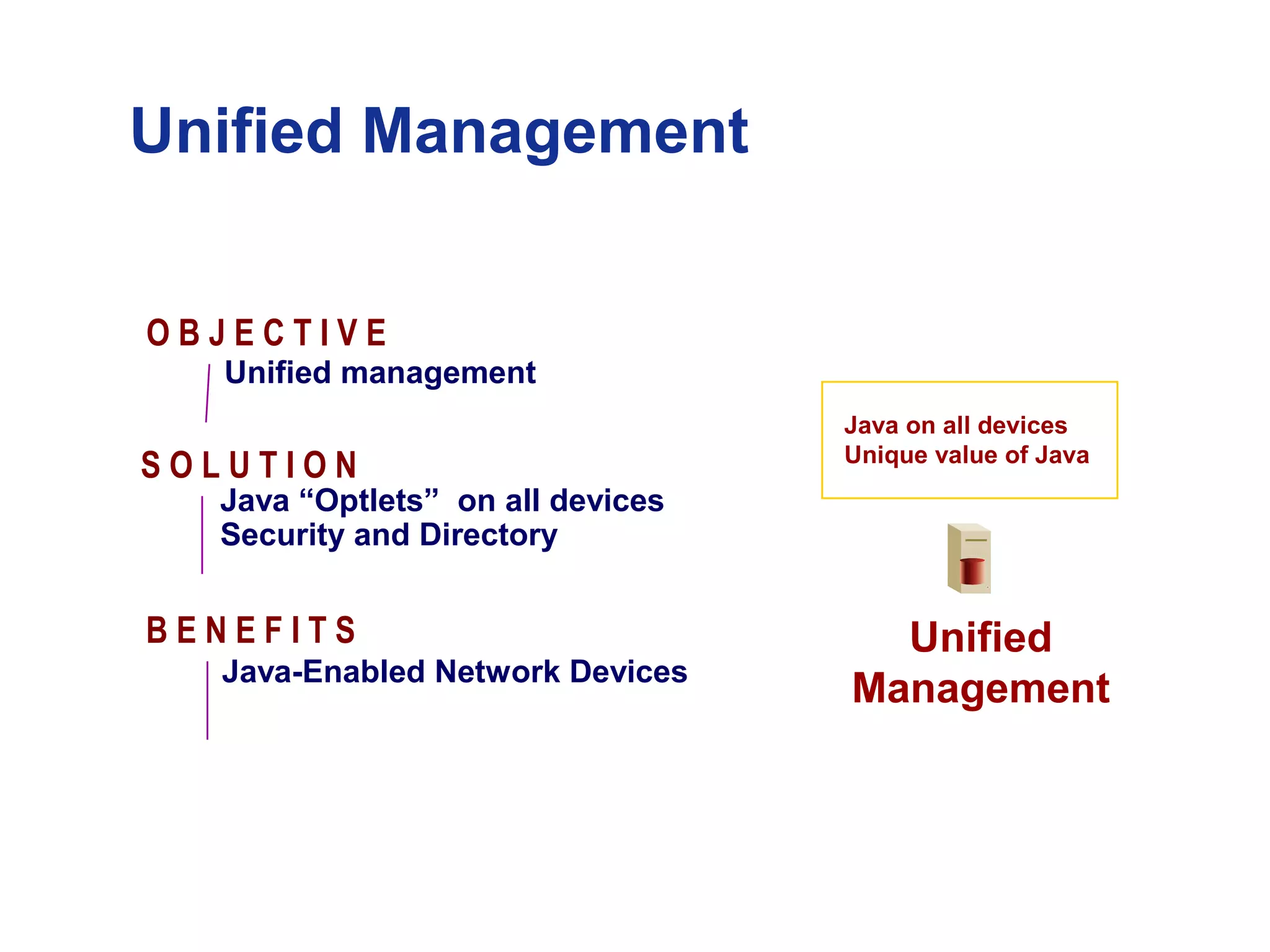
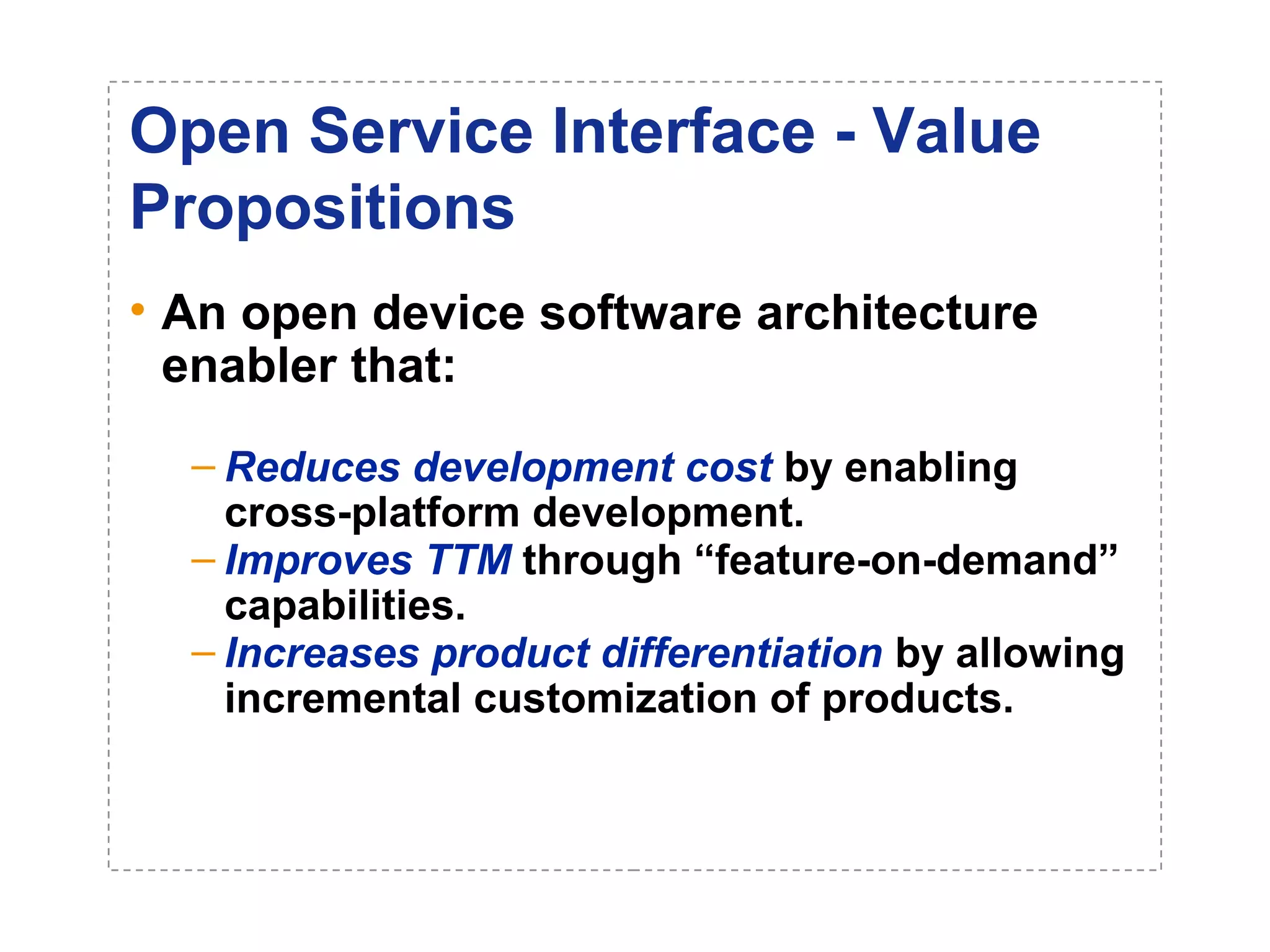
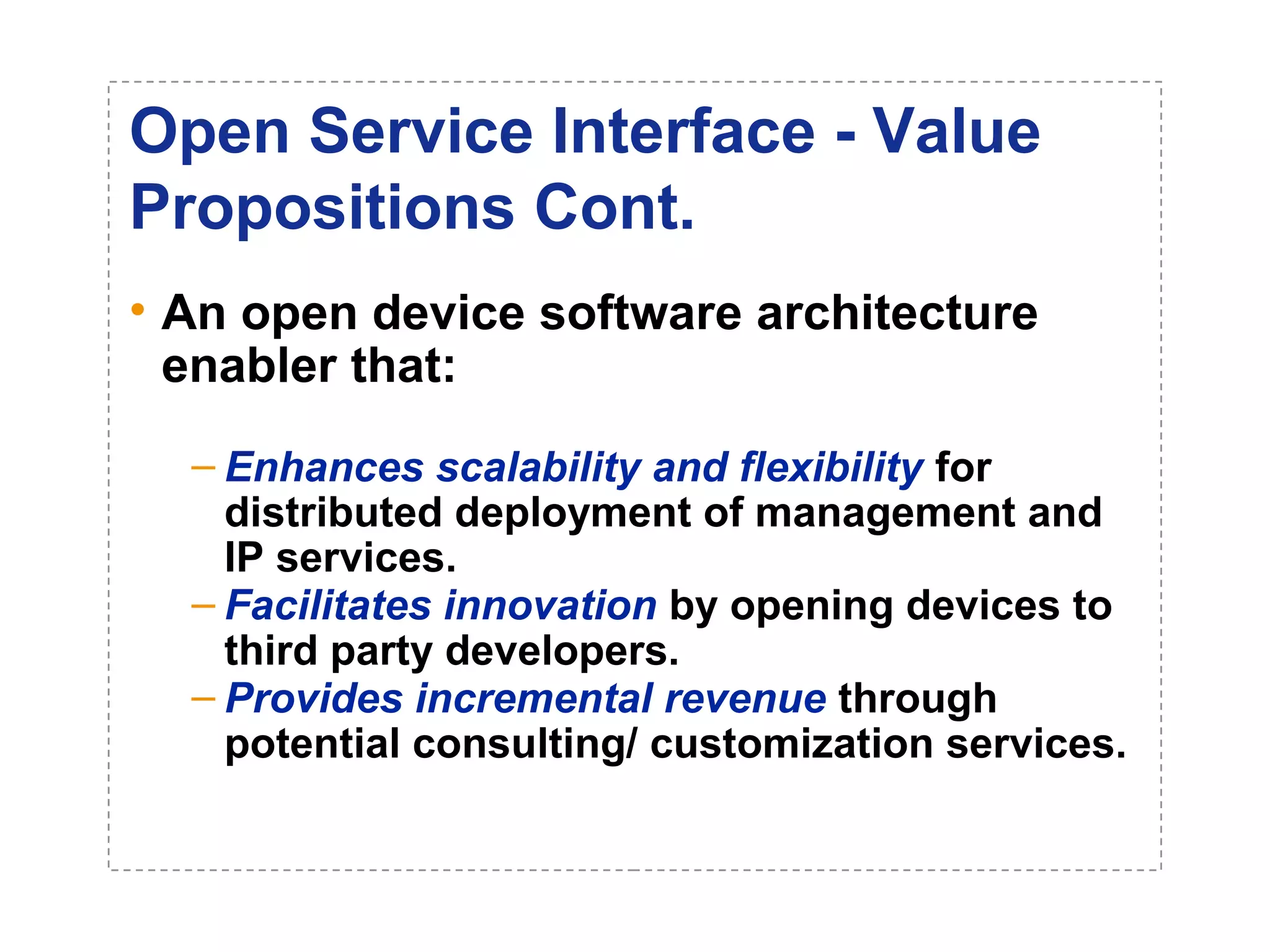
