1. The document discusses concepts related to occupational risk, emergencies, and self-protection plans. It defines key terms like danger, risk, occupational risk, and emergency.
2. It provides an overview of legal regulations in Spain related to self-protection, occupational risk prevention, and technical building codes.
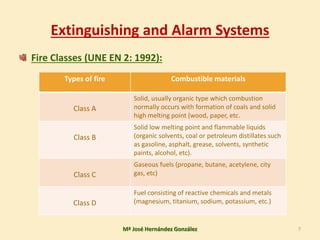
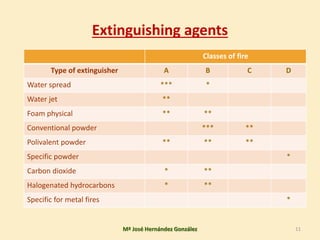
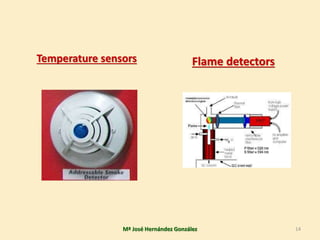
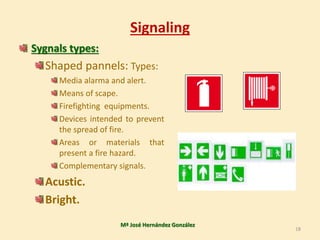
3. The document covers topics like fire classes, the fire tetrahedron, extinguishing agents and systems, alarm detection systems, and signaling of emergency equipment and areas.