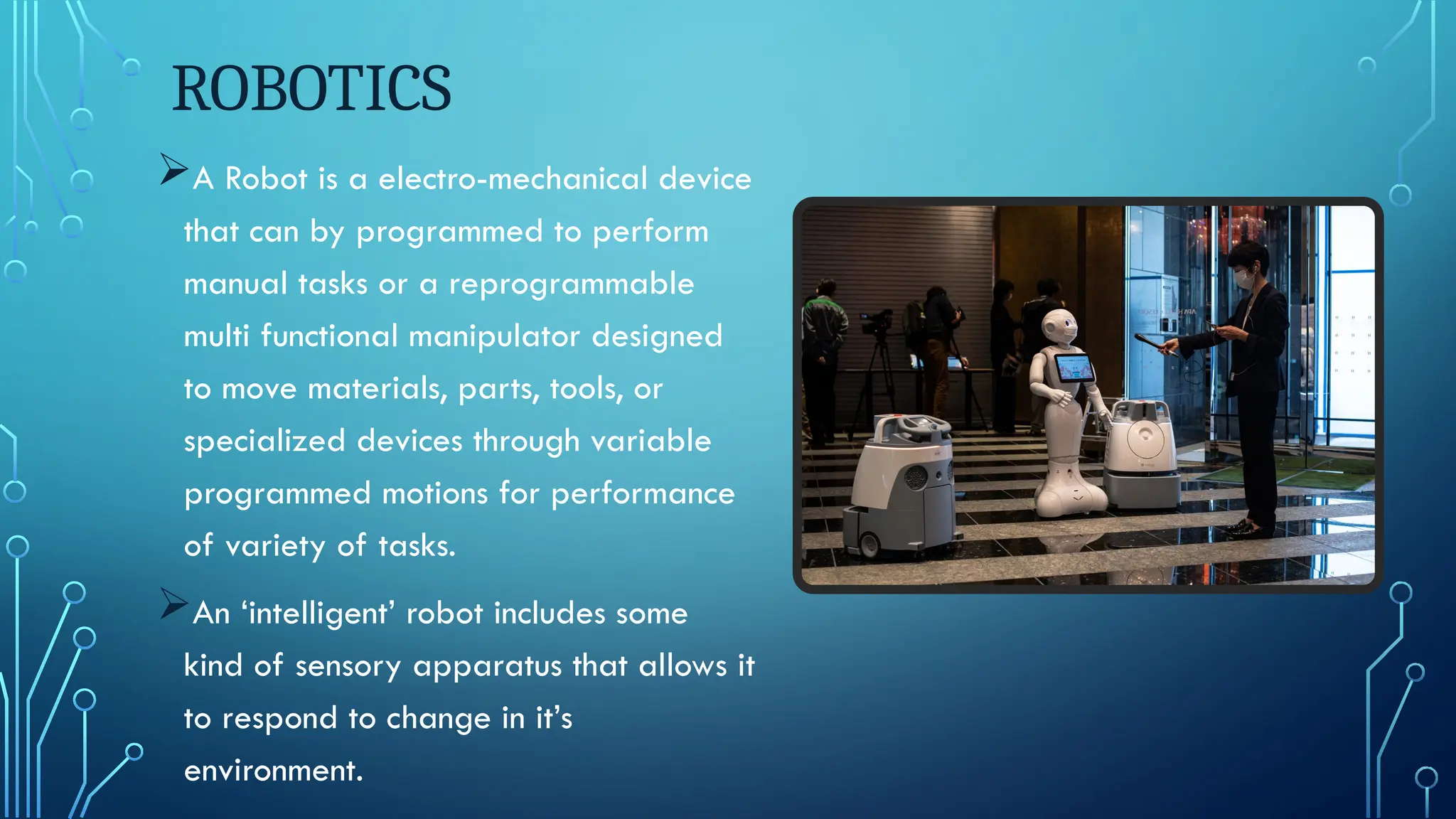
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI), its history, applications, advantages, and disadvantages. AI aims to help machines solve complex problems using algorithms that mimic human intelligence, with applications in expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, computer vision, and robotics. While AI offers benefits such as increased efficiency and reduced error rates, it also presents challenges including high development costs and potential human dependency.


![HISTORY OF AI
1941: First electronic computer [technology finally available]
1956: Term Artificial Intelligence introduced
1960s: Checkers-playing program that was able to play games
with opponents
1980s: Quality Control Systems
2000: First sophisticated walking robot](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-240830094943-3e304fd8/75/Unit-1-of-artificial-intelligence-and-its-introduction-4-2048.jpg)