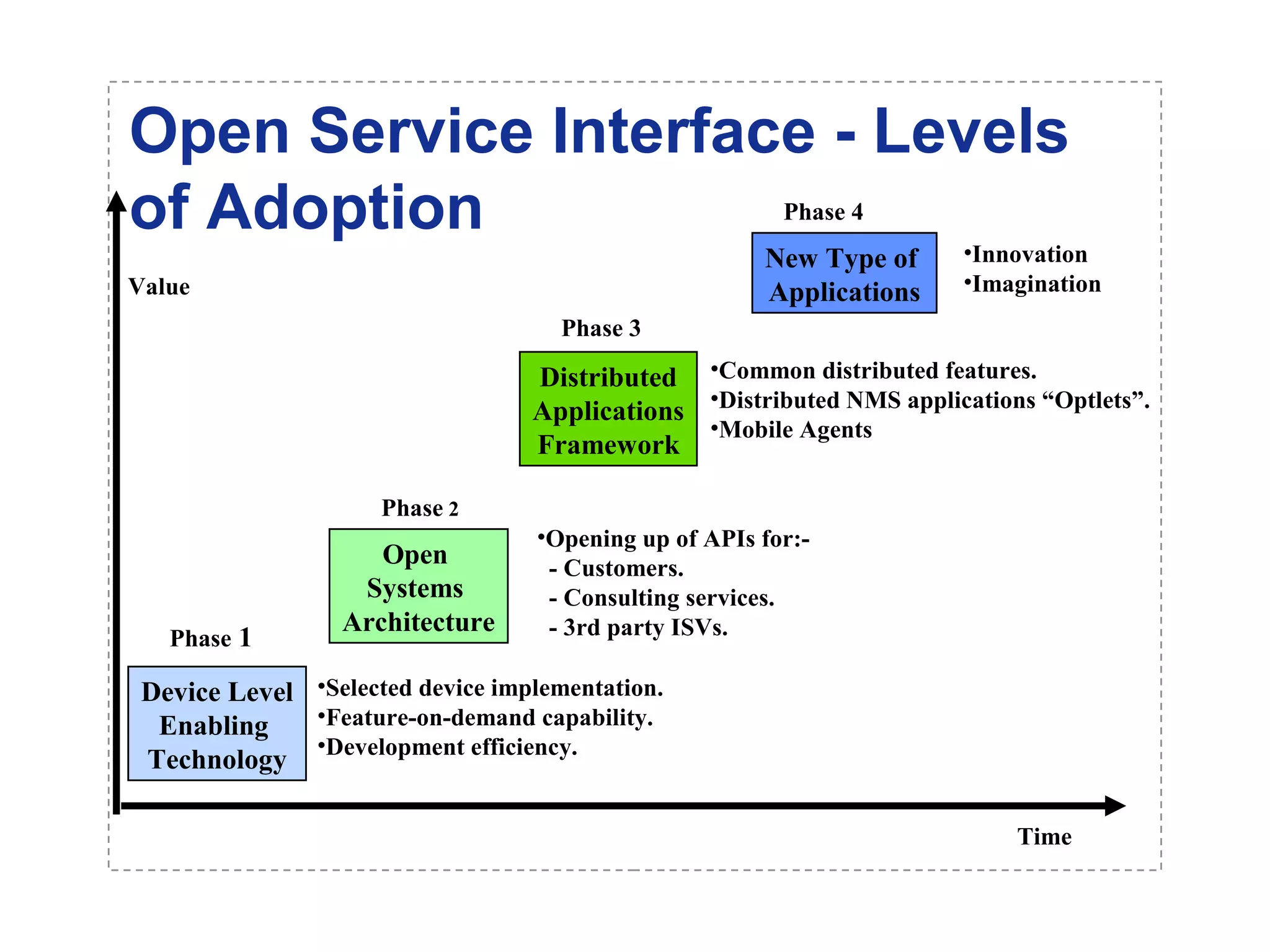
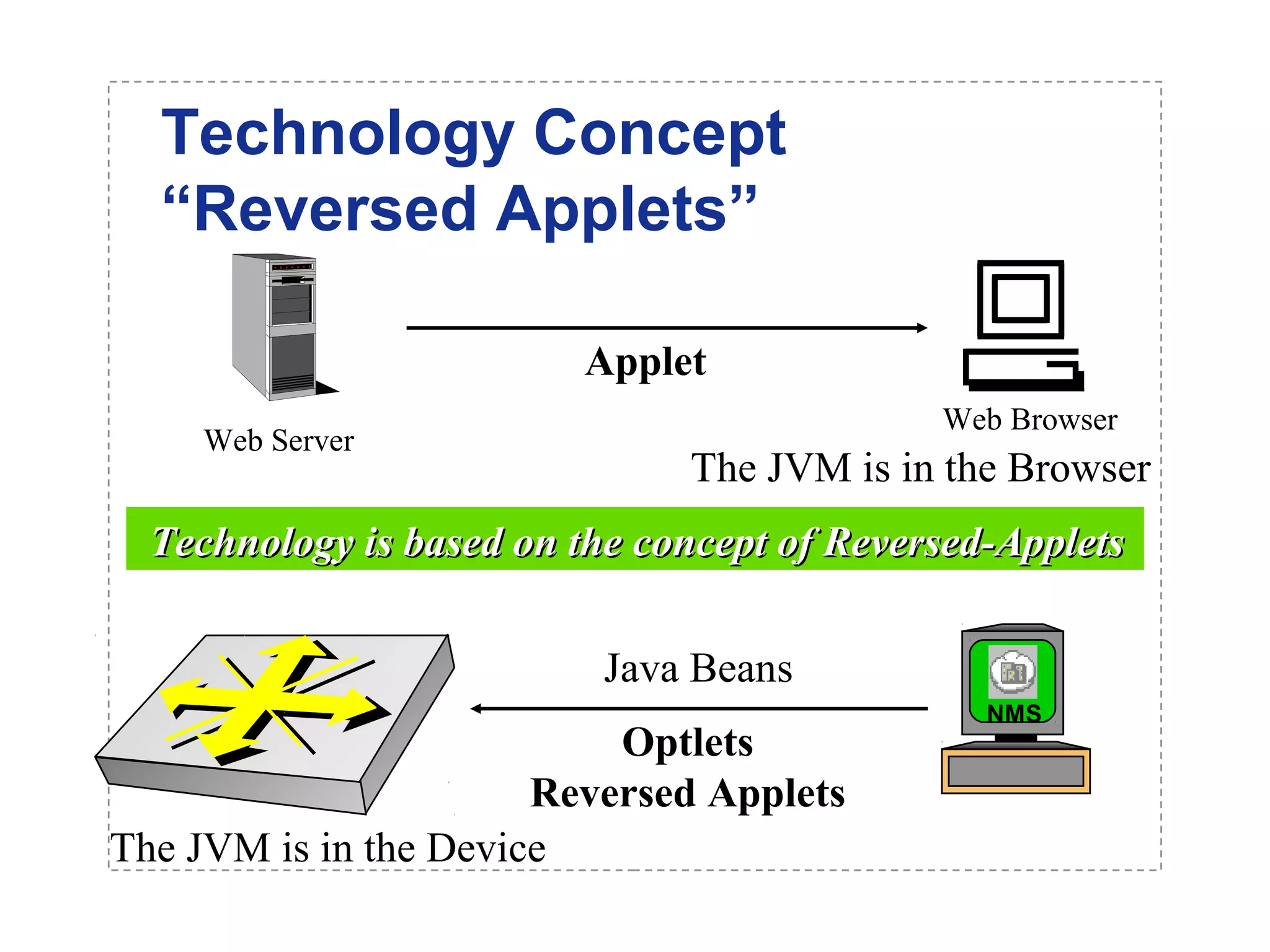
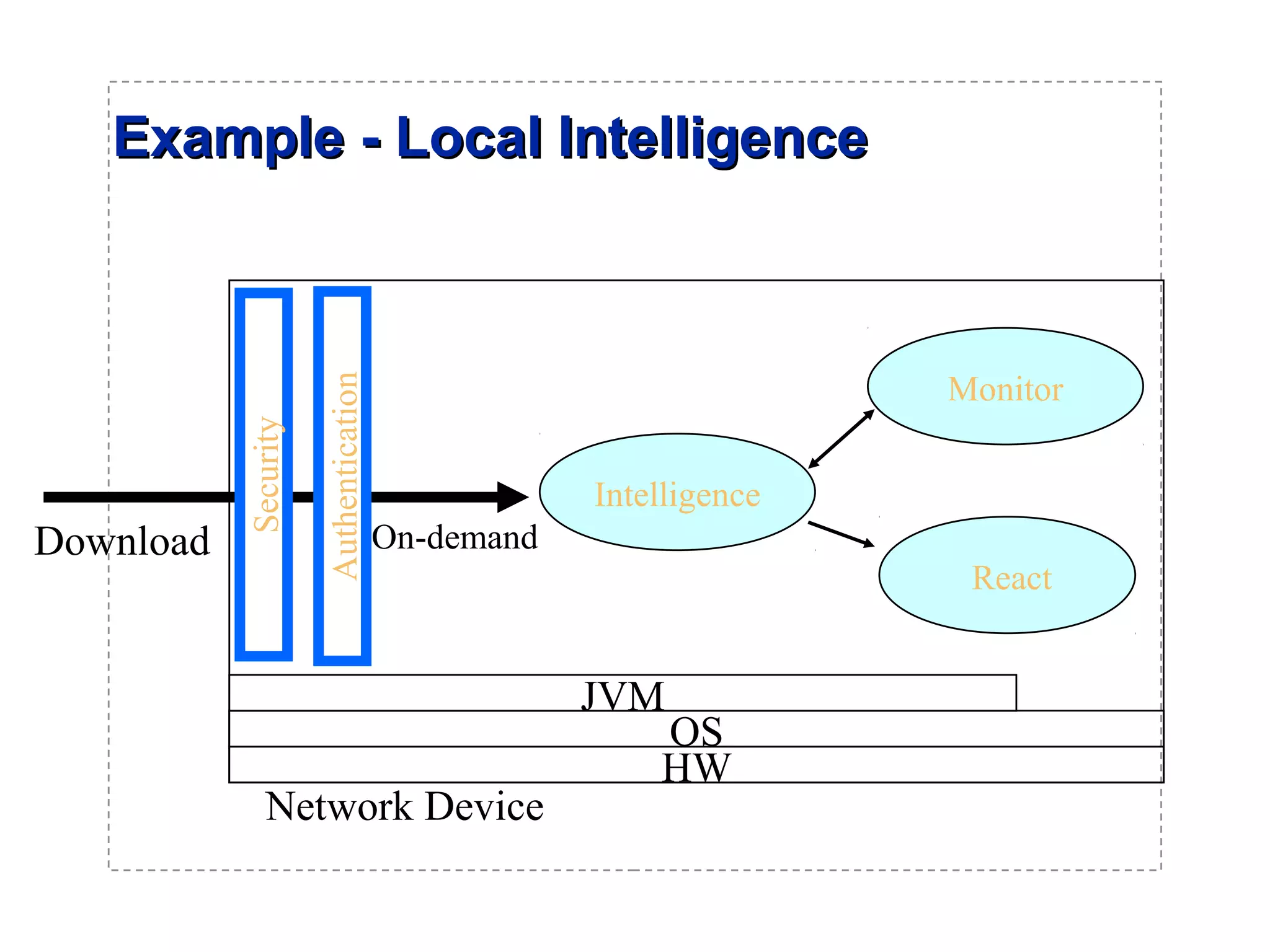
