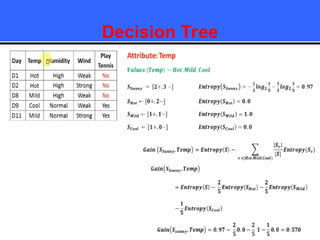
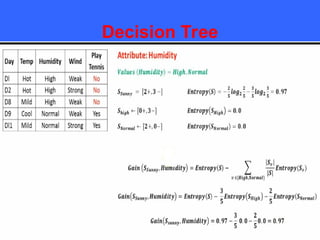
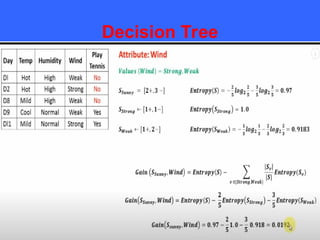
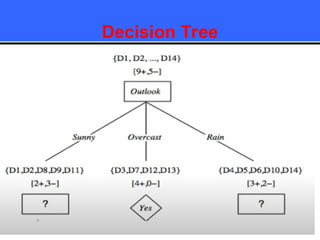
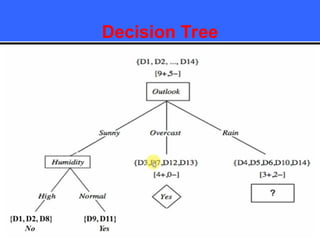
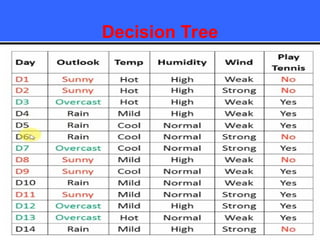
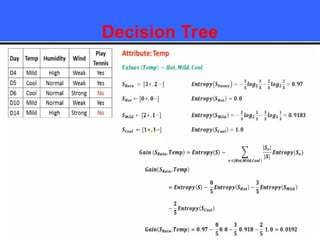
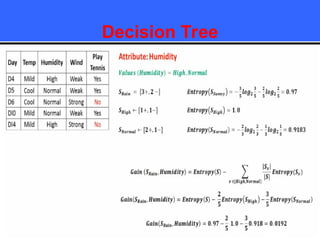
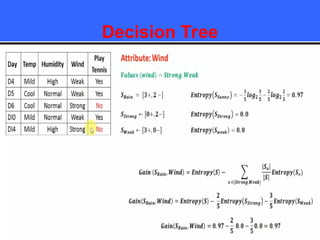
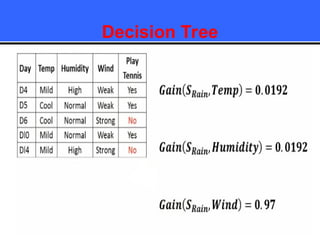
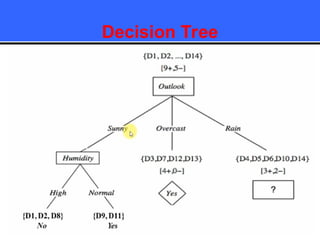
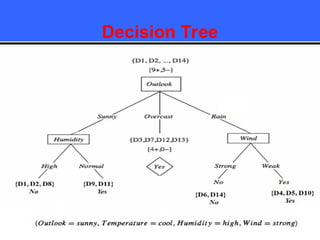
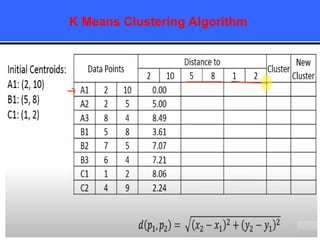
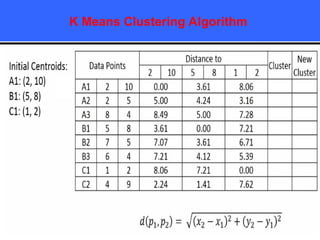
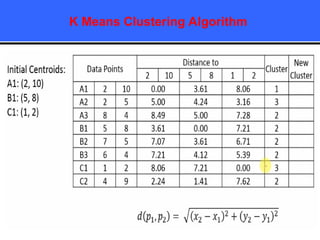
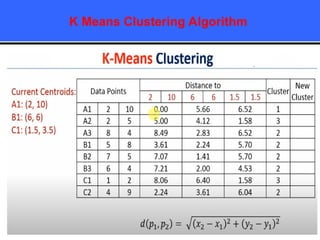
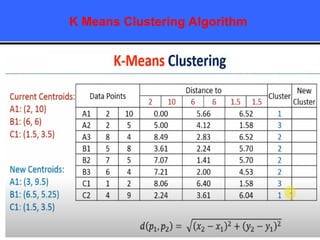
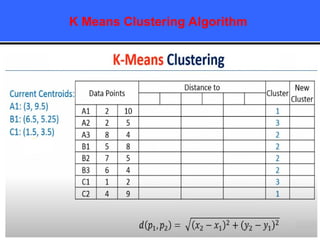
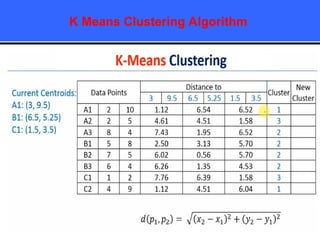
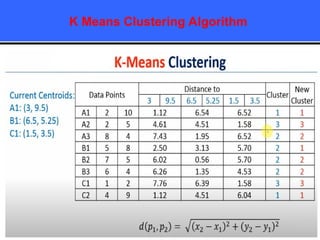
