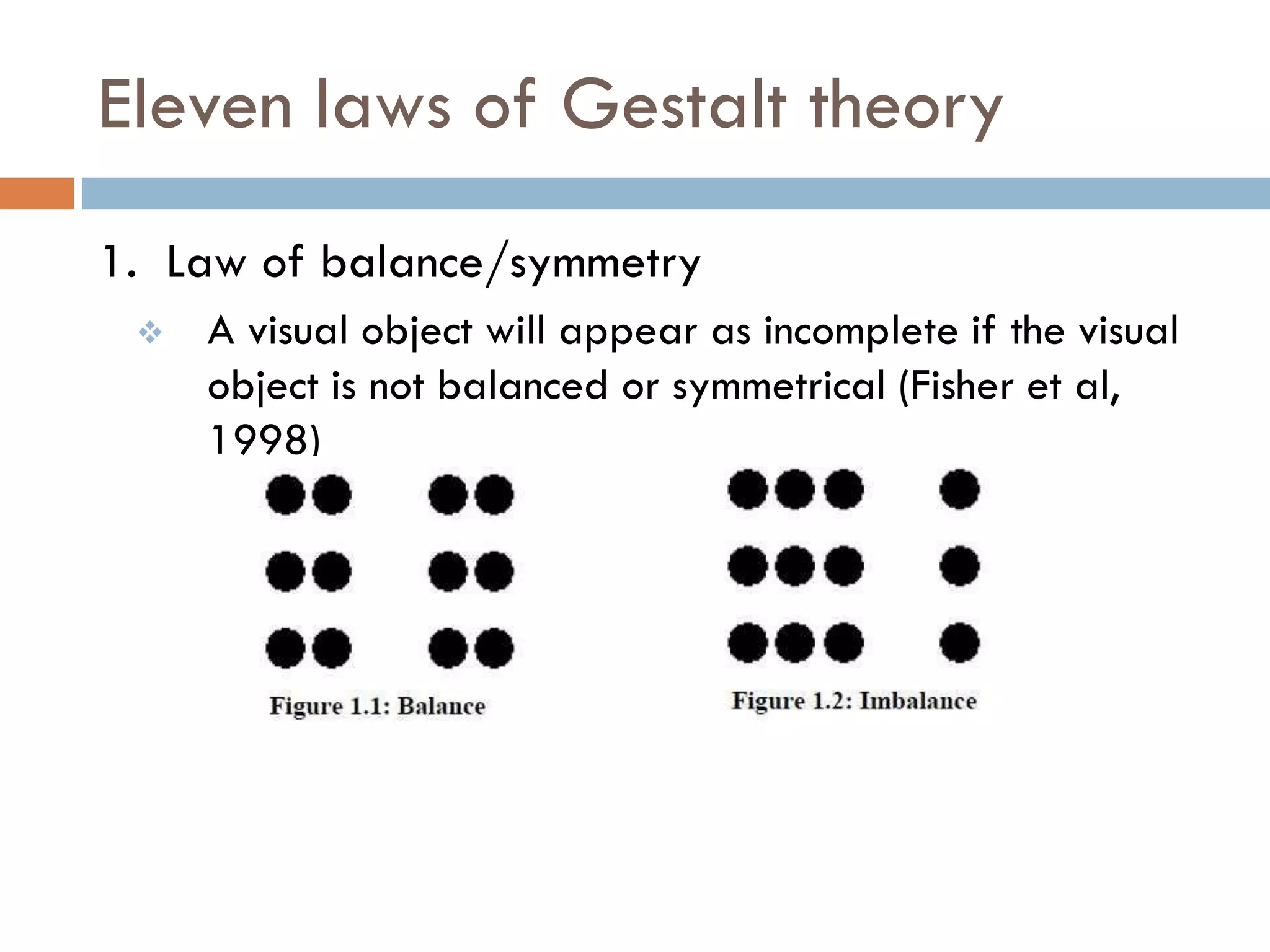
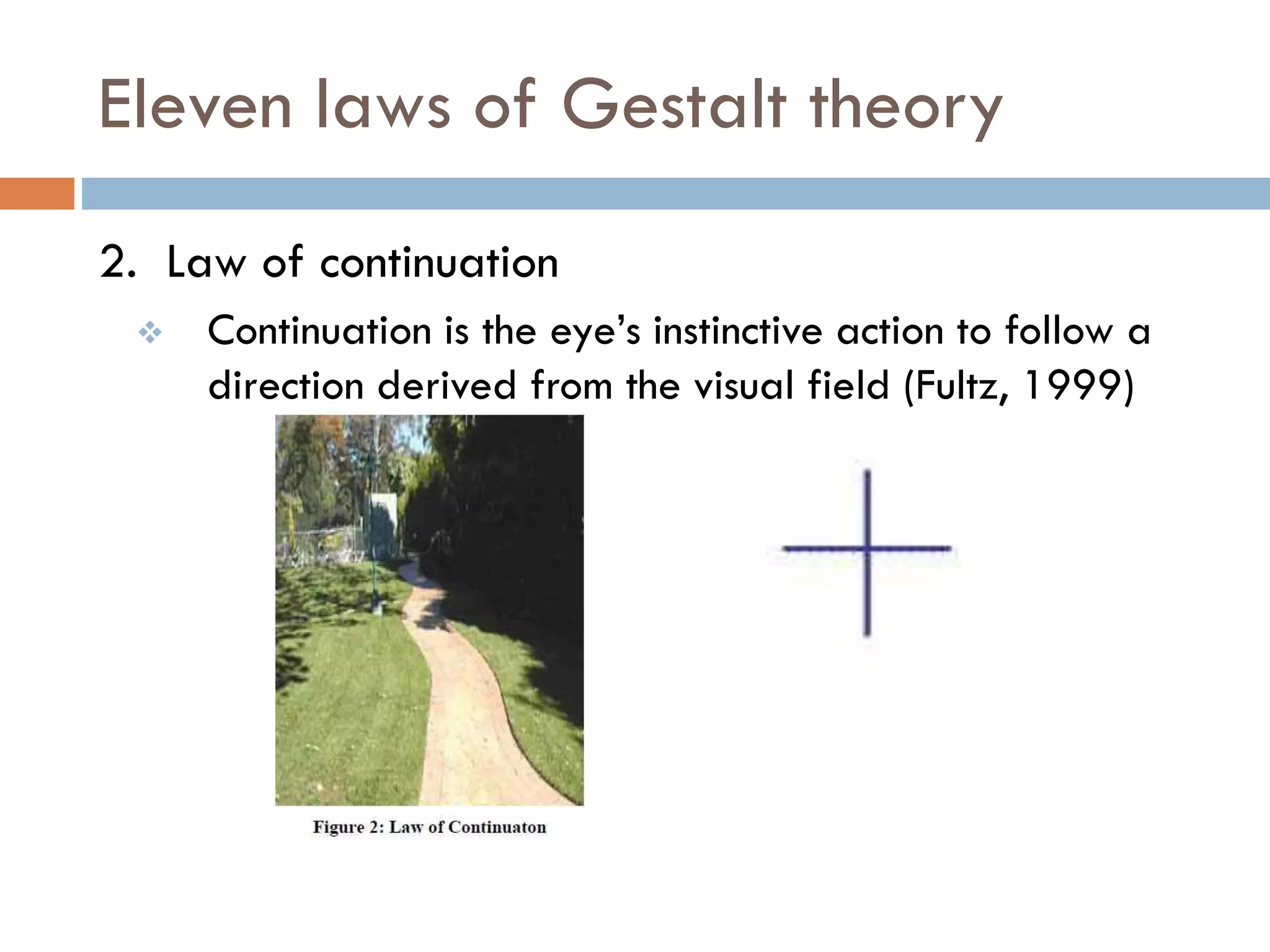
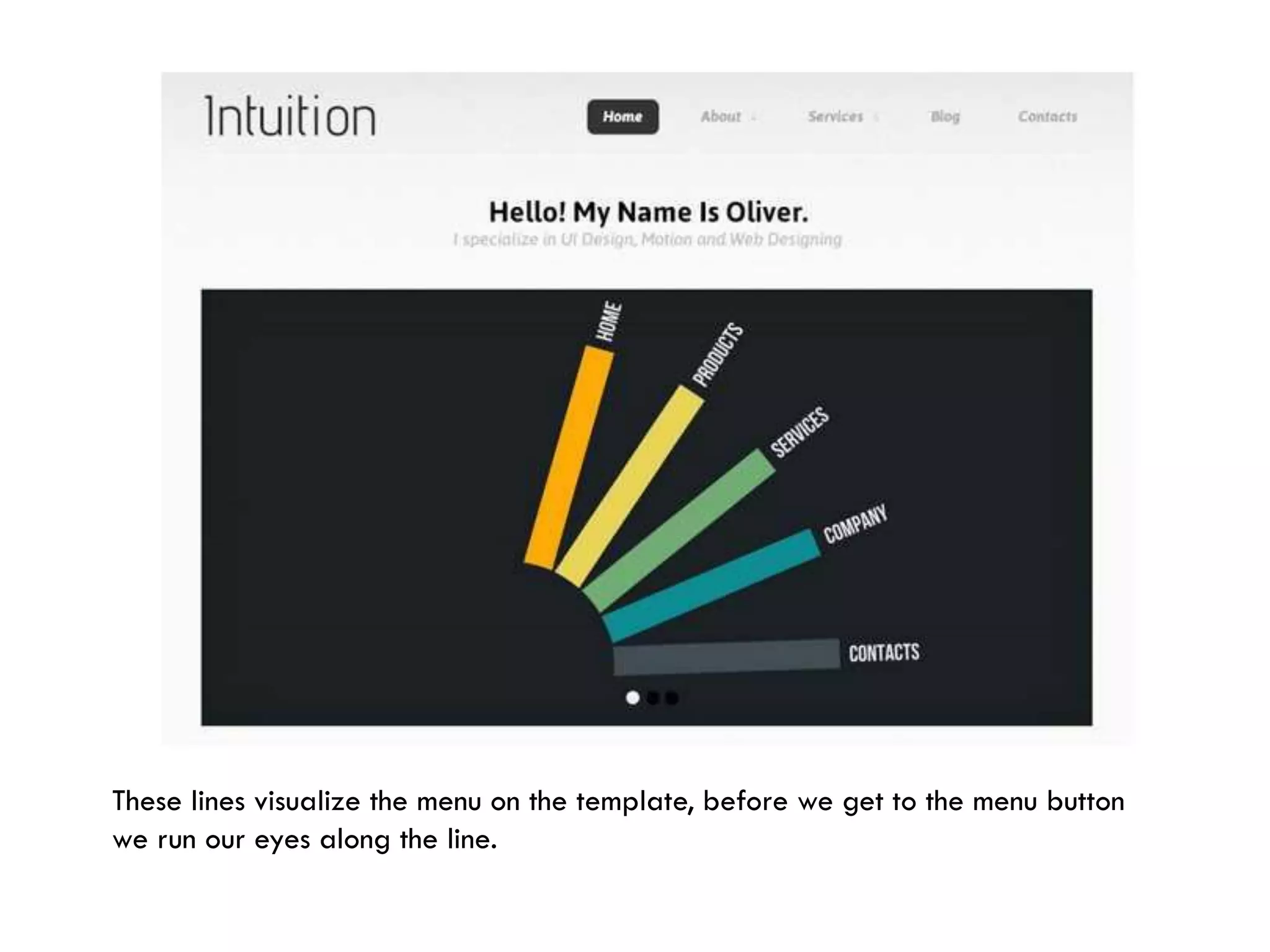
