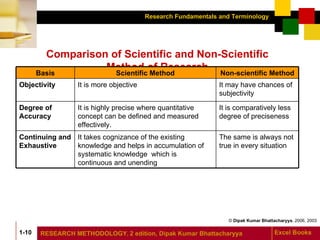
The document defines research and discusses its objectives, features, types, and organization. Research is defined as a systematic investigation through hypothesis formulation, data collection, analysis, interpretation, and reaching conclusions. The objectives of research are to obtain familiarity with phenomena, determine associations, and identify characteristics and frequencies. Research applies in various management fields and should be objective, controlled, generalizable, unbiased, systematic, and reproducible. Types of research include fundamental, applied, descriptive, historical, formulative, experimental, and ex-post facto research. Concept mapping is also discussed as a way to explore knowledge relationships.