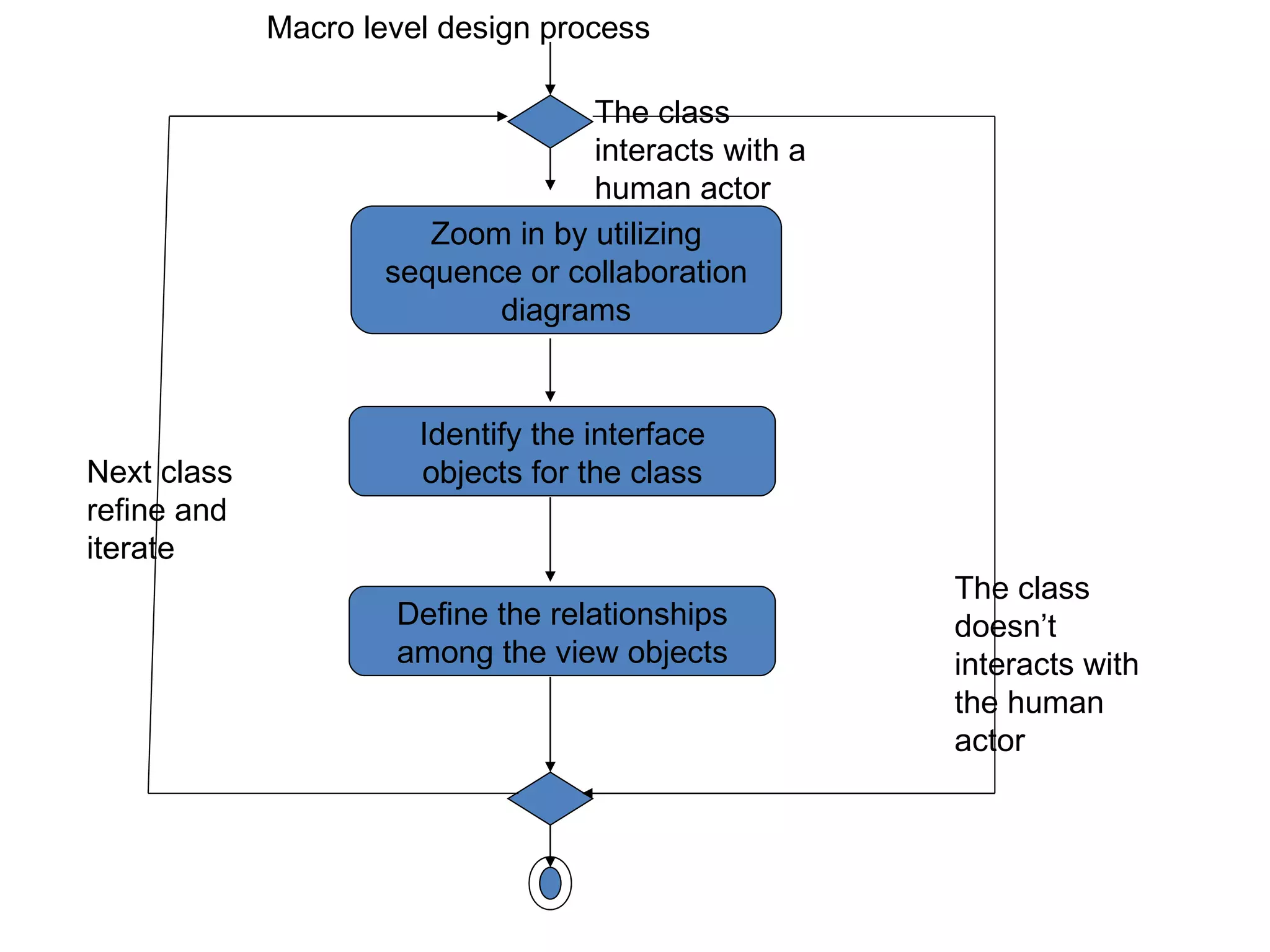
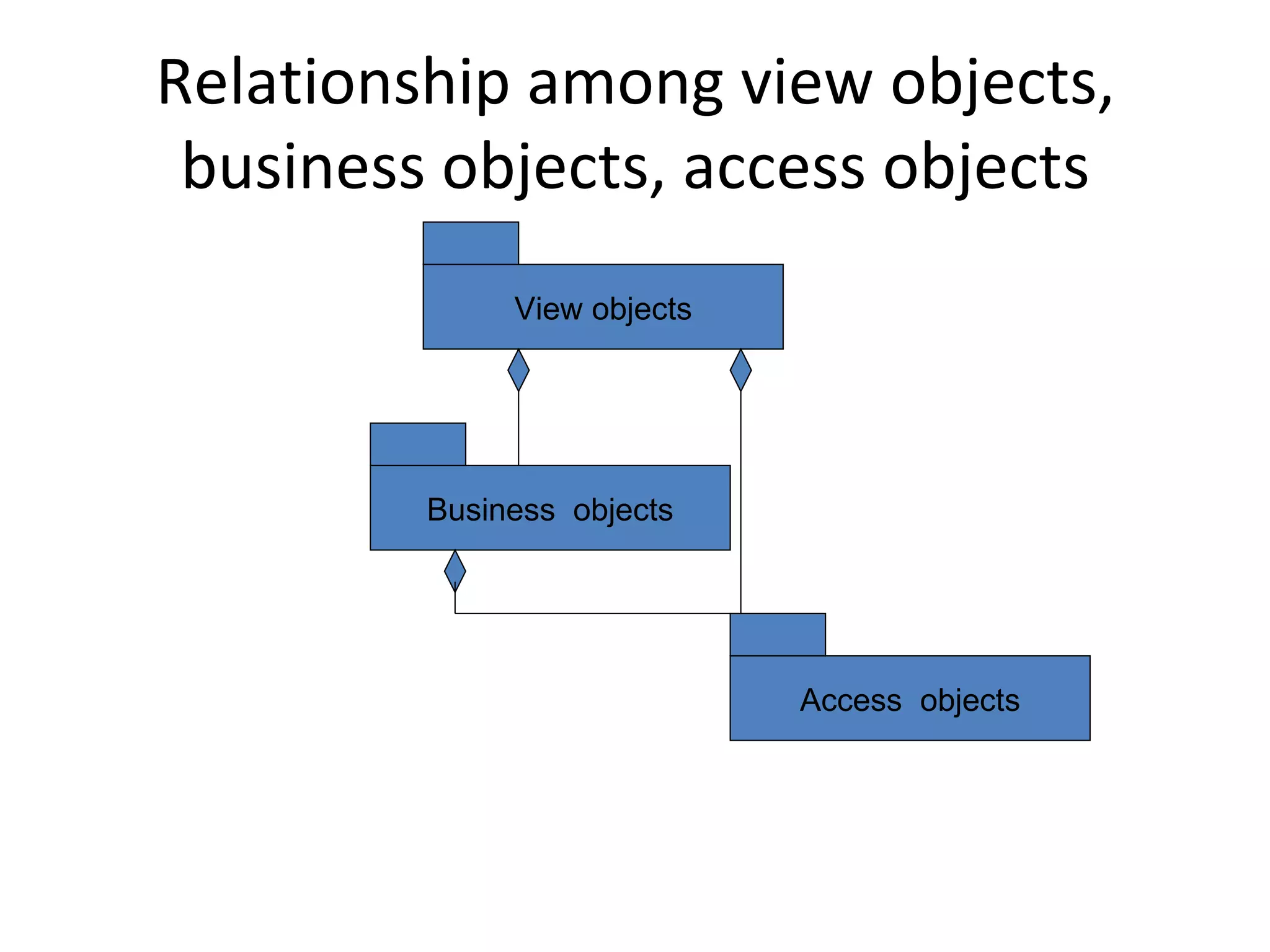
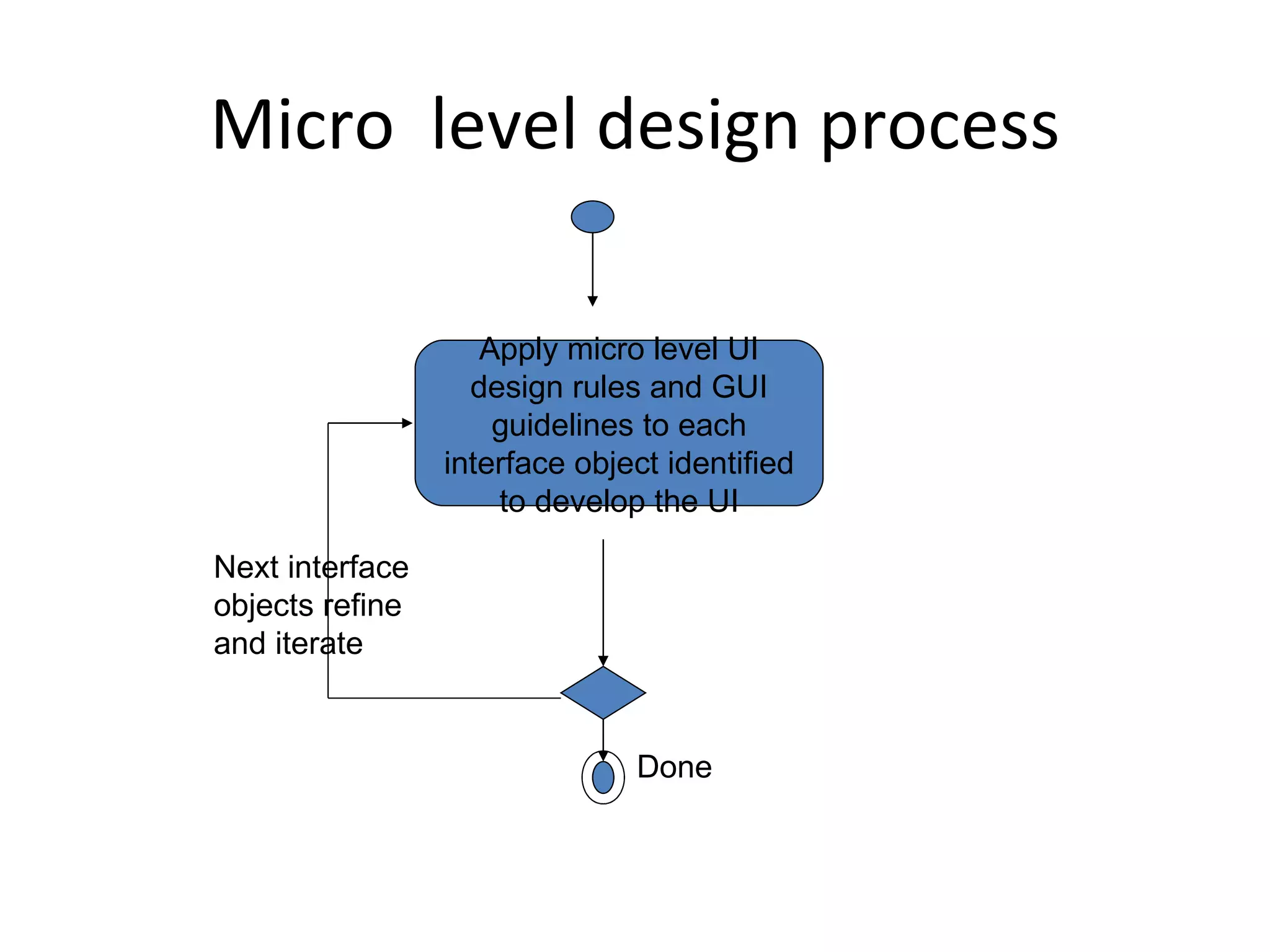
The document discusses the process of designing view layer classes in a user interface. It involves:
1) Identifying view layer objects during analysis by examining use cases and interaction diagrams.
2) Designing individual view layer objects by applying design principles to best support the application functions and provide a usable interface.
3) Prototyping, testing usability, and refining the view layer interface through iterative design.