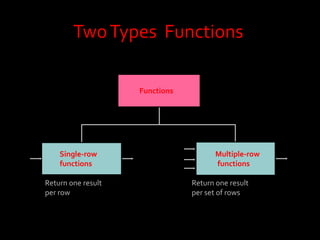
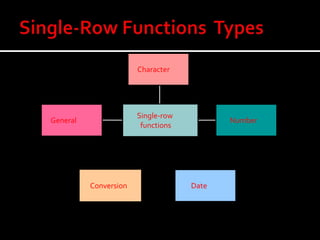
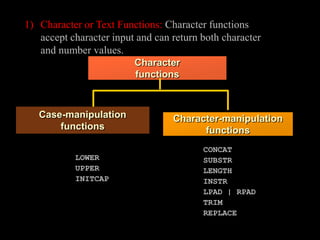
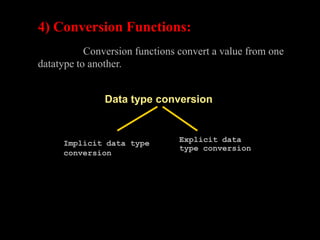
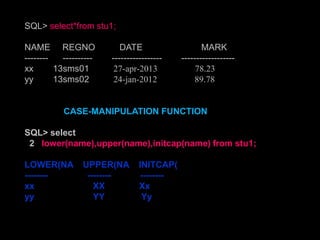
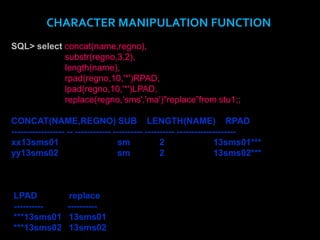
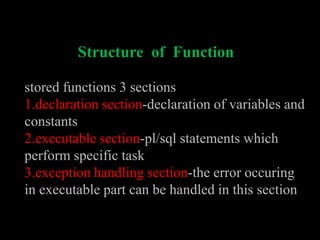
A function in PL/SQL is a named block that can take parameters and return a value. Functions have three sections: declaration, executable, and exception handling. They are created using the CREATE FUNCTION statement and can be single-row or multiple-row. Single-row functions return one result per row while multiple-row functions return one result per group of rows. Common functions include character, numeric, date, and conversion functions for manipulating values.

![CREATE [OR REPLACE] FUNCTION function_name
[ (parameter [,parameter]) ]
RETURN return_datatype
IS | AS
[declaration_section]
BEGIN
executable_section
[EXCEPTION
exception_section]
END [function_name];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/function-copy-131002001646-phpapp02/85/Function-and-types-3-320.jpg)
![CREATE [OR REPLACE] FUNCTION fa(m number)
RETURN number
IS
f number:=1;
BEGIN
for I in 1….m
Loop
F:=f*I;
End loop;
return f;
End;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/function-copy-131002001646-phpapp02/85/Function-and-types-4-320.jpg)