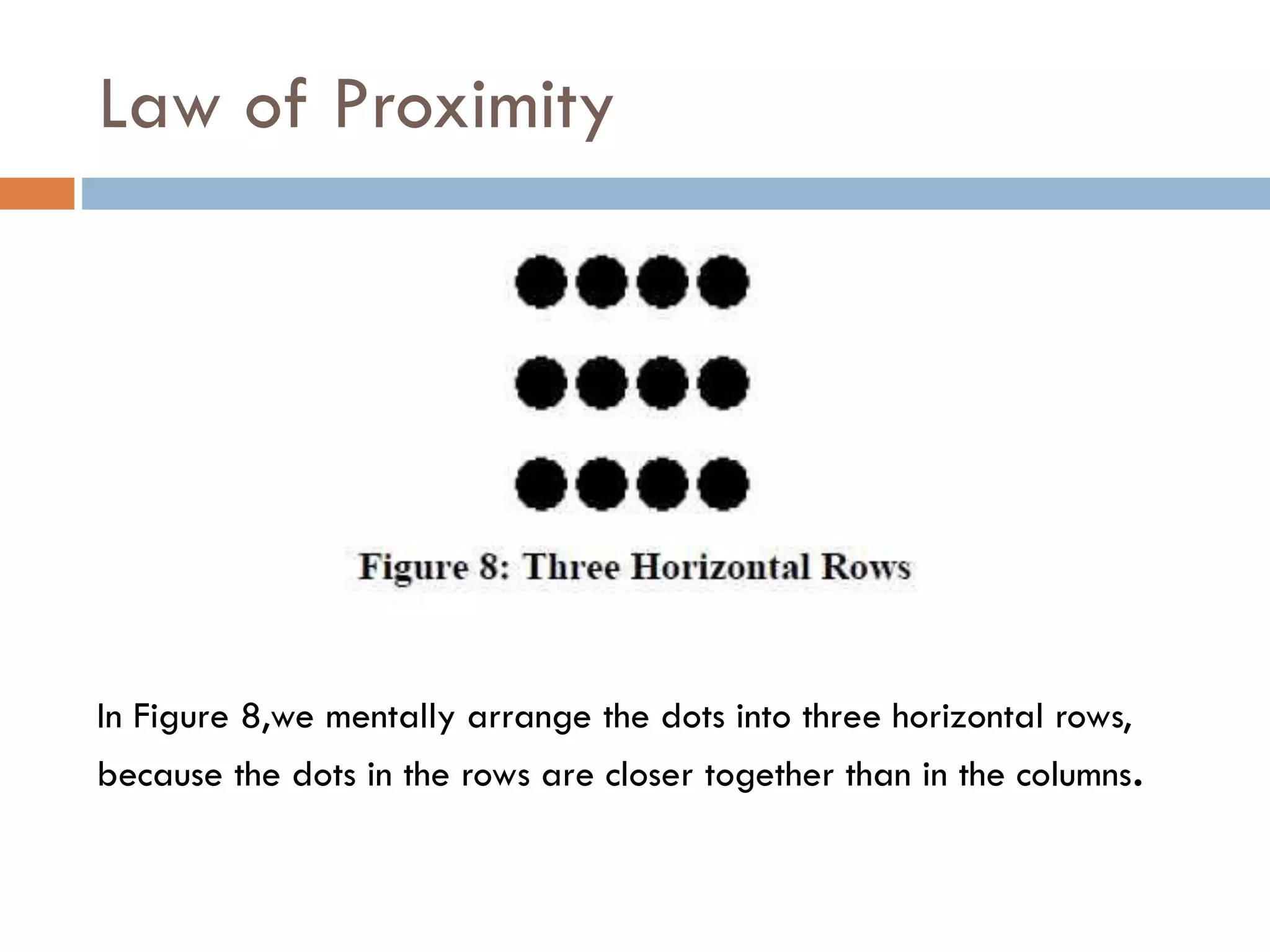
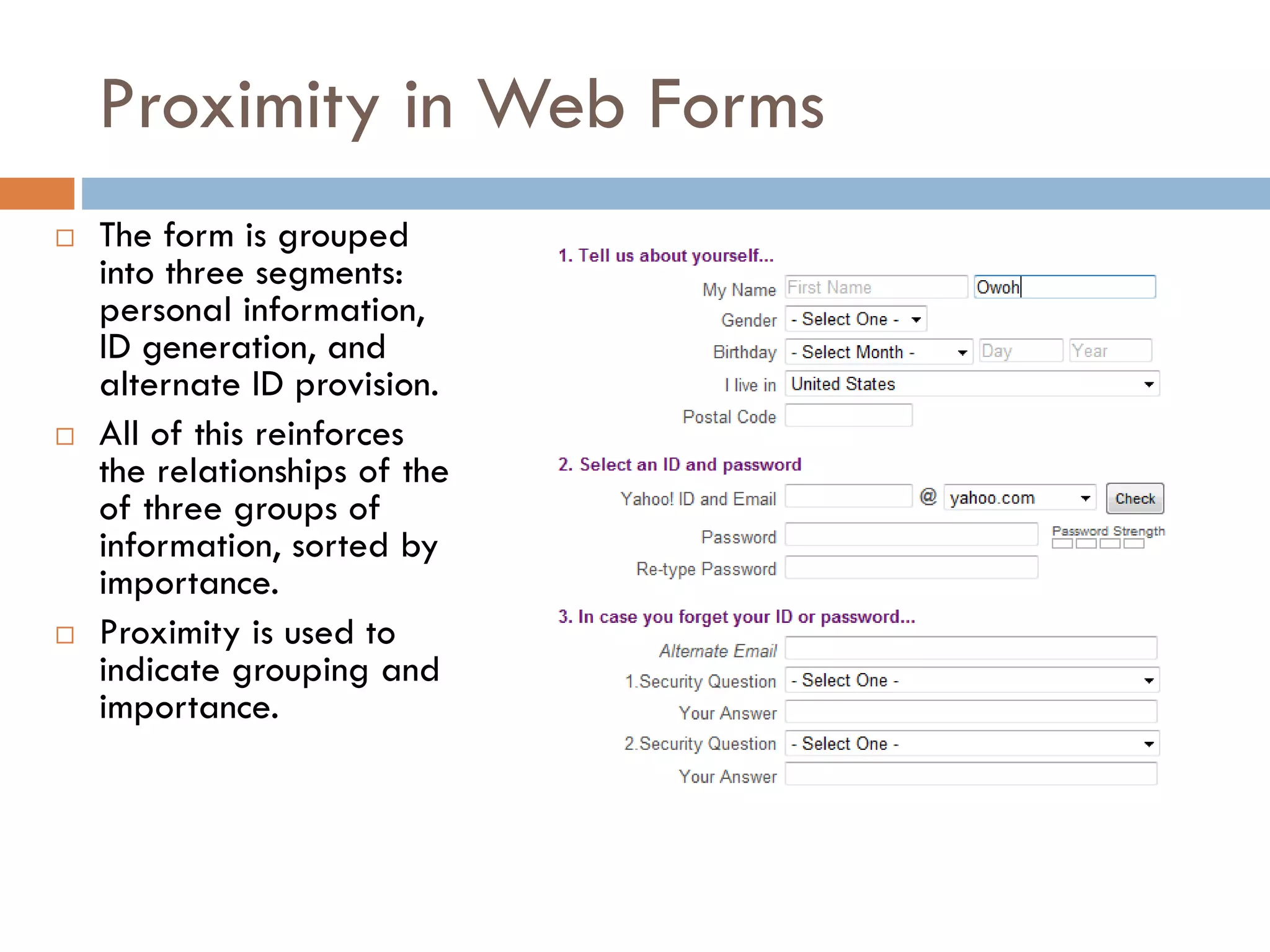
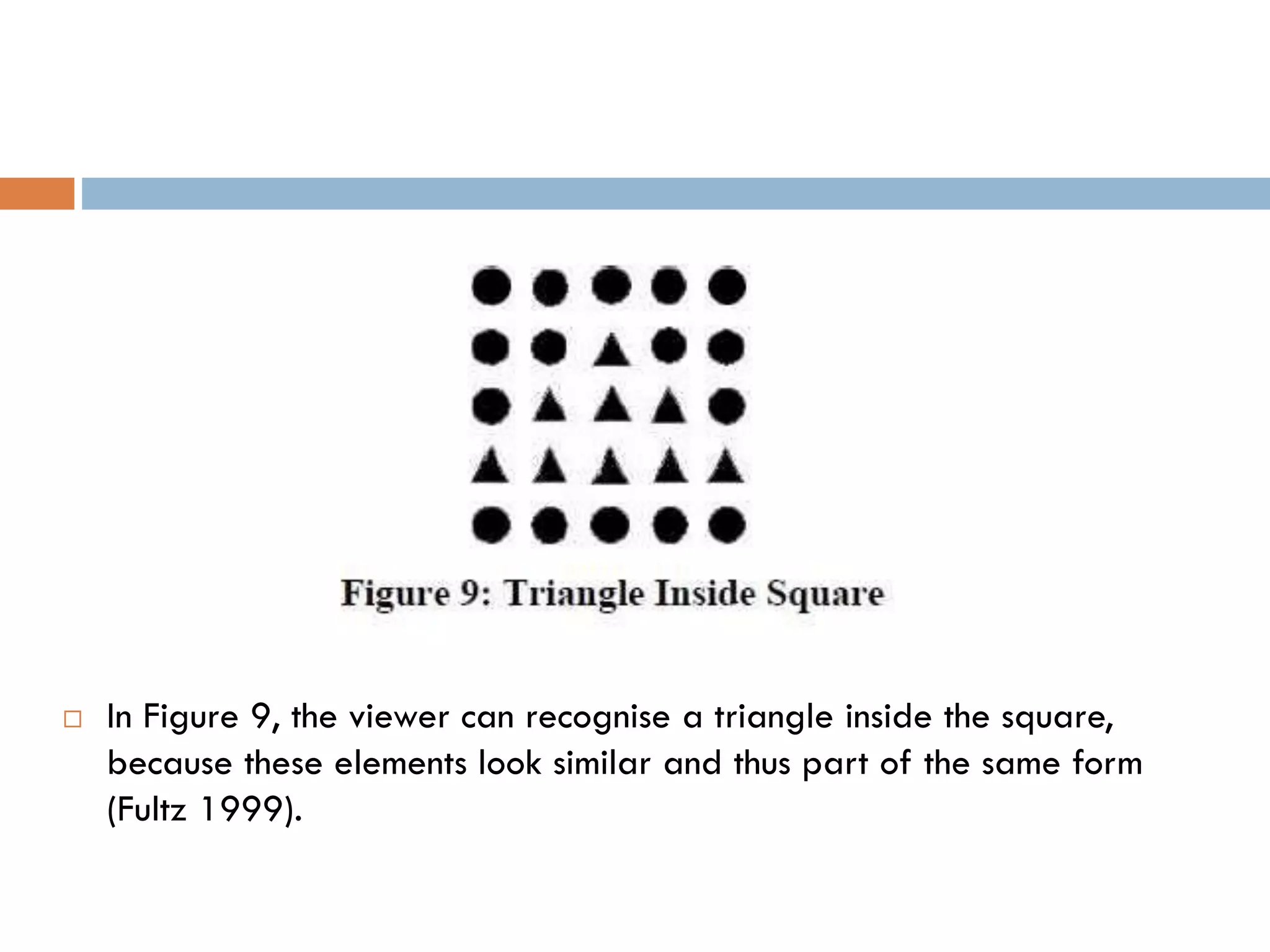
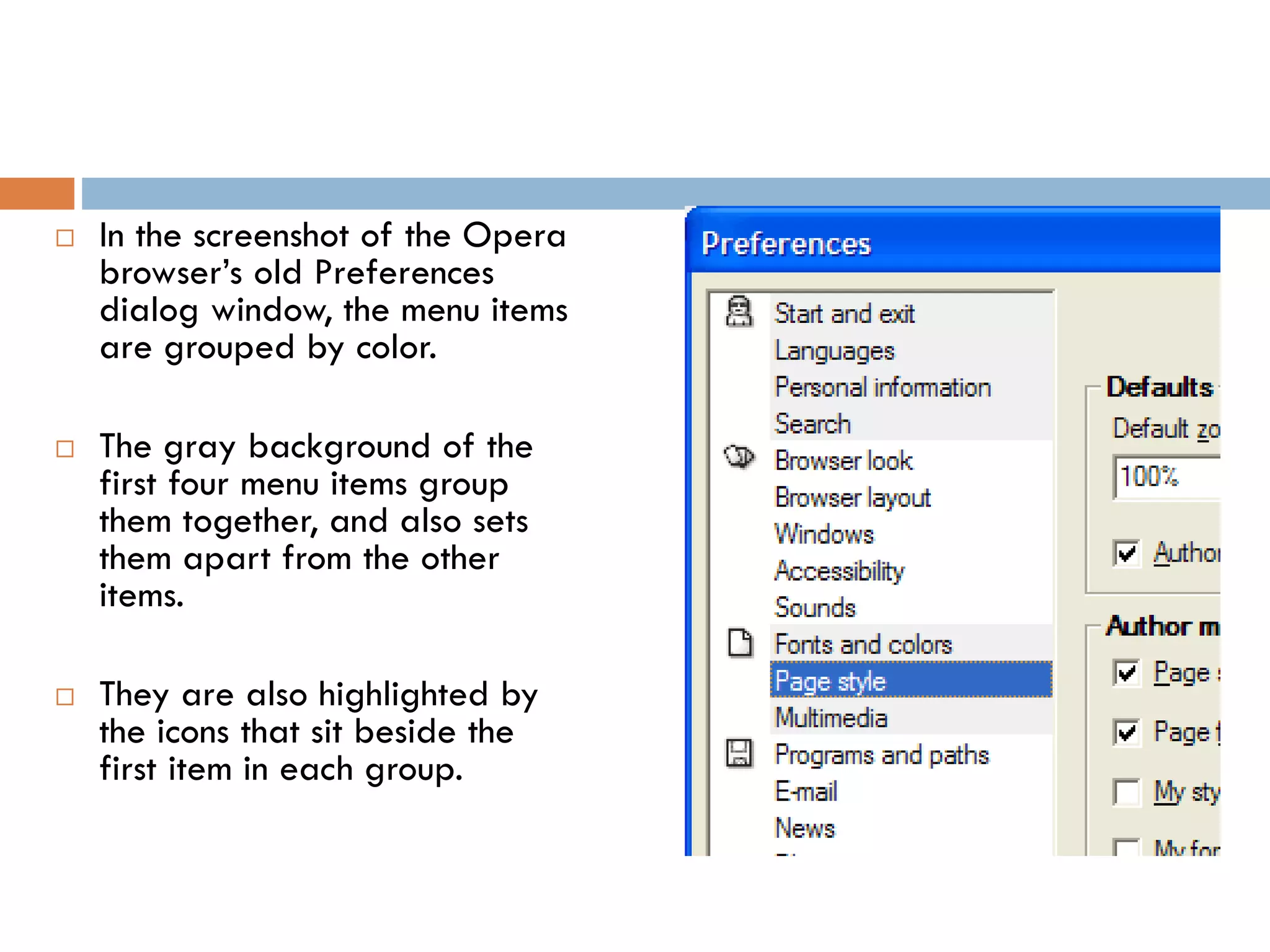
