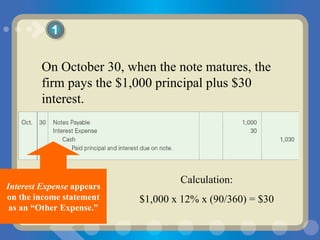
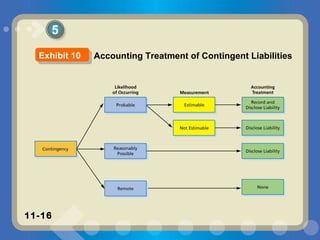
The document discusses current liabilities such as accounts payable, the current portion of long-term debt, and notes payable. It also describes contingent liabilities like product warranties. Companies estimate potential warranty costs based on past experience and record an expense and liability if the warranty obligations are probable and estimable. Journal entries are provided to record estimated warranty expenses and adjustments when warranty work is performed.