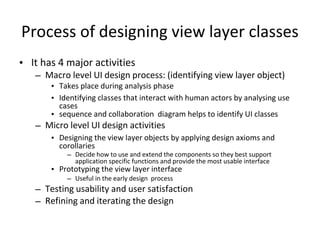
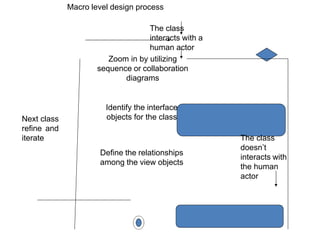
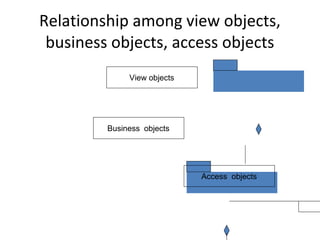
The document discusses the design of user interface (UI) layers, emphasizing the responsibilities of view layer objects in responding to user interactions and displaying business objects. It outlines a four-step design process involving both macro and micro levels, where macro design focuses on identifying and defining interactions through analysis and diagrams, while micro design applies specific rules and guidelines to enhance usability. Key considerations include simplicity in interface design and the impact of additional features on performance and complexity.