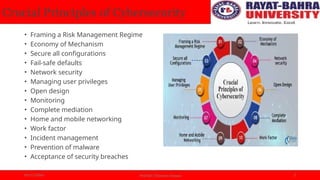
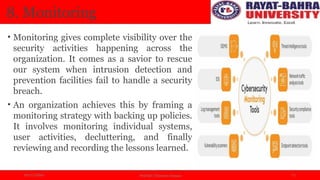
The document discusses essential principles of cybersecurity, emphasizing the need for advanced security measures due to rising cyber crimes. Key principles include risk management, secure configurations, fail-safe defaults, network security, and managing user privileges, which collectively enhance organizational data protection. The document highlights the importance of these principles in achieving robust defense against cyber threats and maintaining data integrity.