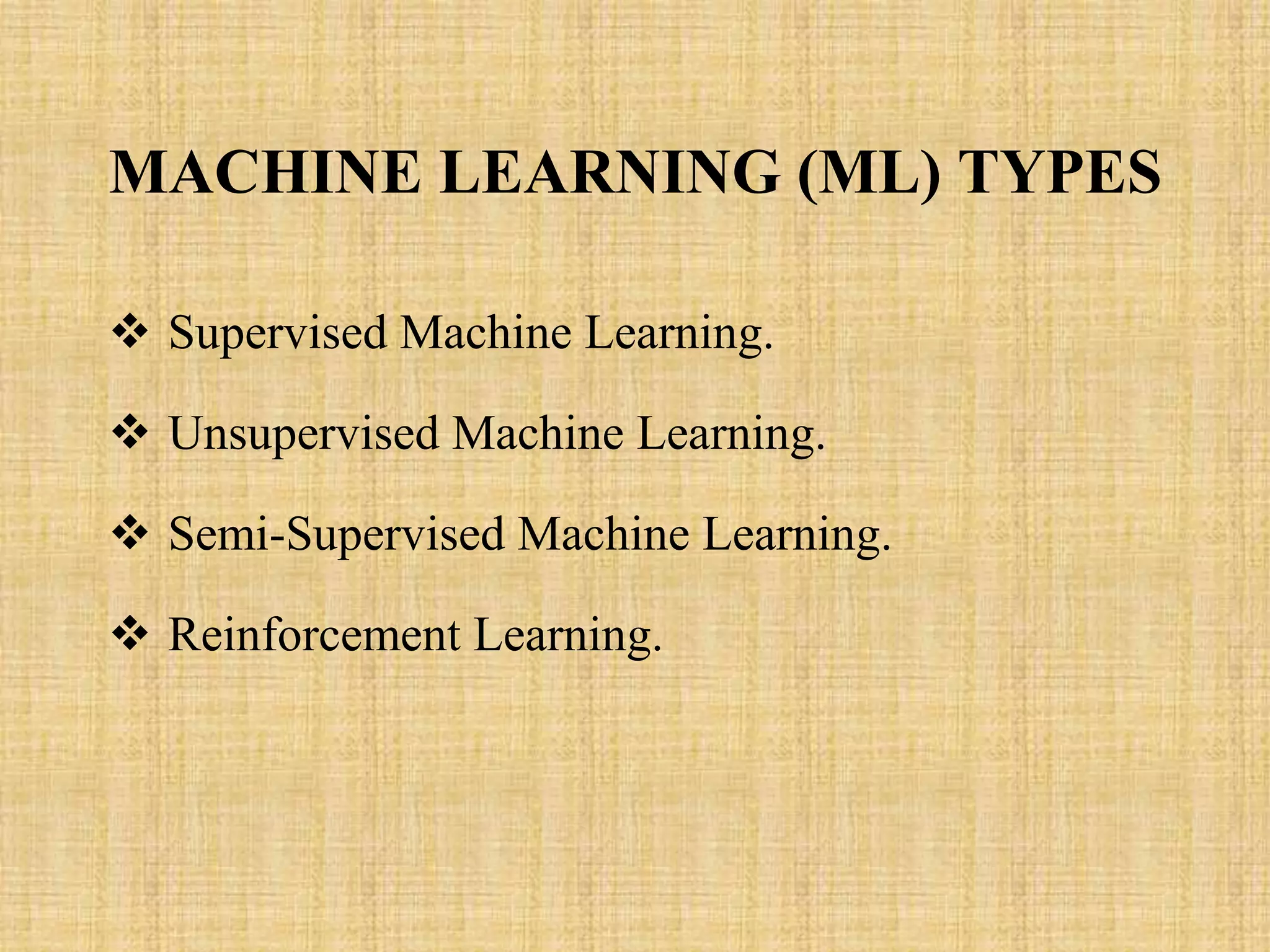
This document provides an overview of machine learning types including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training a model on labeled data to predict labels for new data. Unsupervised learning finds patterns in unlabeled data through techniques like clustering and association. Semi-supervised learning uses a combination of labeled and unlabeled data for training. Reinforcement learning involves an agent learning through trial-and-error interactions with an environment.