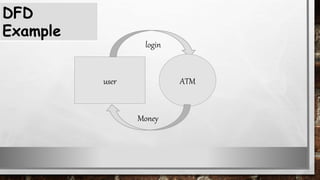
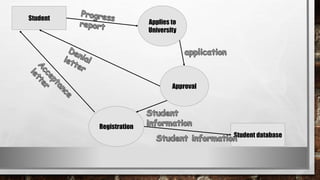
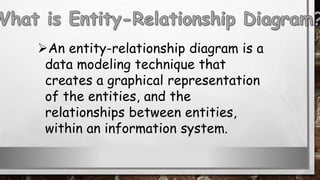
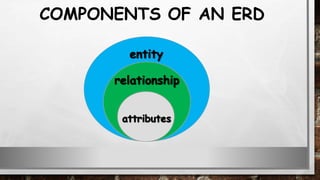
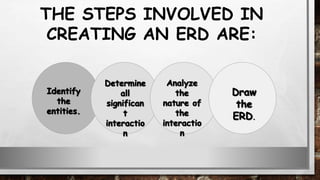
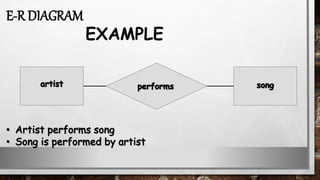
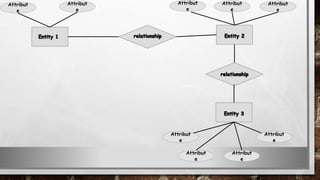
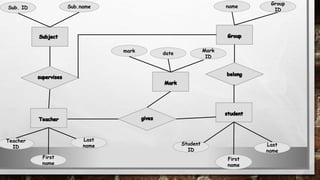
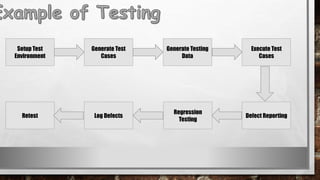
This document discusses various types of diagrams and design phases used in software development lifecycle. It describes entity-relationship diagrams, data flow diagrams, logical design, physical design, architectural design, detailed design, testing strategies, unit testing, integration testing and functional testing. The key aspects covered are modeling entities and relationships, inputs/outputs, data flows, user requirements, interfaces, processes, databases and testing at different stages of development.