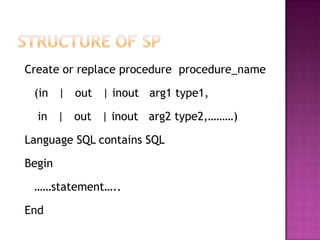
The document discusses functions and stored procedures in SQL. Functions are logical grouped SQL/PL statements that perform a specific task and return a value, while stored procedures perform a specific task without returning a value. The document provides examples of creating simple SQL functions that return values and a stored procedure that updates employee salaries and bonuses.