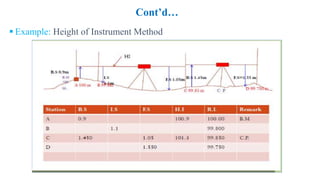
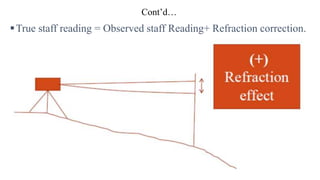
This document discusses levelling and levelling procedures. It covers different levelling instruments like dumpy, tilting, wye, and automatic levels. It also describes levelling staffs and their types. Various levelling methods like simple, differential, fly, profile, check, reciprocal, trigonometric and precise levelling are explained. Methods to reduce levels including height of instrument and rise and fall are provided. Finally, sources of errors in levelling like personal, instrumental and natural causes are outlined along with corrections for curvature and refraction.