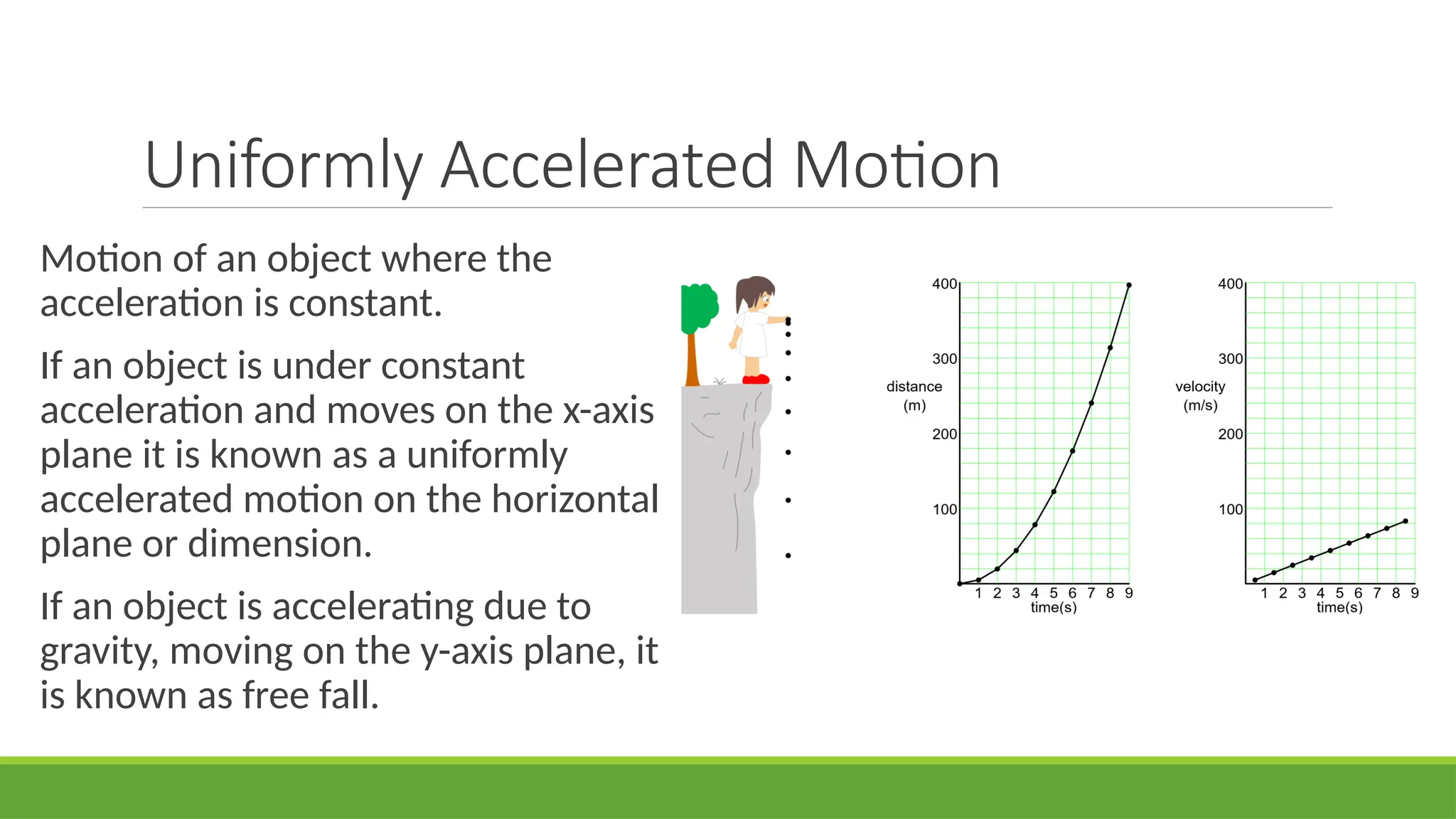
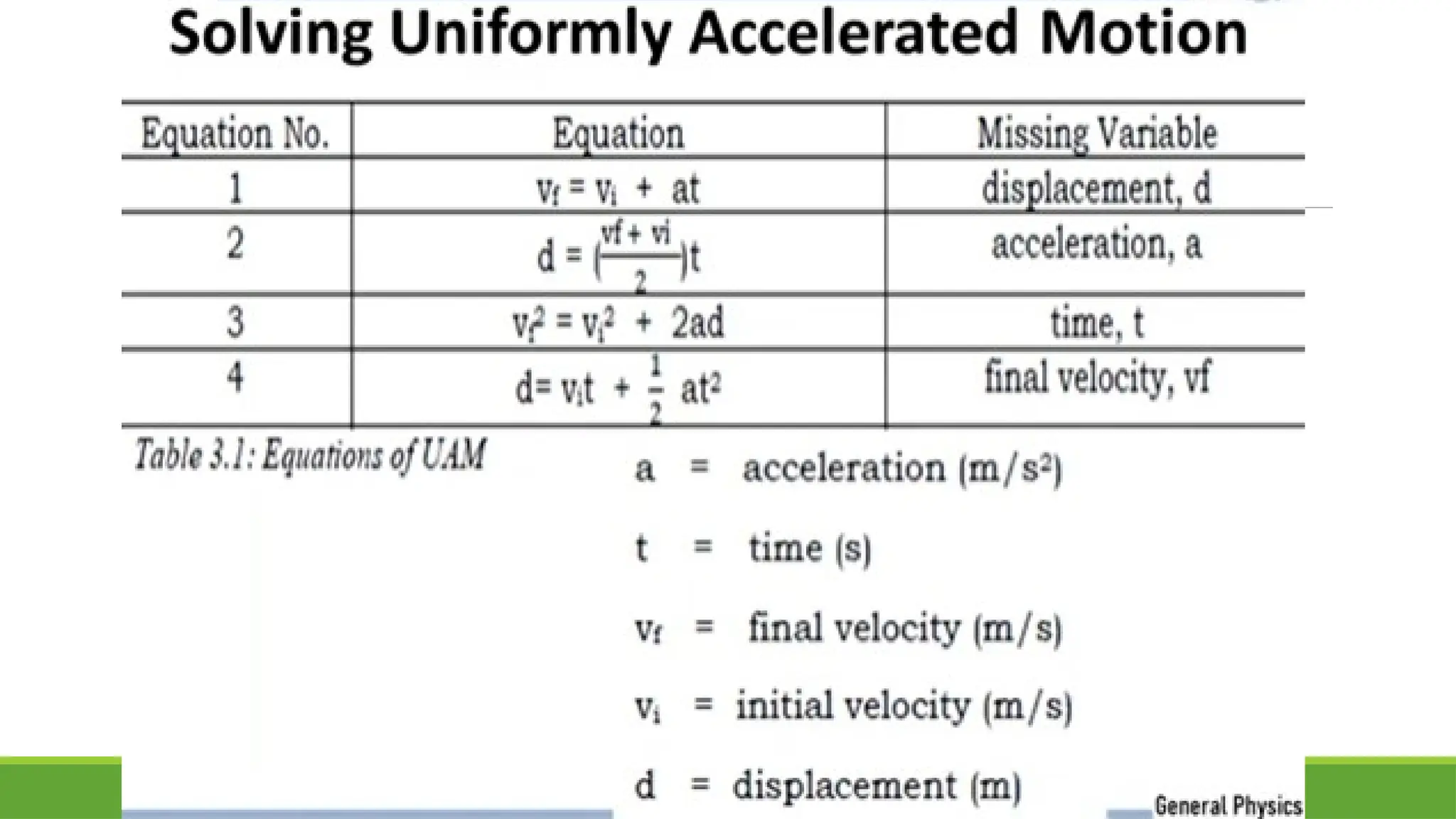
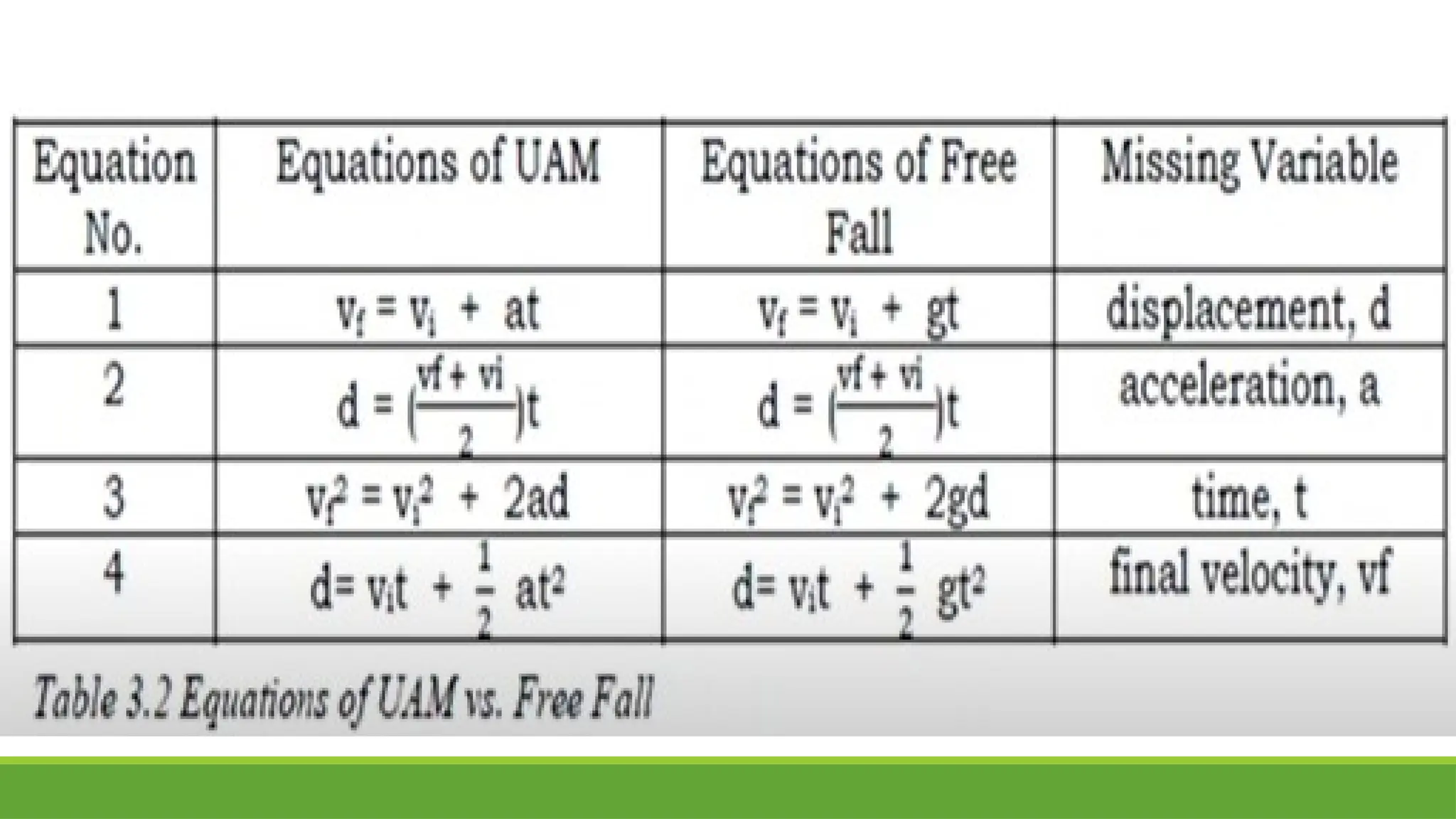
The document explores uniformly accelerated motion, distinguishing between horizontal motion and free fall, and provides sample problems to illustrate concepts of acceleration and distance in both contexts. It details how objects accelerate under constant forces, such as gravity, and includes practical examples of calculating acceleration and distance for varying scenarios. The document concludes with activities and questions to reinforce understanding of gravity and its applications.