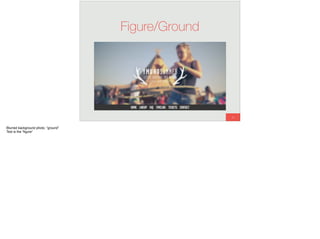
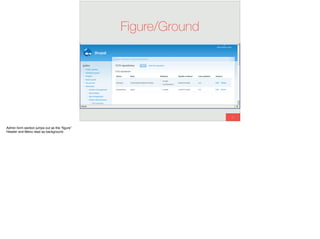
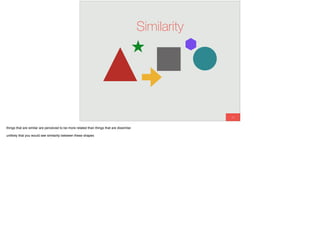
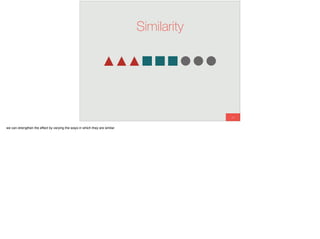
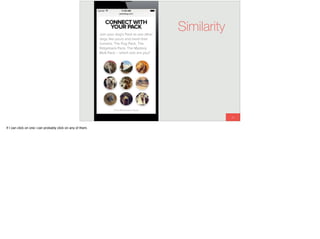
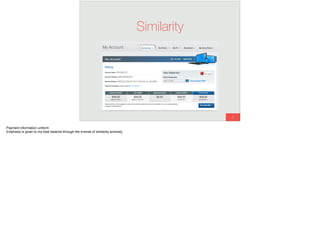
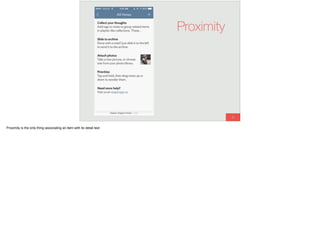
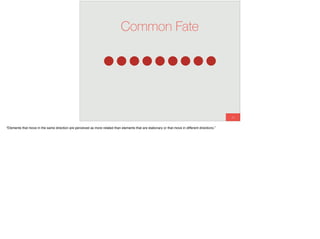
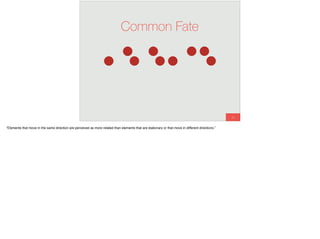
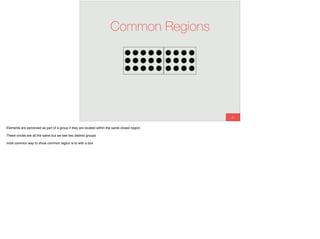
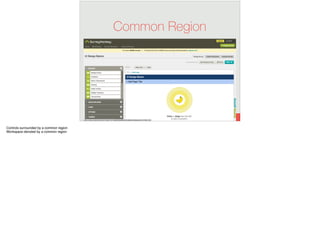
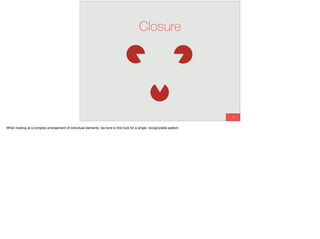
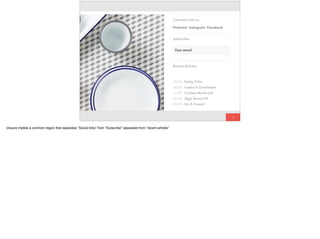
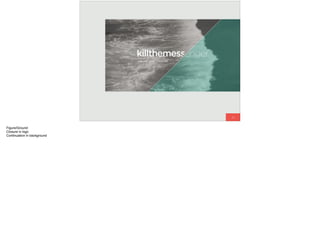
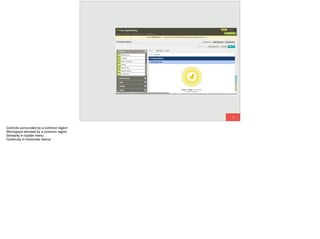
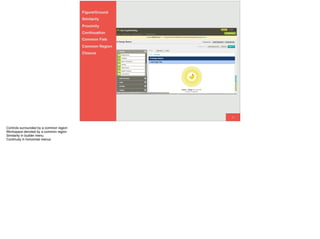
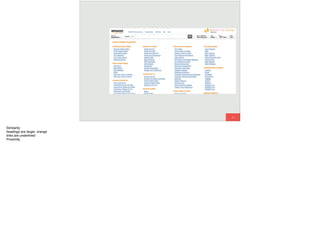
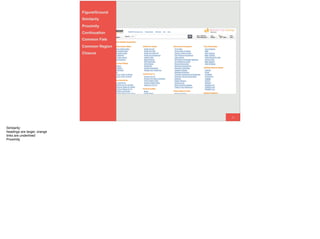
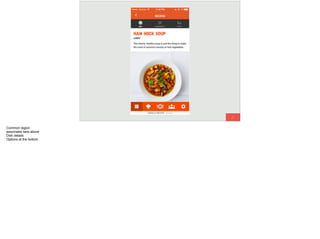
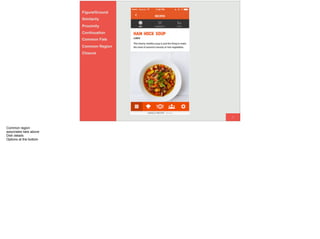
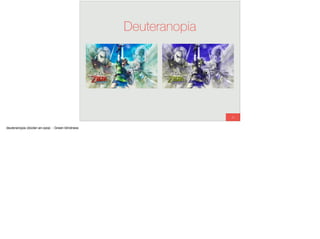
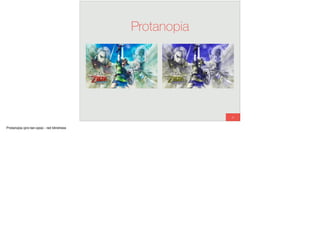
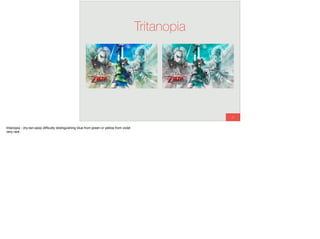