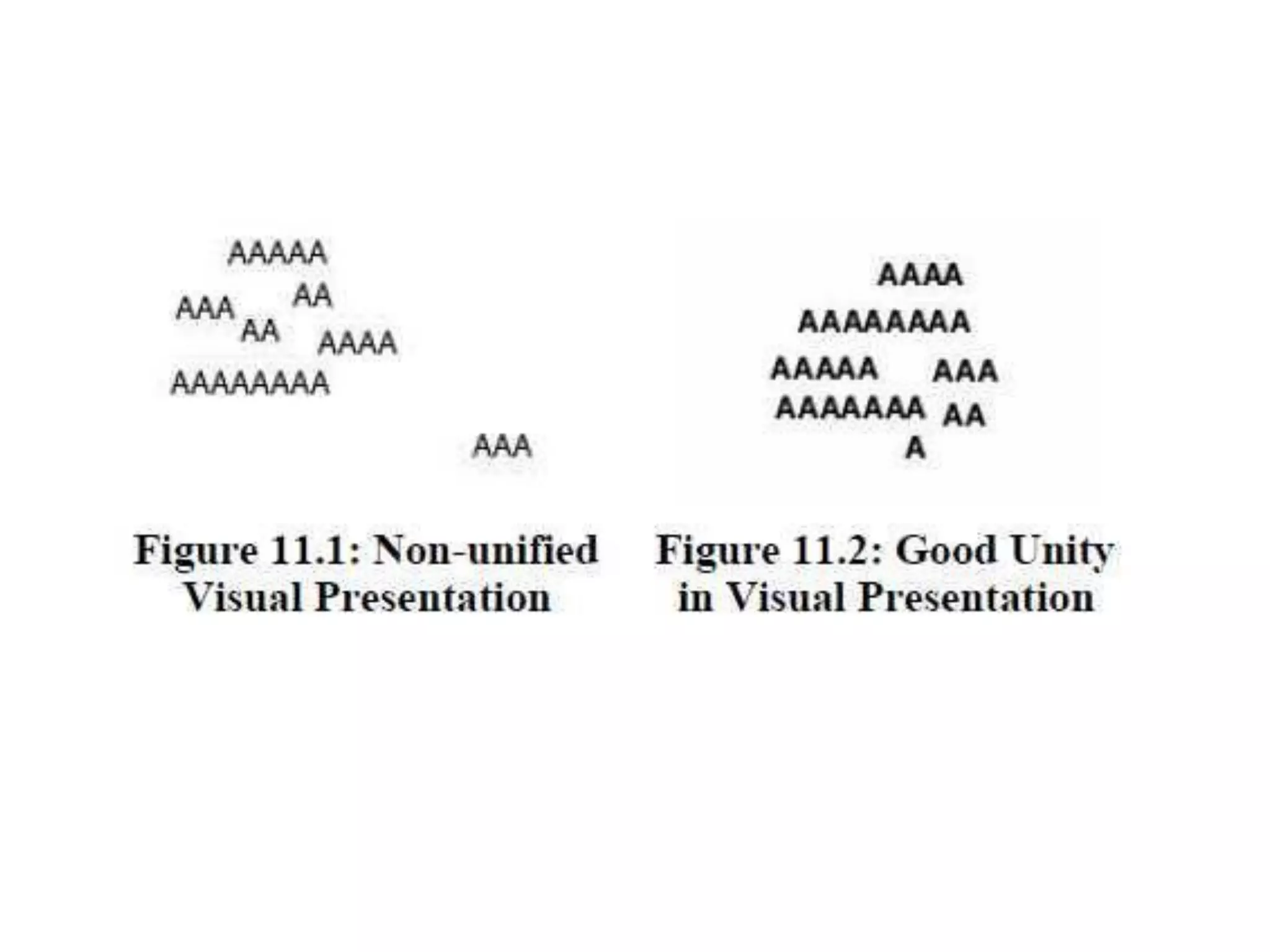
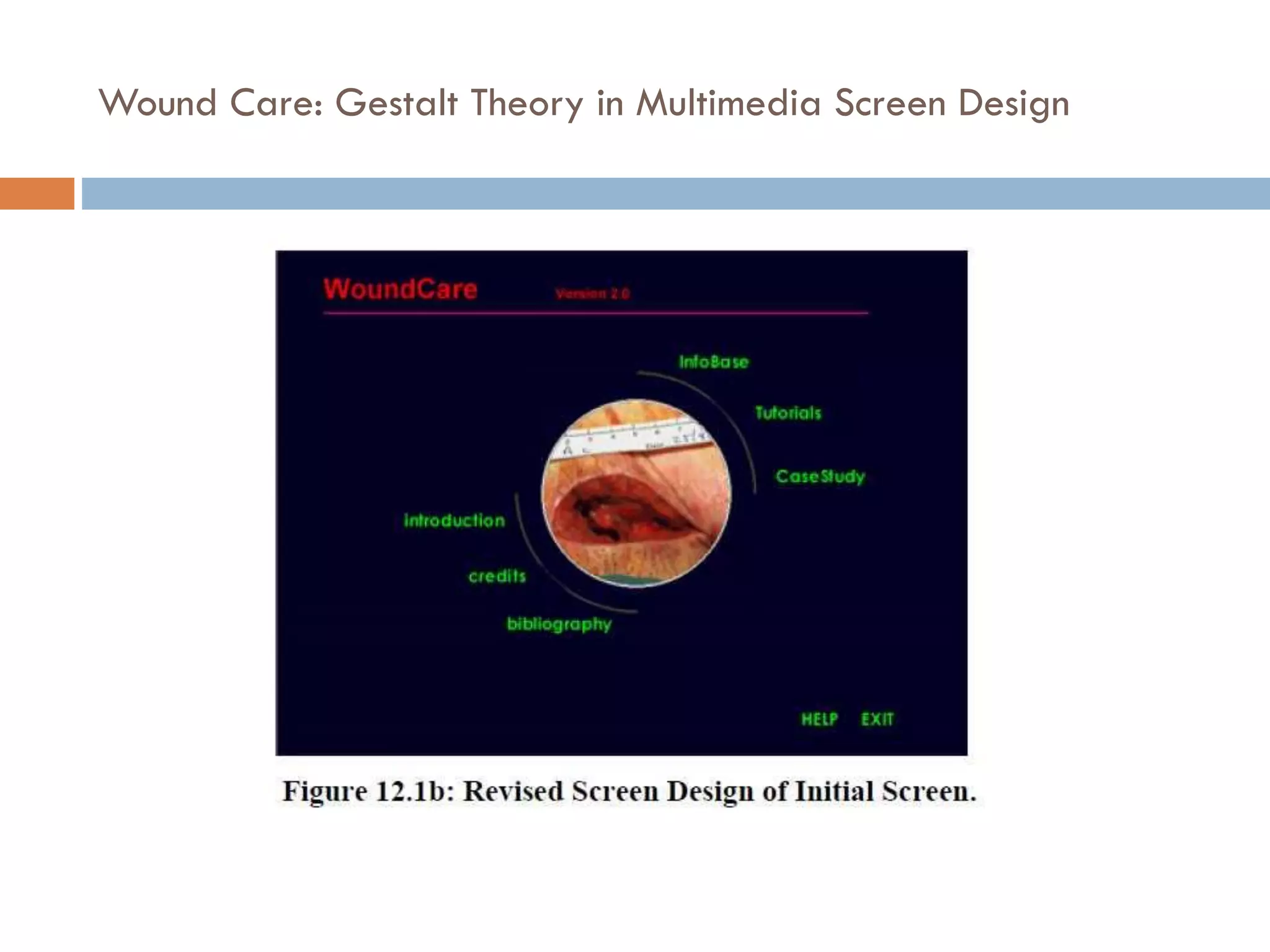
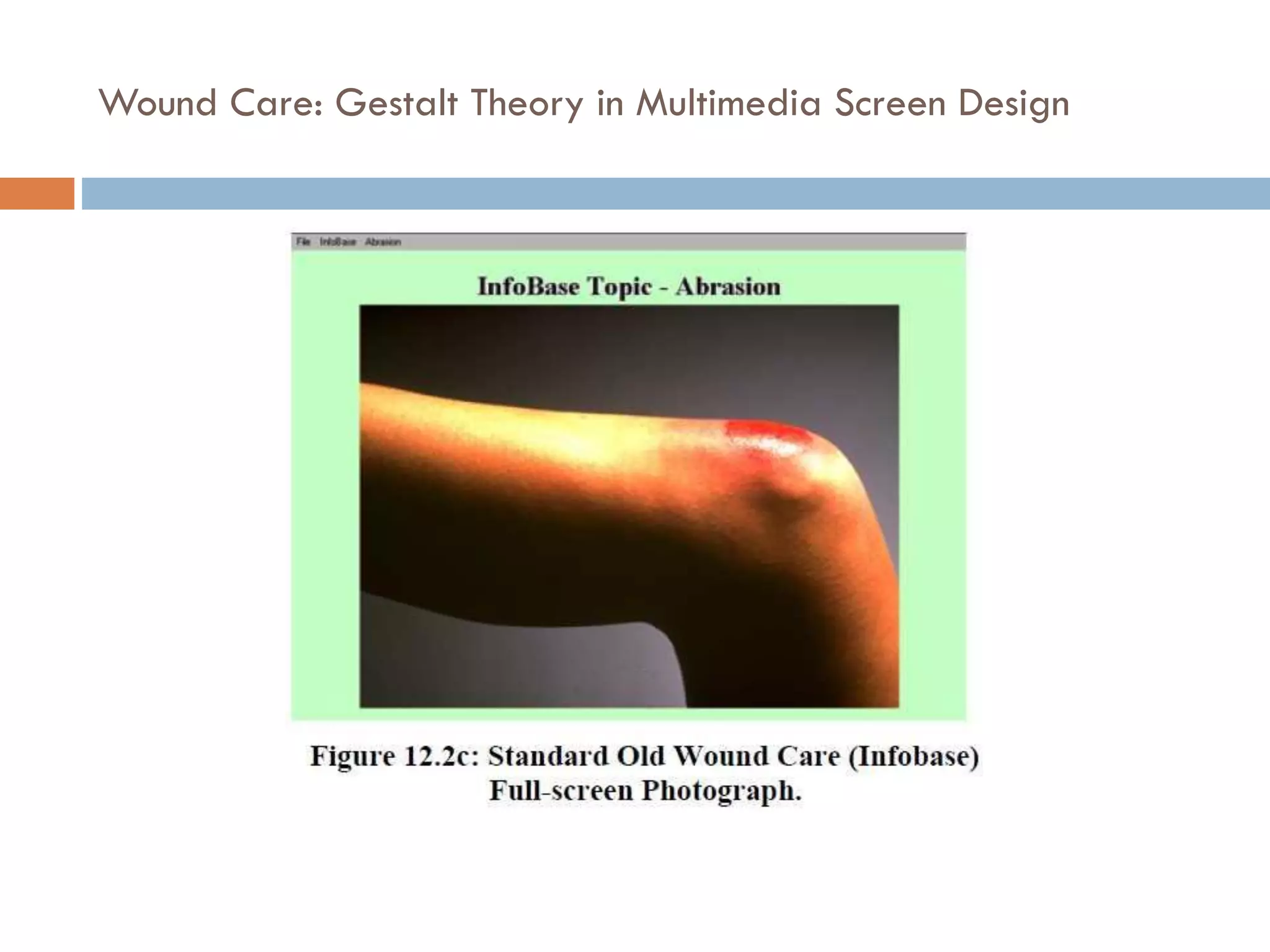