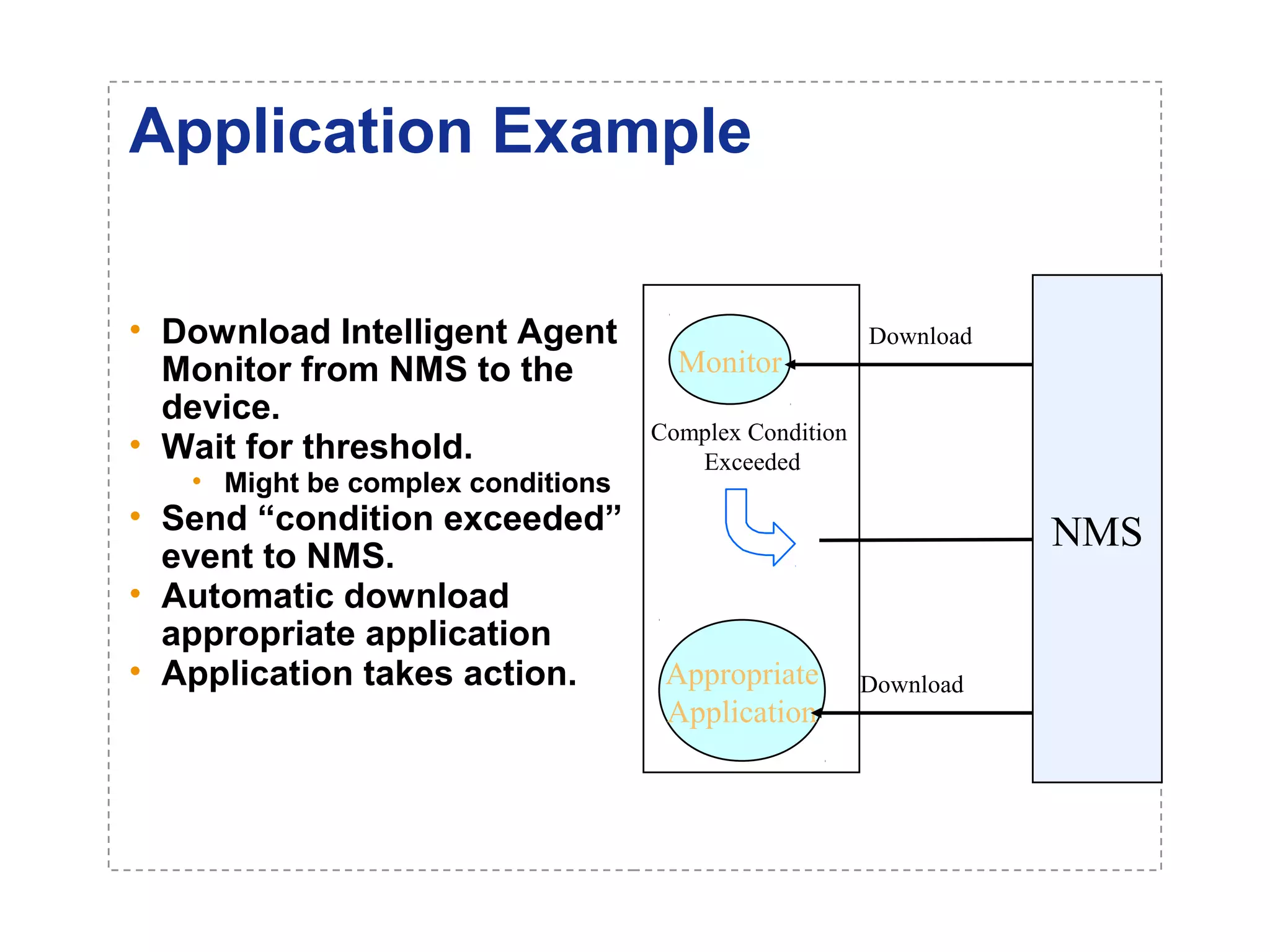
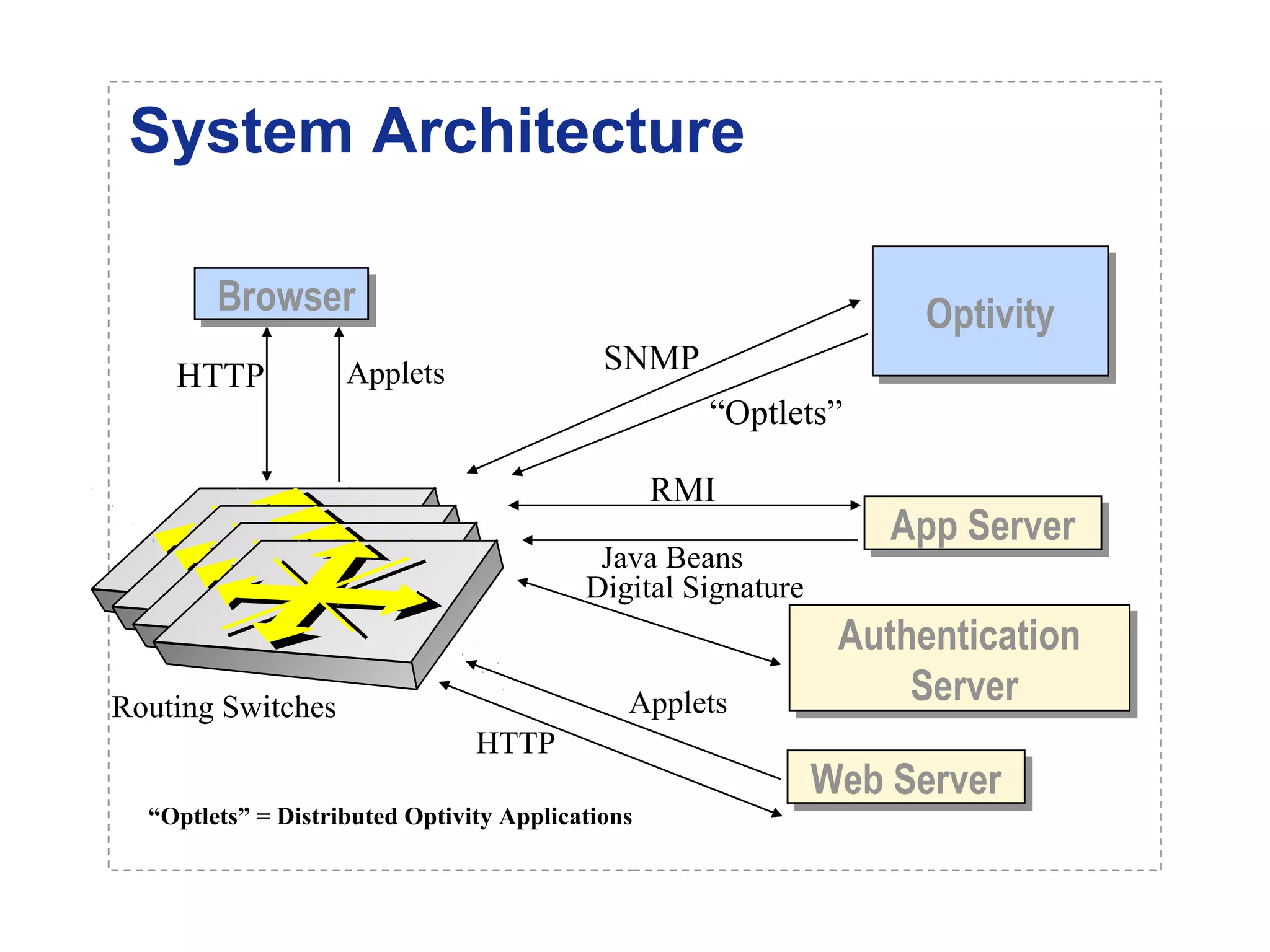
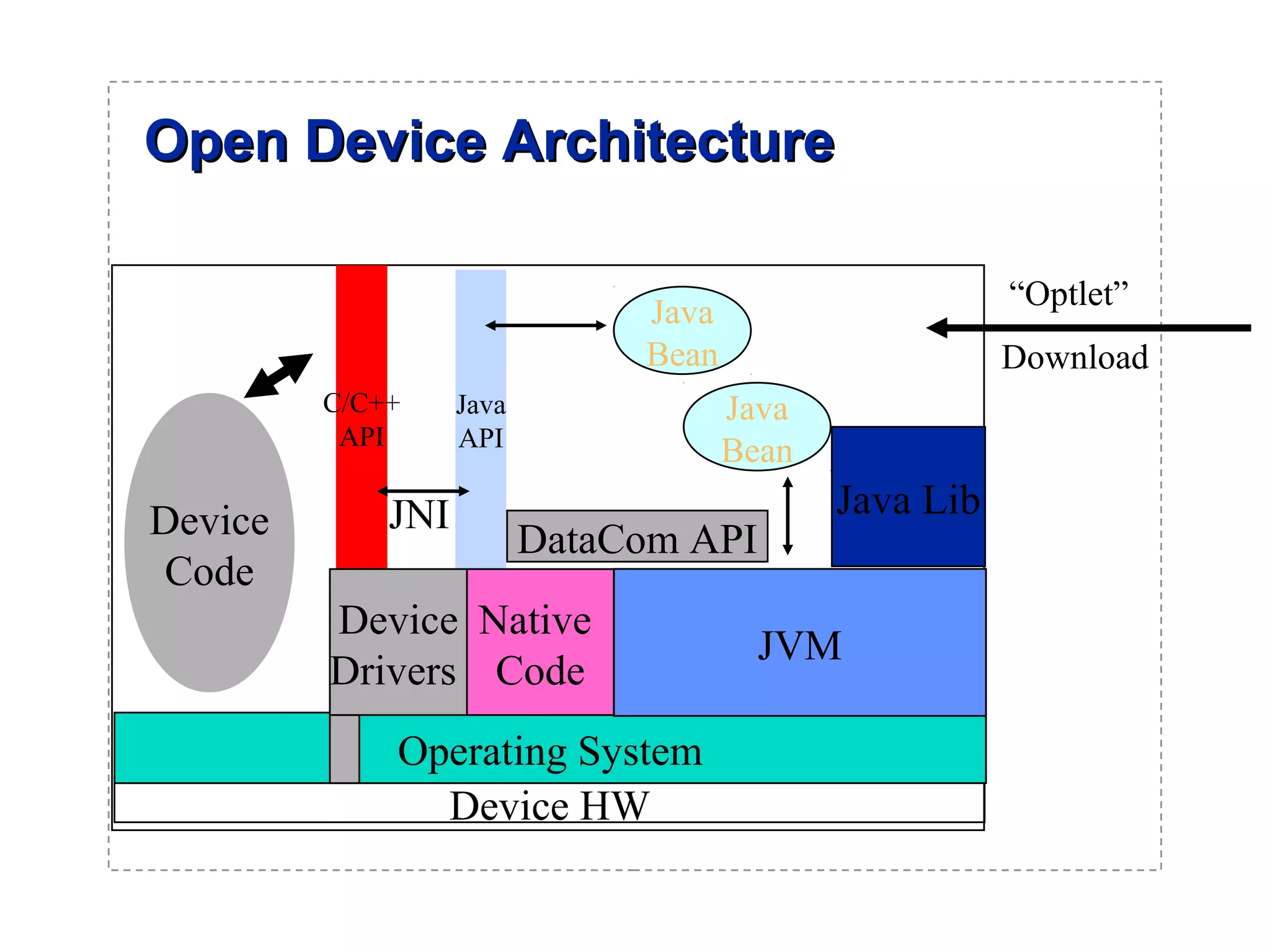