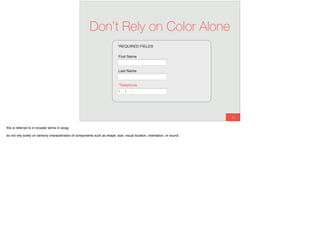
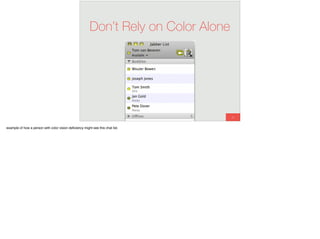
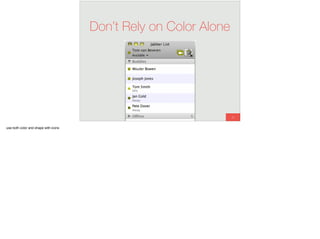
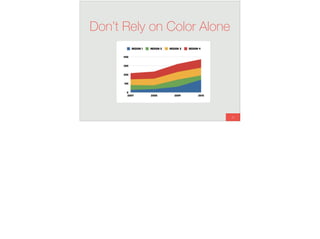
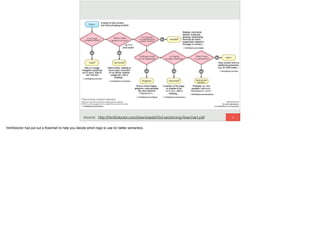
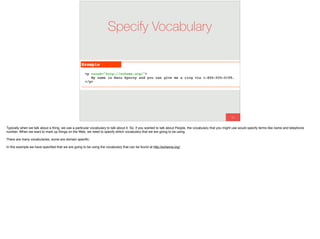
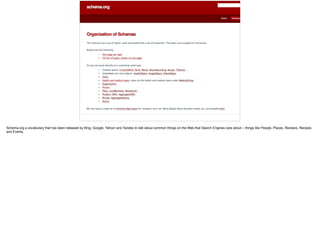
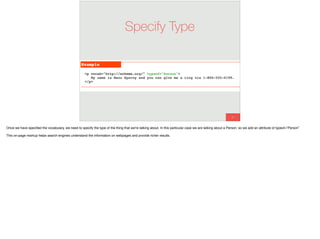
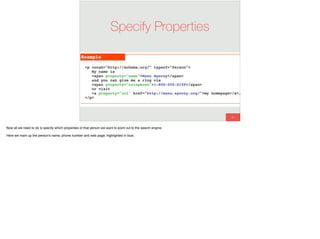
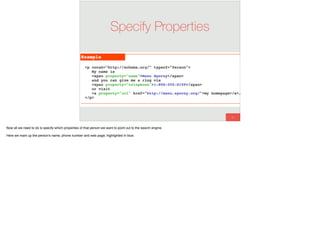
The document discusses the significance of visual perception in UI design, emphasizing the Gestalt principles that explain how humans interpret visual data. It covers various principles such as figure/ground, similarity, proximity, and closure, detailing their application in creating effective user interfaces. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of web accessibility and provides guidelines to accommodate users with disabilities, alongside semantic HTML for better communication with machines.