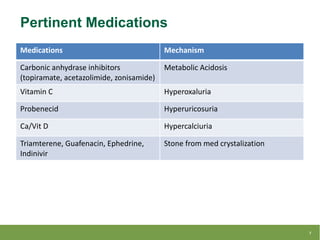
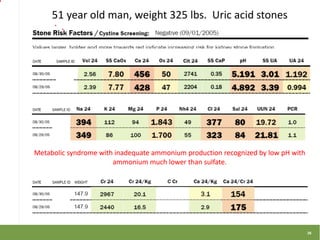
This document summarizes a lecture on metabolic stone work-up with a focus on 24-hour urine evaluation. It discusses guidelines for metabolic testing, specific abnormalities found on 24-hour urine tests like hypercalciuria and hyperoxaluria, and how to interpret results and guide treatment. Case examples from a litholink database are also reviewed to demonstrate real-world applications of 24-hour urine testing and metabolic stone work-up.