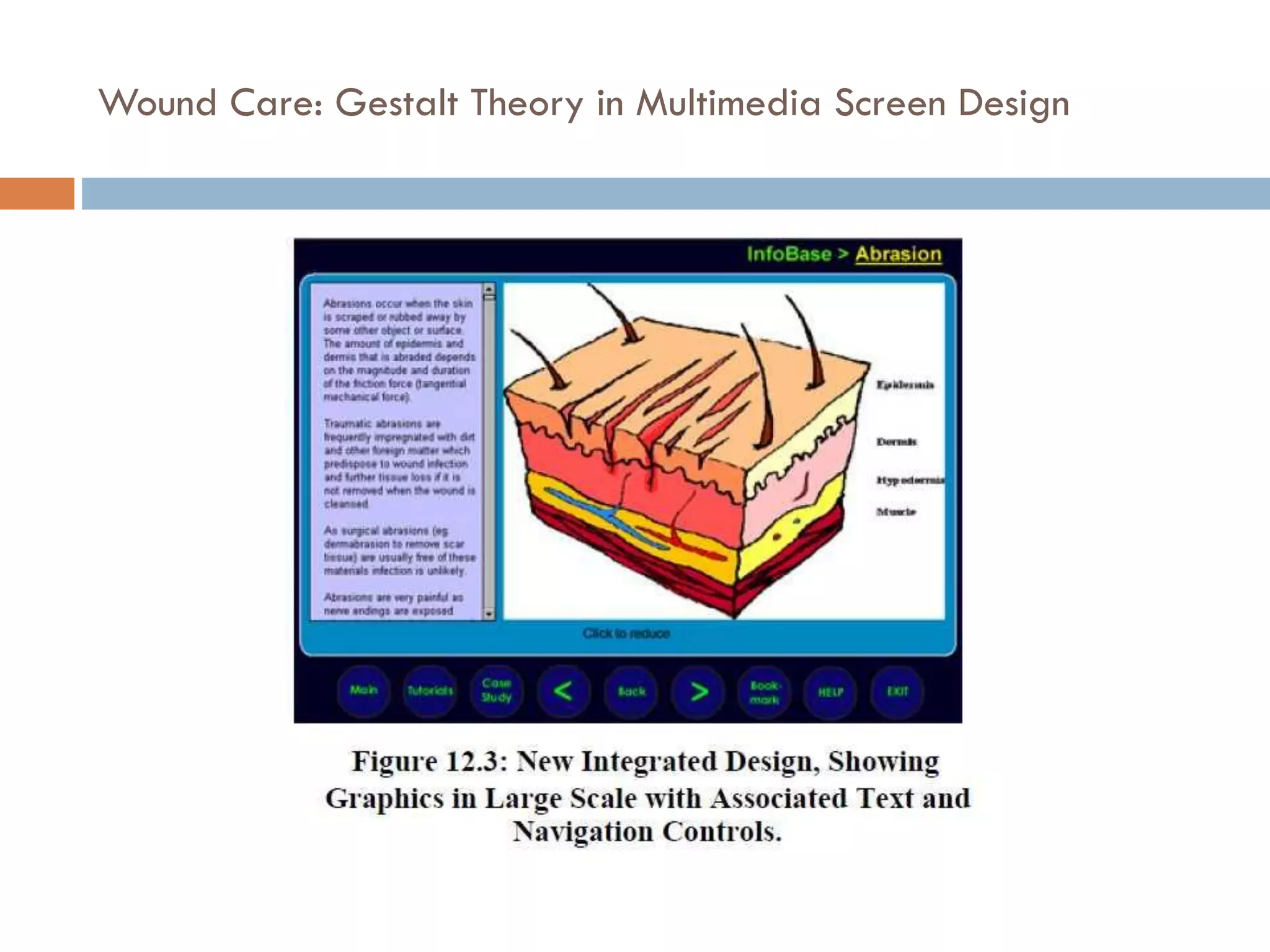
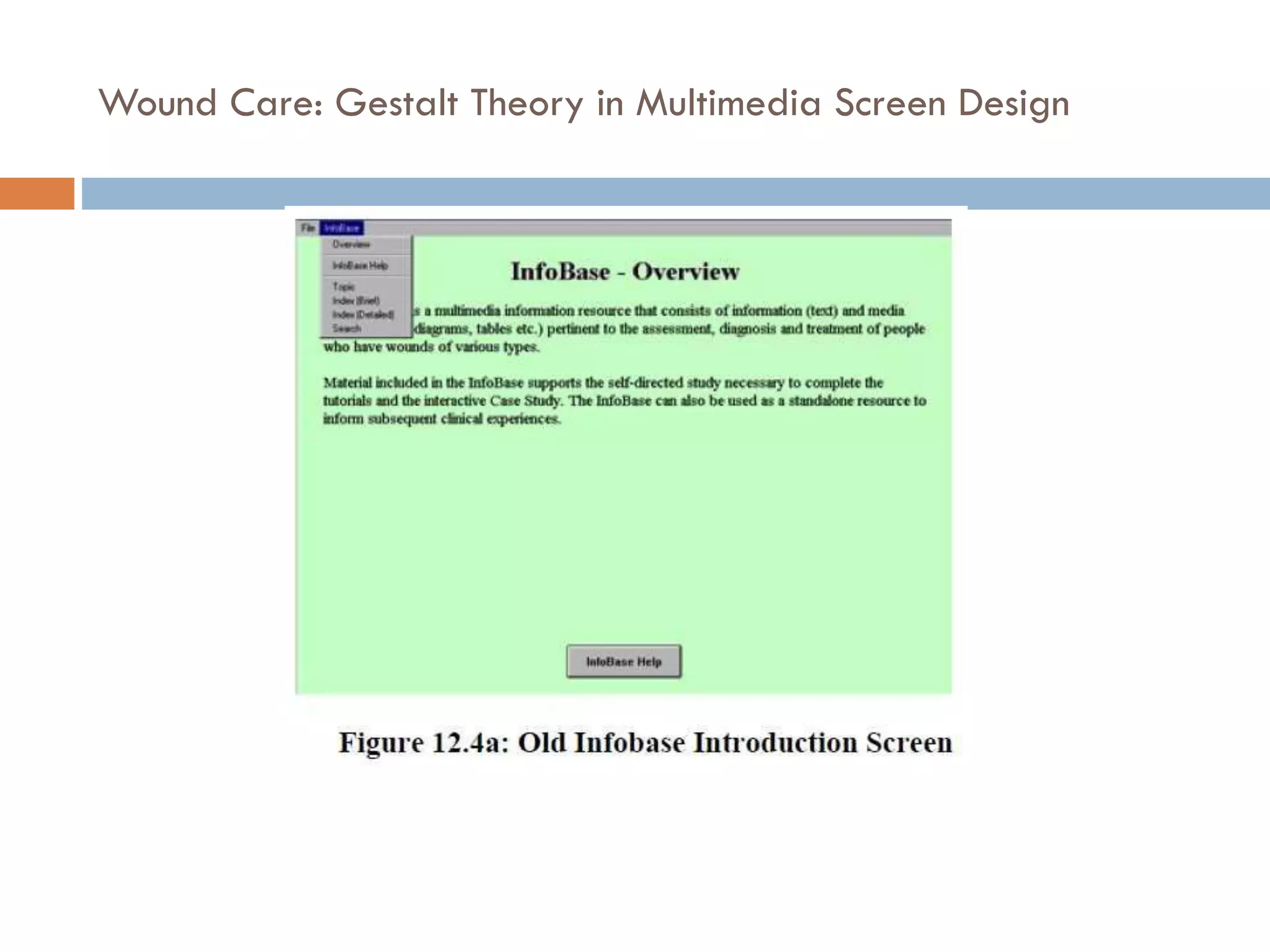
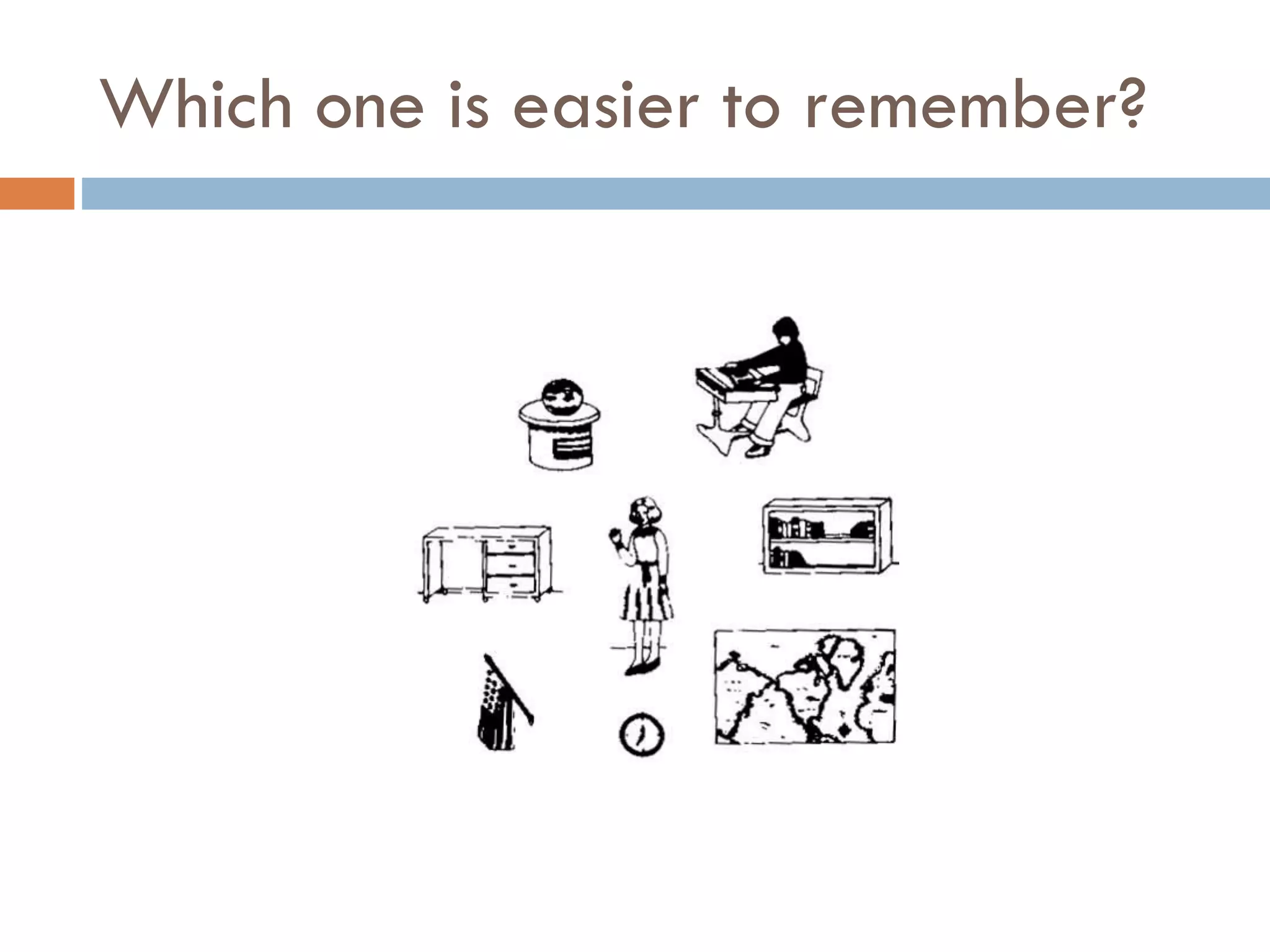
