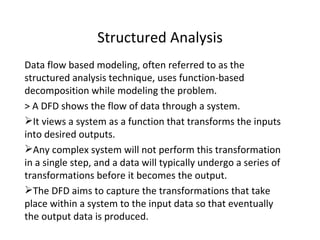
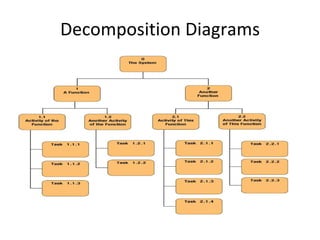
The document discusses software requirements analysis and outlines the key aspects of developing requirements for software systems. It notes that a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) describes what a software system should do without describing how it will do it. An SRS establishes agreement between clients and suppliers and provides a reference for validation. Characteristics of an effective SRS include being correct, complete, unambiguous, verifiable, consistent, modifiable and traceable. Components of an SRS include functionality, performance, design constraints and external interfaces. Data flow diagrams are used to model systems and show the flow of data through transformations.