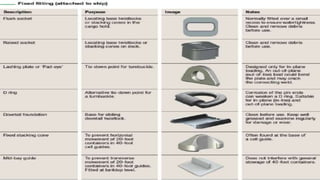
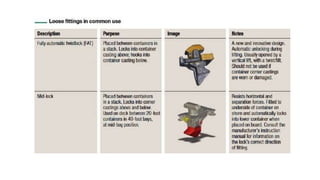
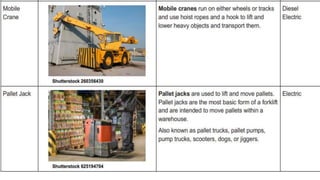
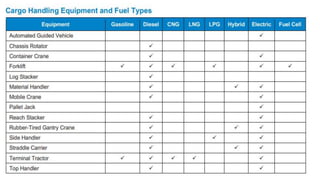
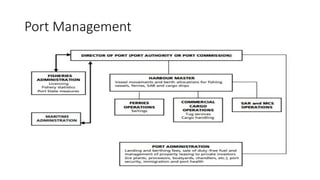
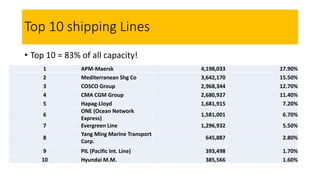
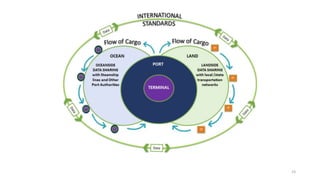
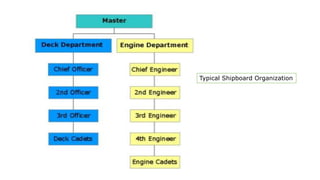
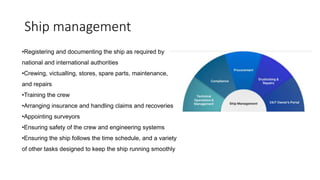
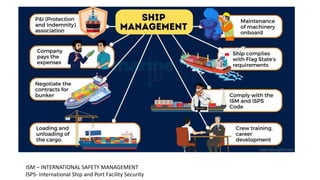
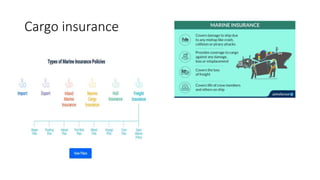
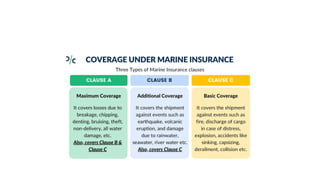
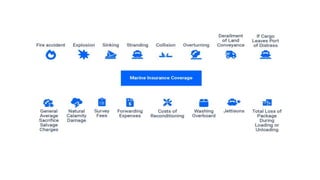
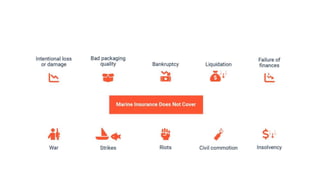
This document discusses various types of cargo handling equipment used on container ships such as twist locks, lashing rods, and turnbuckles. It also covers IMO classifications for dangerous goods, functions of port authorities, types of ports, responsibilities of terminal managers, duties of ship officers, ship management, and cargo insurance terms like CIF and FOB.