The document defines and describes six main types of operating systems: single user; multi user; multitasking; multi-processing; embedded; and real-time. Single user operating systems are designed for one user and can be single task or multi-tasking. Multi user OS allow multiple users simultaneous access. Multitasking OS allow more than one program to run concurrently by rapidly switching between tasks. Multi-processing OS utilize multiple CPUs. Embedded OS are designed for small devices with limited resources. Real-time OS aim to process and respond to events within a specified time interval to control external environments.


![TYPES OF OS [1]
Single User
Multi User
Multitasking
Multi Processing
Embedded
Real Time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/types-of-operating-system-221027110028-22972569/75/Types-of-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-3-2048.jpg)
![[1]SINGLE USER [1]
Two types:
Single user, single task
Single user, multi tasking](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/types-of-operating-system-221027110028-22972569/75/Types-of-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-4-2048.jpg)


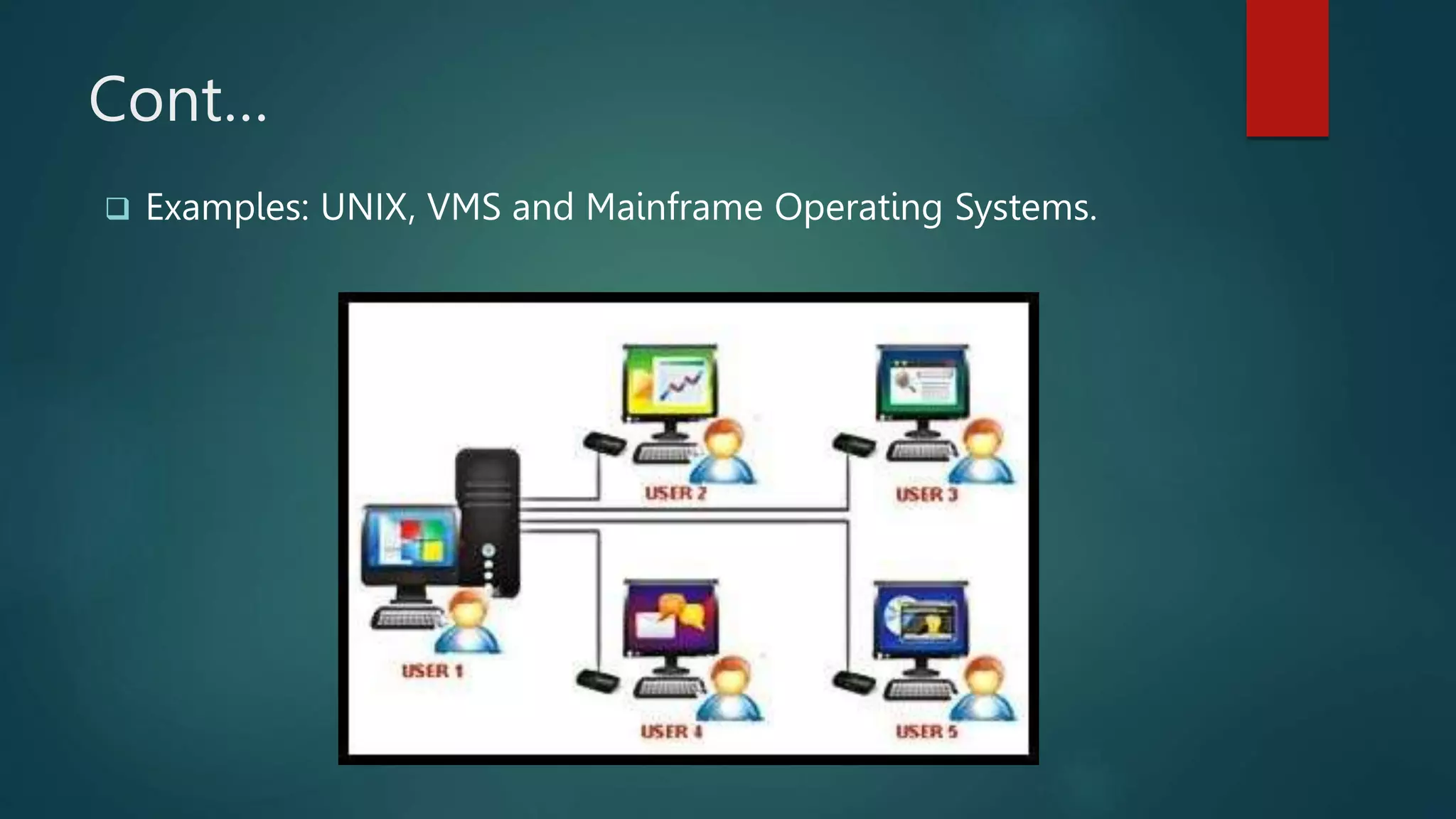
![[2] MULTI USER [2]
Allows many different users to take advantages of the
computer’s resources simultaneously,
Allows multiple users to access the computer system at the
same time.
Time sharing system and the internet servers as the multi
users systems.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/types-of-operating-system-221027110028-22972569/75/Types-of-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-9-2048.jpg)
![[3] MULTI TASKING [3]
Allows more than one program to run concurrently.
The task share commonly processing resources, such as a
CPU and main memory.
In the process, only one CPU is involved, but it switches
from one program to another so quickly that it gives the
appearance of executing all the programs at the same time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/types-of-operating-system-221027110028-22972569/75/Types-of-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-11-2048.jpg)

