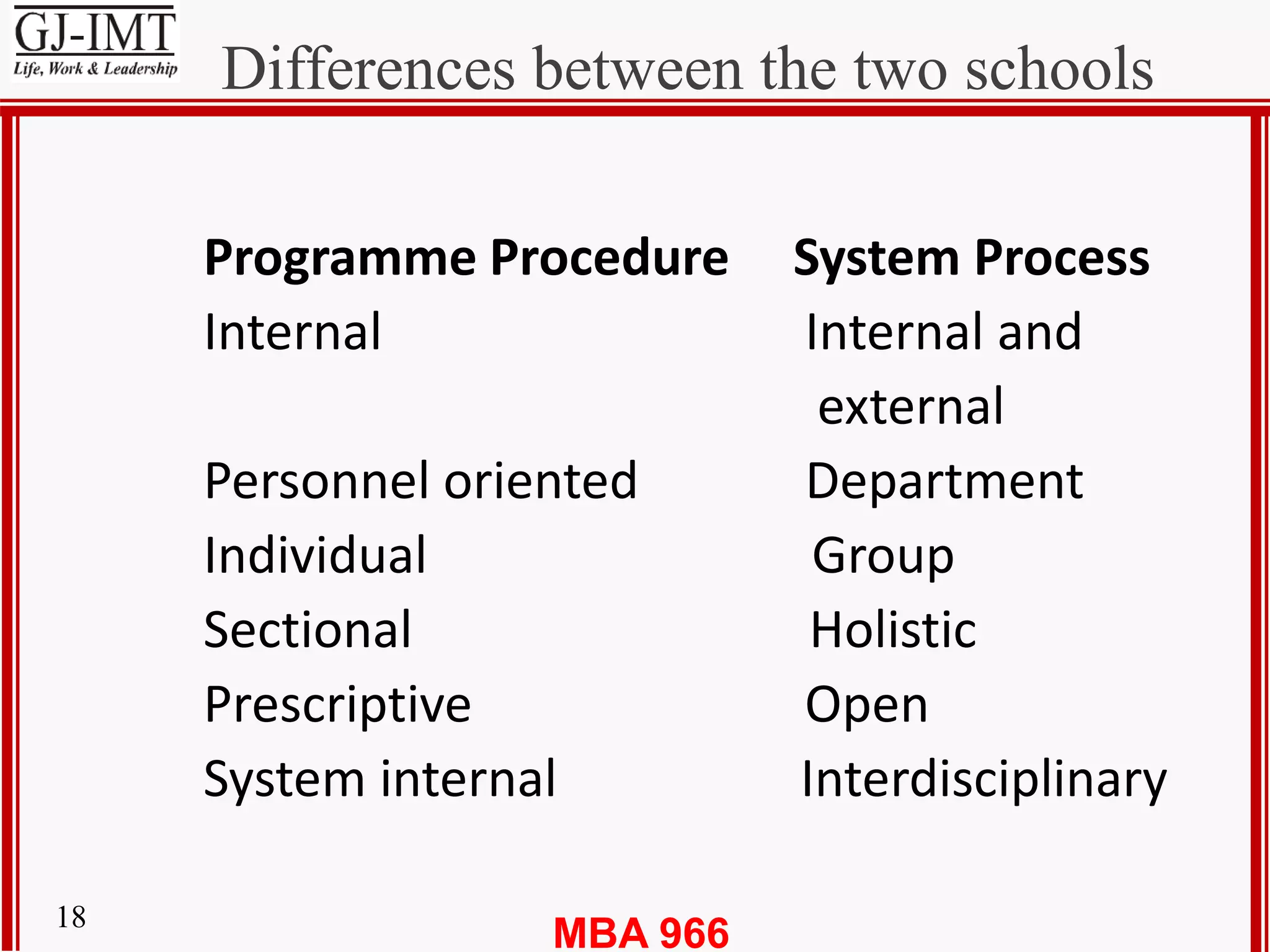
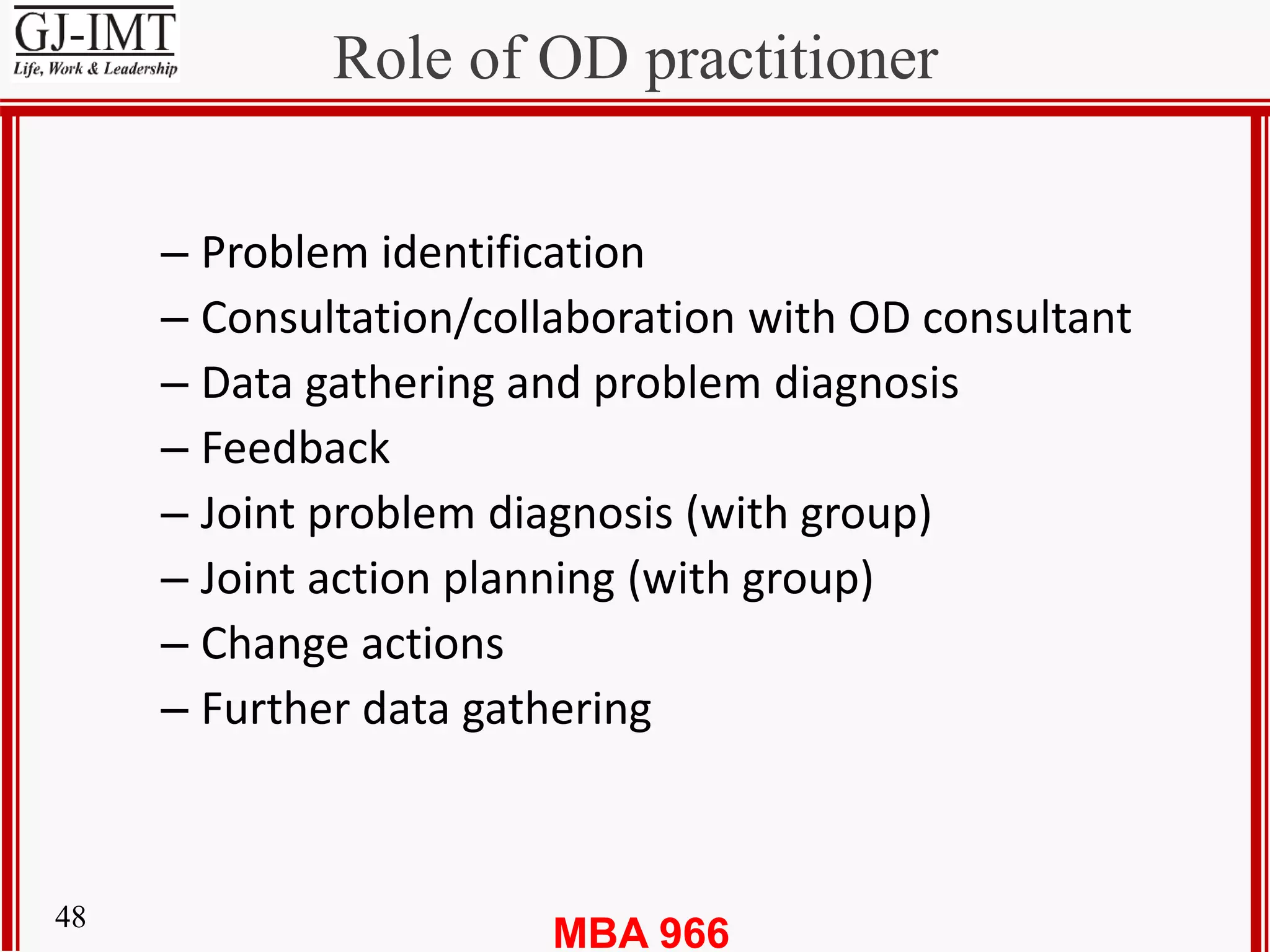
The document discusses organization development (OD) and provides several definitions of OD. It states that OD is a planned process of change involving the whole organization that aims to improve how the organization functions and achieves its goals. Some key characteristics of successful OD efforts mentioned include being long-term, action-oriented, focusing on changing attitudes and behaviors, and working primarily with groups. The objectives of OD programs outlined include individual and group development, developing an empowering organizational culture through collaboration, inculcating team spirit, and achieving organizational transformation and competitive advantage through evaluation and system changes.