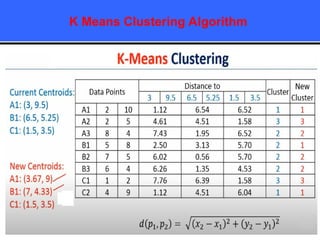
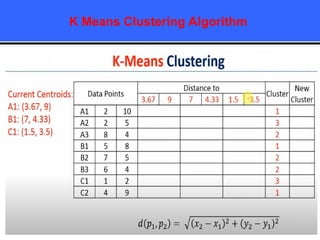
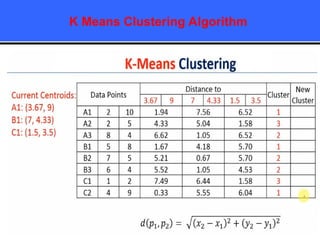
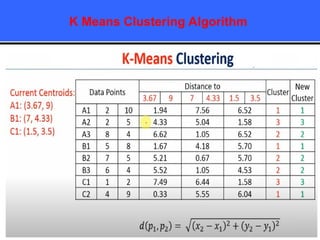
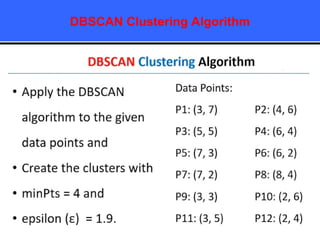
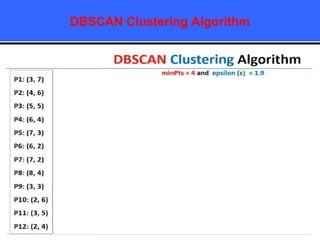
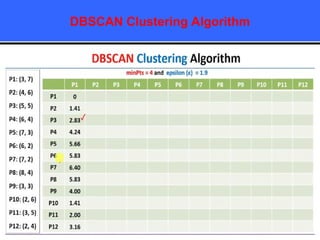
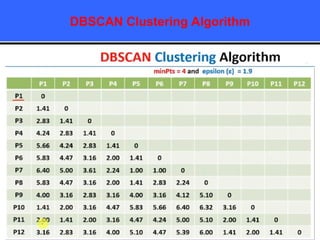
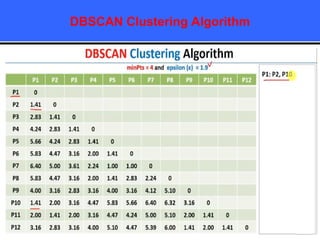
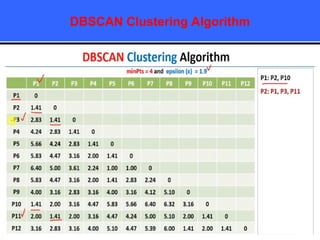
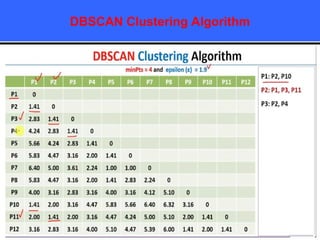
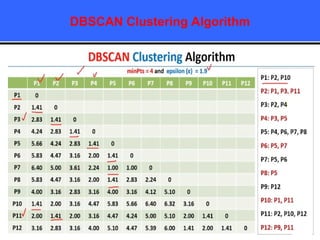
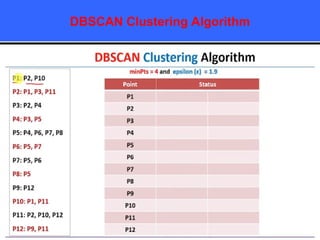
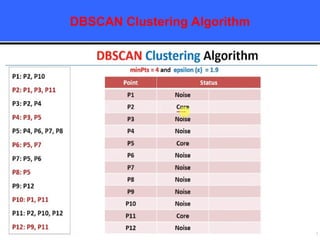
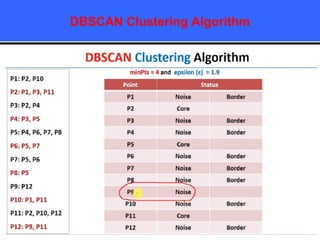
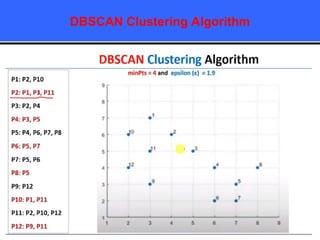
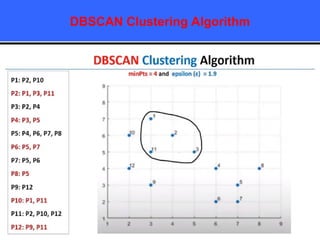
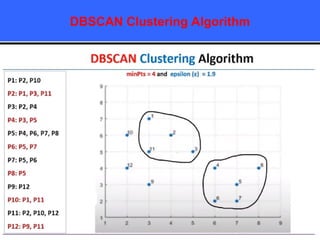
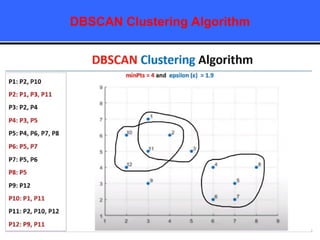