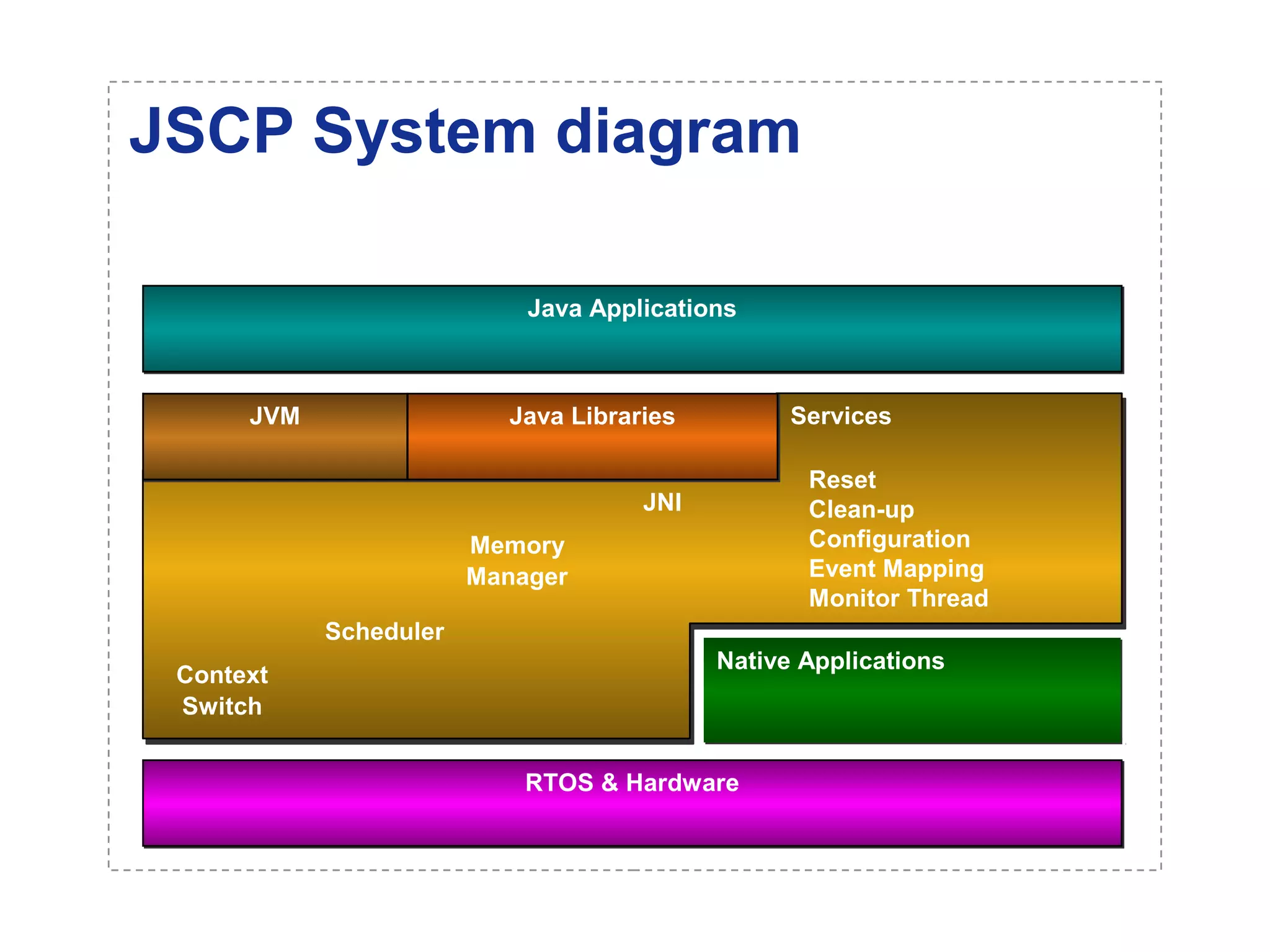
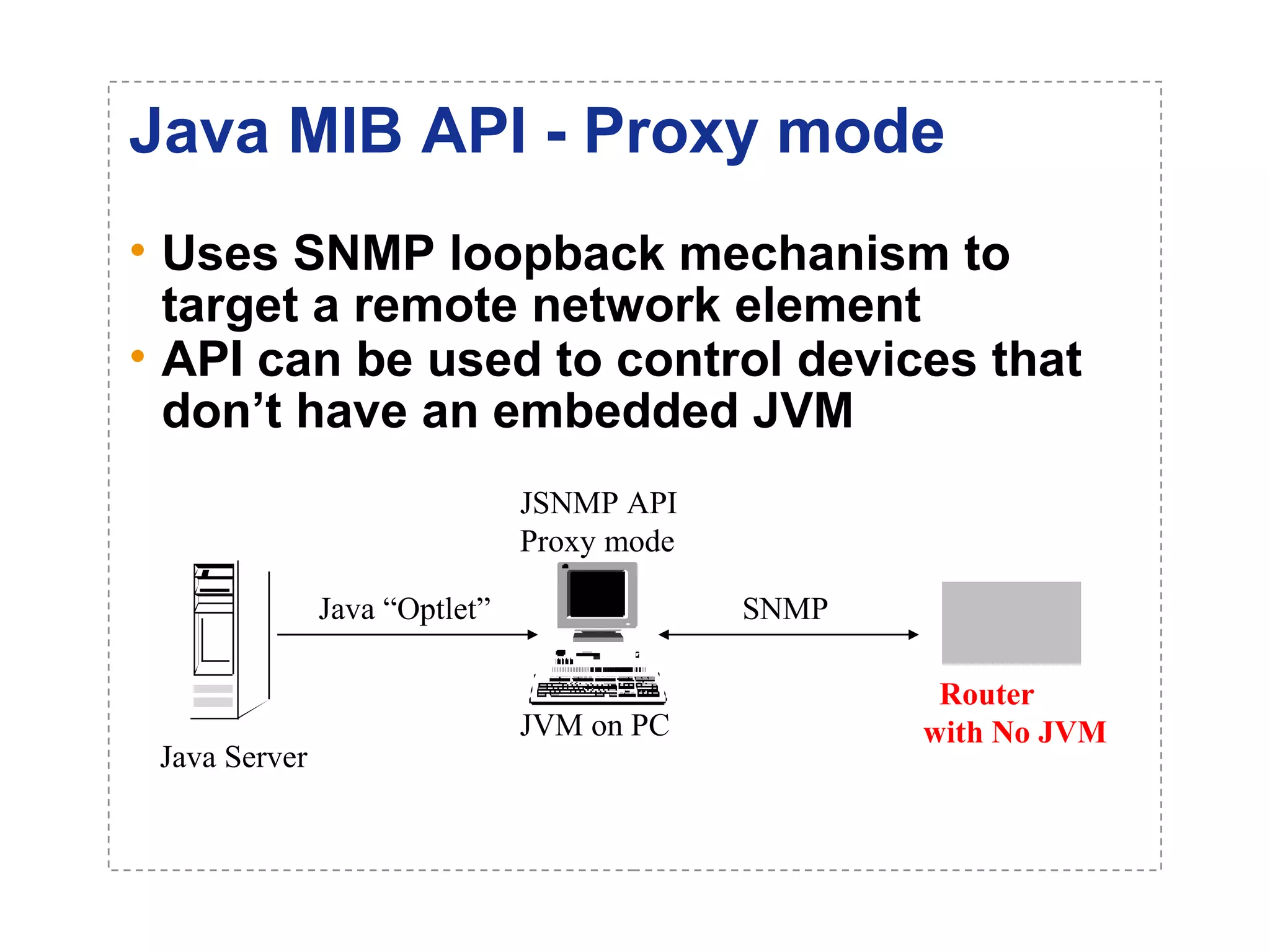
The document introduces a new open networking architecture that leverages Java-enabled network devices for unified management, enhancing security and enabling cross-platform development. It outlines the value propositions of an open service interface, emphasizing reduced development costs, improved scalability, and the potential for innovation through third-party contributions. Additionally, it discusses the Java SNMP MIB API, which simplifies client use and optimizes access while maintaining a strong security model.