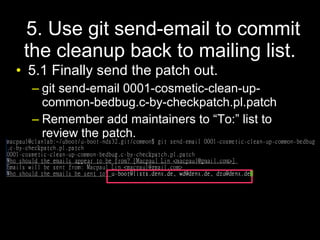
This document outlines a process for volunteers to join a U-boot source code cleanup project. It explains that U-boot contains old code that could benefit from standardization. Volunteers would use git and mailing lists to identify unclean code, fix issues found by checkpatch.pl, and submit cleanup patches for review. The goal is to organize contributions to improve code quality and make U-boot easier for new developers to understand and modify.