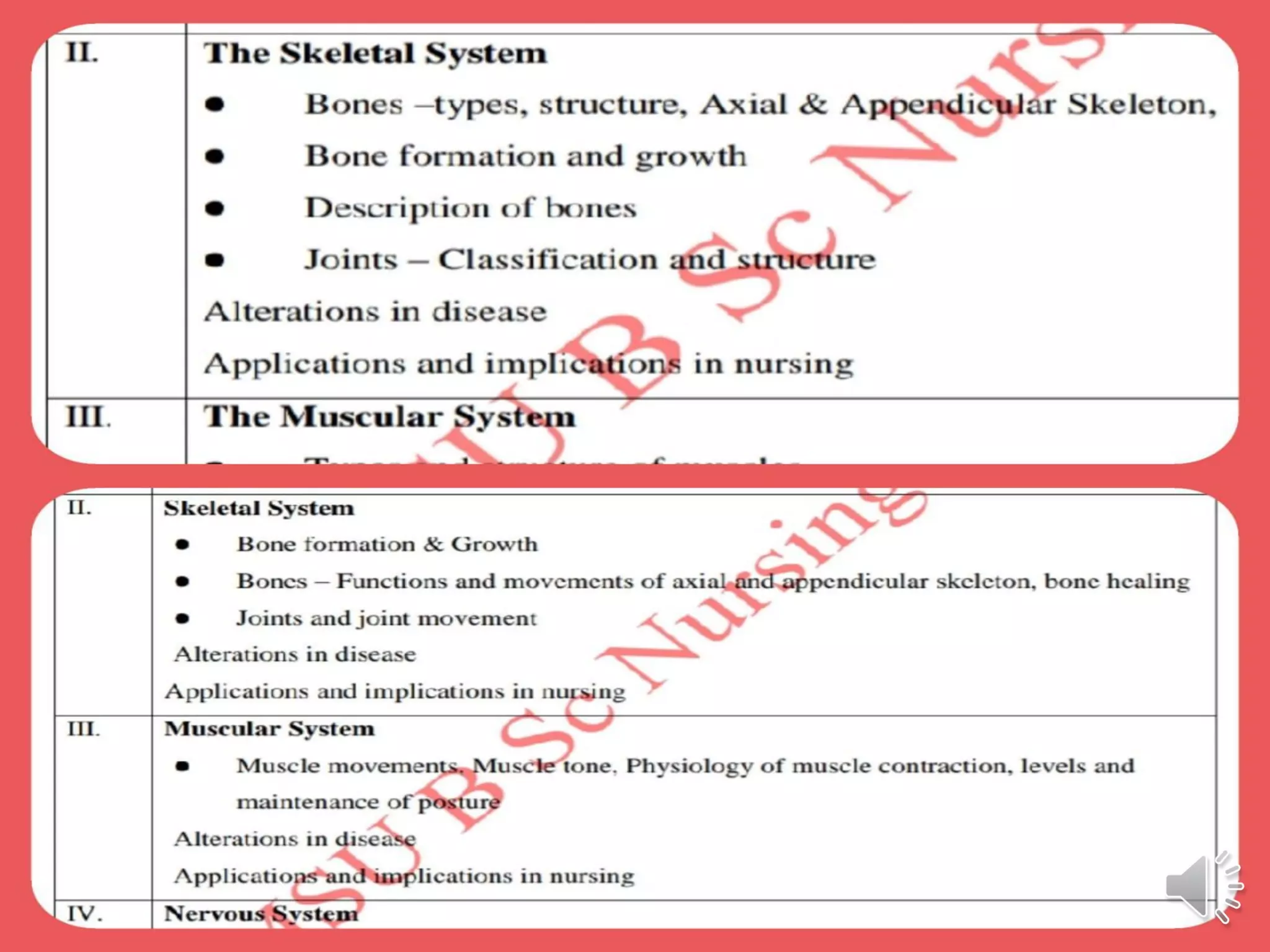
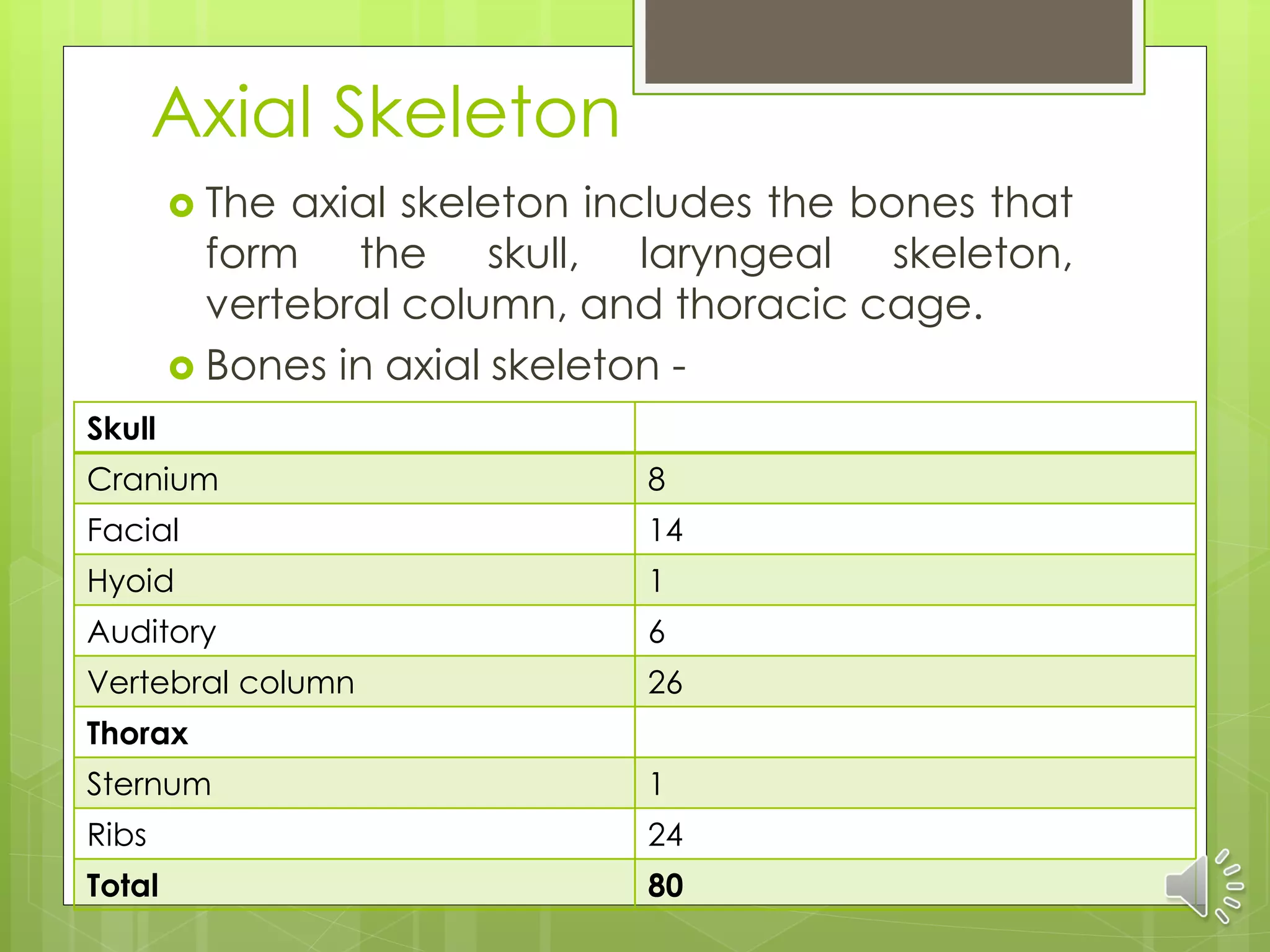
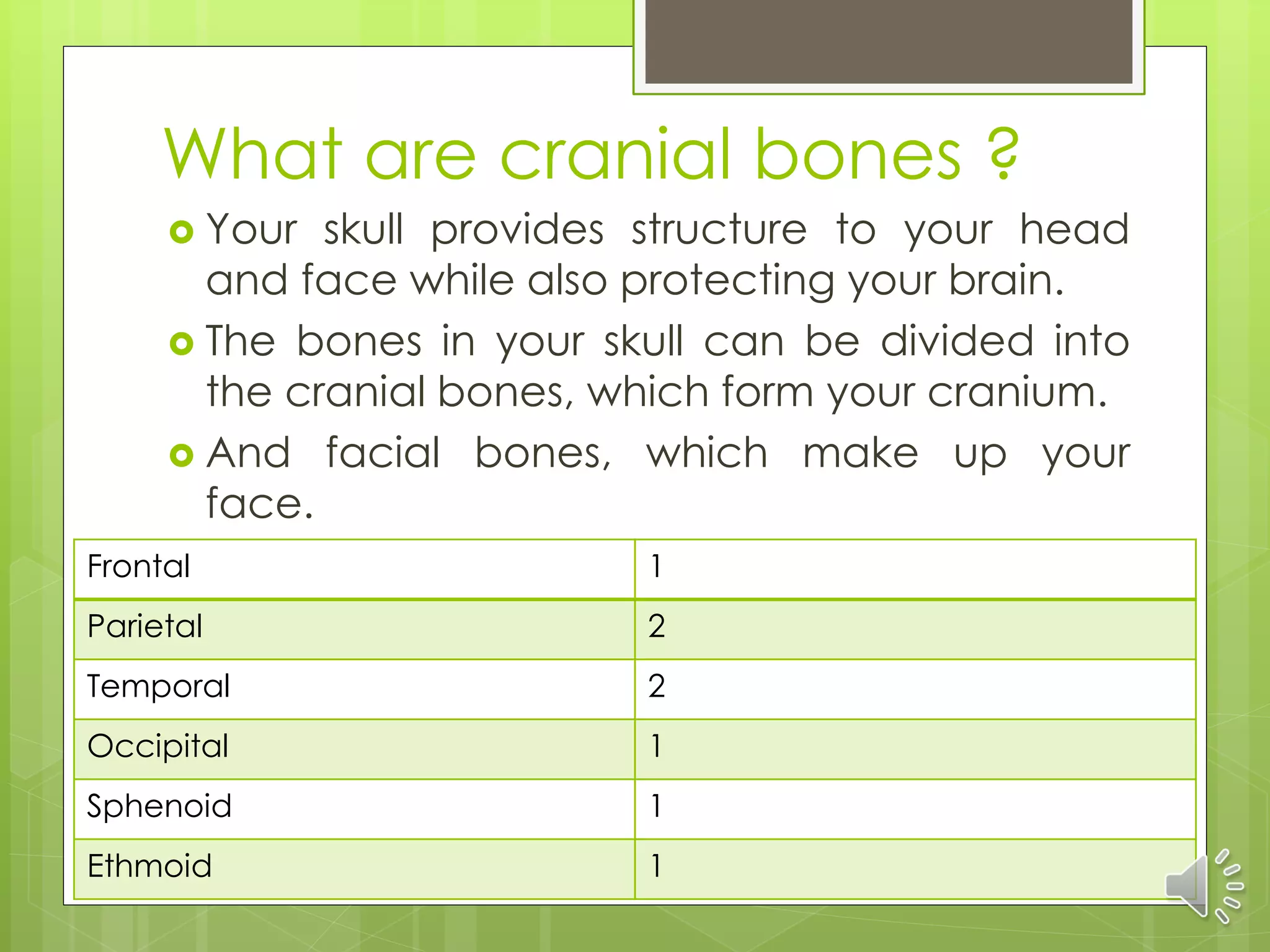
The skeletal system consists of the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. The axial skeleton includes the bones of the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage, totaling 80 bones. The skull contains 8 cranial bones that form the cranium and 14 facial bones. The vertebral column is made of 26 vertebrae. The thorax contains the sternum and 24 ribs. The appendicular skeleton includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles, totaling 126 bones. It is made up of the pectoral girdle, upper extremities, pelvic girdle and lower extremities. Bone is a living connective tissue that provides structure, protects organs, allows body movement,