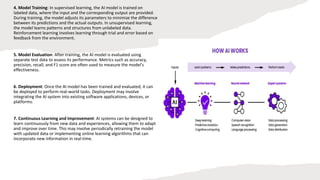
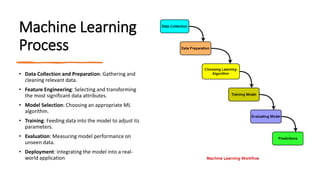
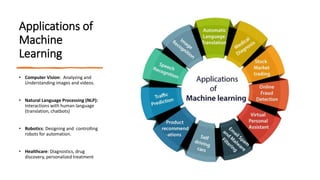
Artificial intelligence (AI) involves creating computer systems that perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence, such as learning and decision-making. It can be categorized into narrow AI, designed for specific tasks, and general AI, which is theoretical and would replicate human intelligence across various tasks. Machine learning, a subset of AI, focuses on algorithms that allow computers to learn from data, improving performance over time without explicit programming.