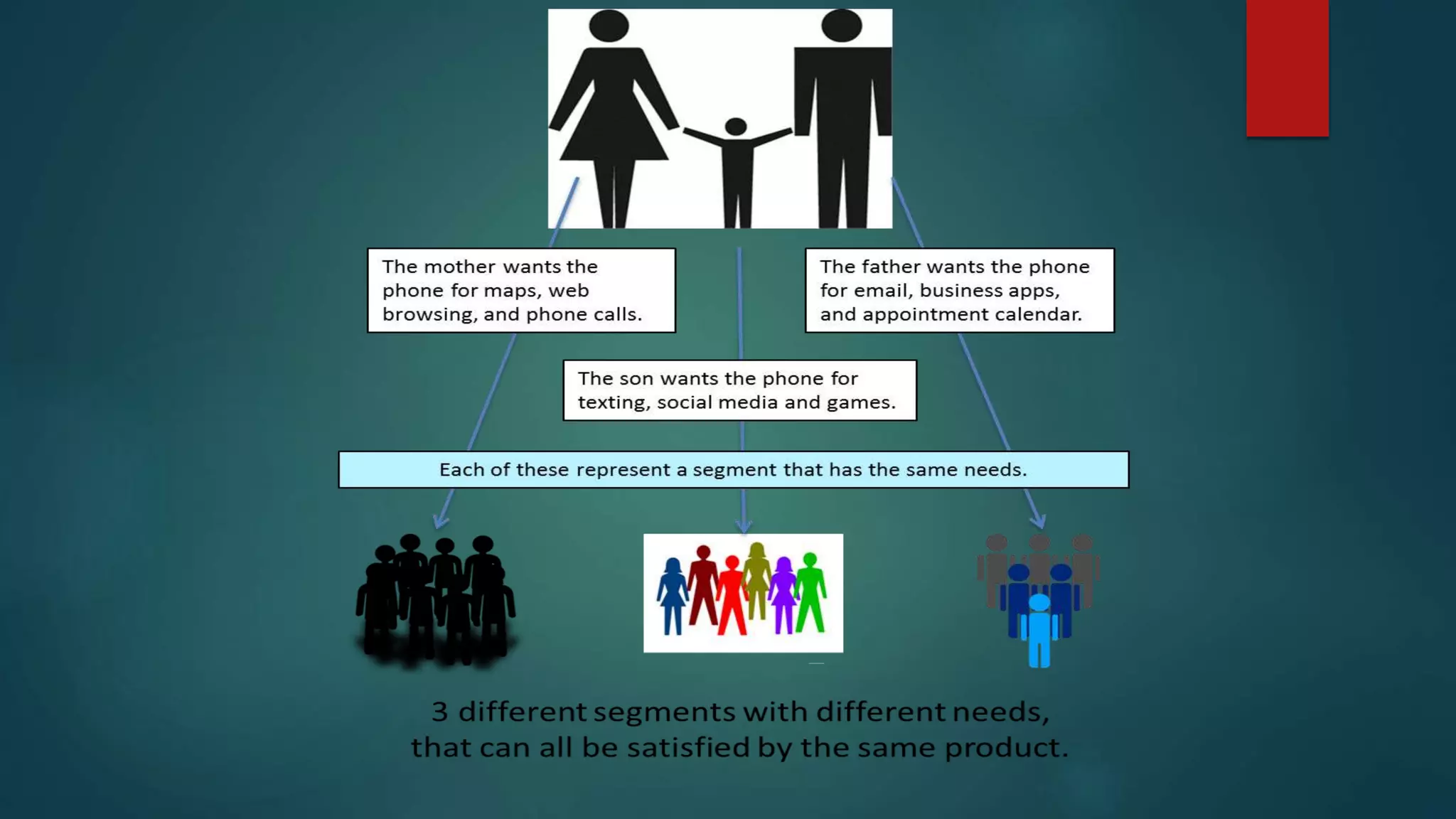
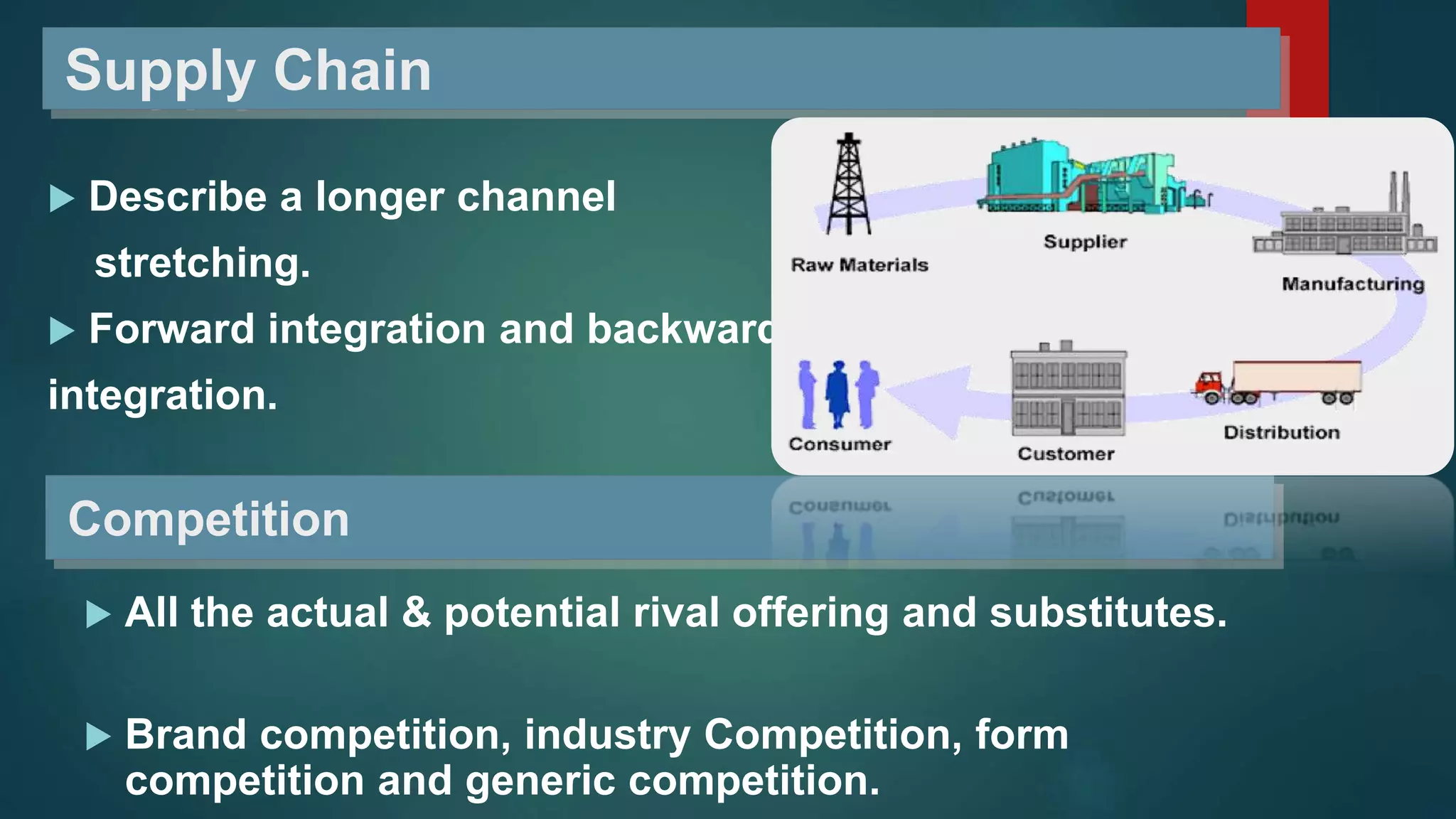
This document provides an overview of a marketing management presentation prepared by six students. It includes sections on demand states and marketing tasks, the core marketing concept covering topics like segmentation, branding, and the marketing mix. It also discusses different marketing philosophies like the production, product, and marketing concepts. Finally, it outlines some ways companies can respond and adjust to changes like reengineering, outsourcing, and adopting e-commerce.