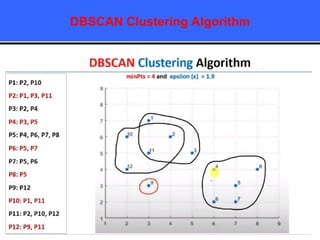
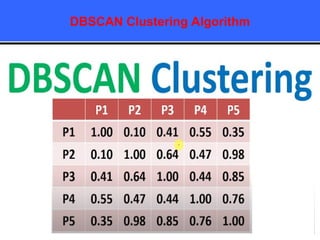
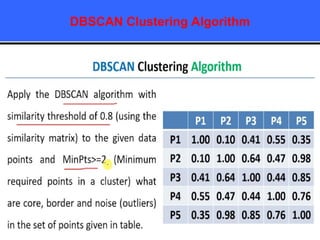
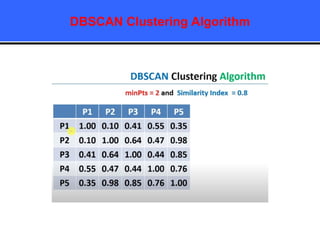
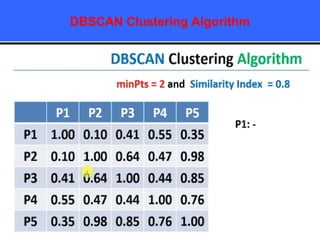
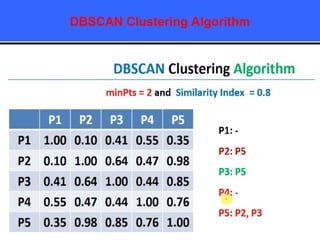
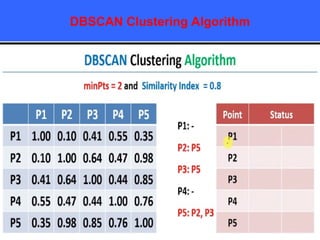
The document provides an overview of classification techniques in data mining, emphasizing its role in categorizing data into predefined classes using supervised learning. It outlines the steps to build a classification model, including data preparation, feature selection, model training, and evaluation, along with different types of classification algorithms. Additionally, it compares classification with regression and discusses specific algorithms like Naive Bayes and decision trees, along with their applications.