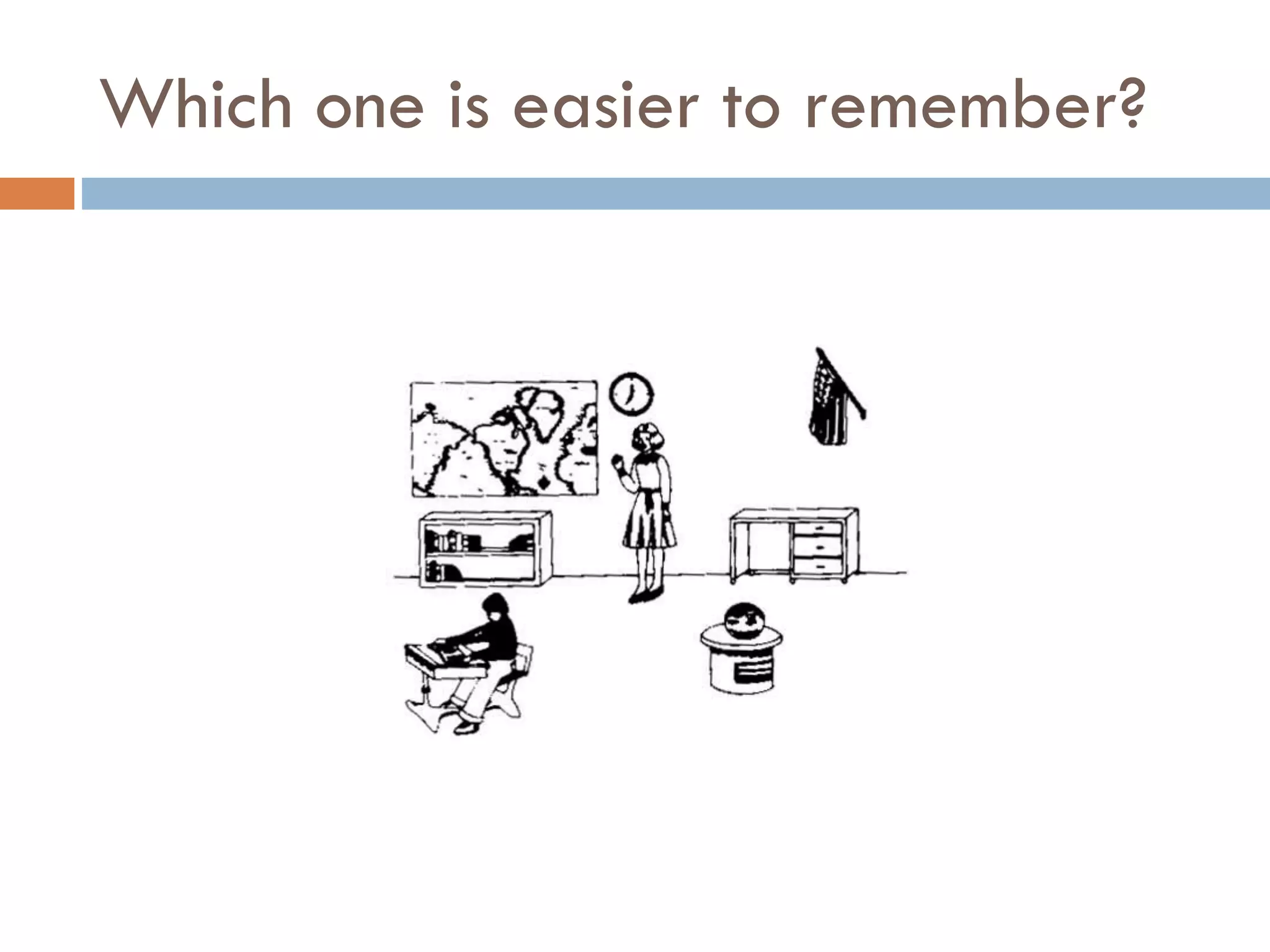
The document provides an overview of design principles in multimedia applications based on Gestalt theory. It discusses 11 Gestalt laws including proximity, similarity, closure, and balance. Examples are given to illustrate how each law can be applied, such as using color and spacing to group related elements. The document also summarizes how the Gestalt laws were applied in redesigning screens for a wound care multimedia application to make the design simpler, more unified, and visually balanced.