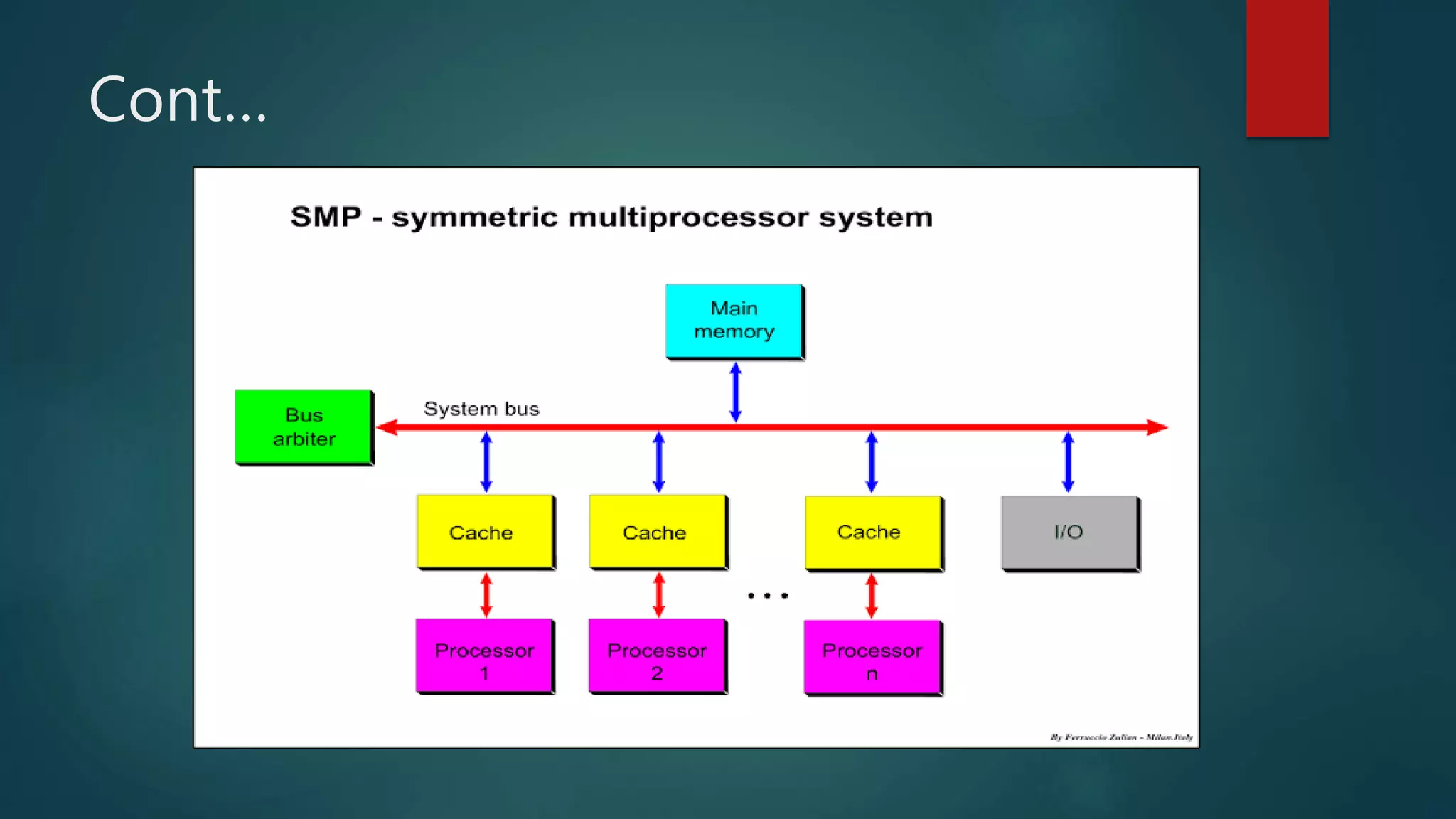
![[4] MULTI PROCESSING [4]
Multiprocessing, in general, refers to the utilization of
multiple CPUs in a single computer system.
Enables several programs to run concurrently.
The term also refers to the ability of a system to support
more that one processor and/or the ability to allocate task
between them.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/types-of-operating-system-221027110028-22972569/75/Types-of-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-13-2048.jpg)
![[5] EMBEDDED OS [4][5]
Designed to be used in embedded computer systems.
Are able to operate with a limited number of resources on
small machines like PDAs (personal device assistant)
Are very compact and extremely efficient by design.
Examples include computer in cars, digital televisions, ATMs,
airplane controls, digital cameras, GPS navigation systems,
elevators, and among other possibilities.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/types-of-operating-system-221027110028-22972569/75/Types-of-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-15-2048.jpg)

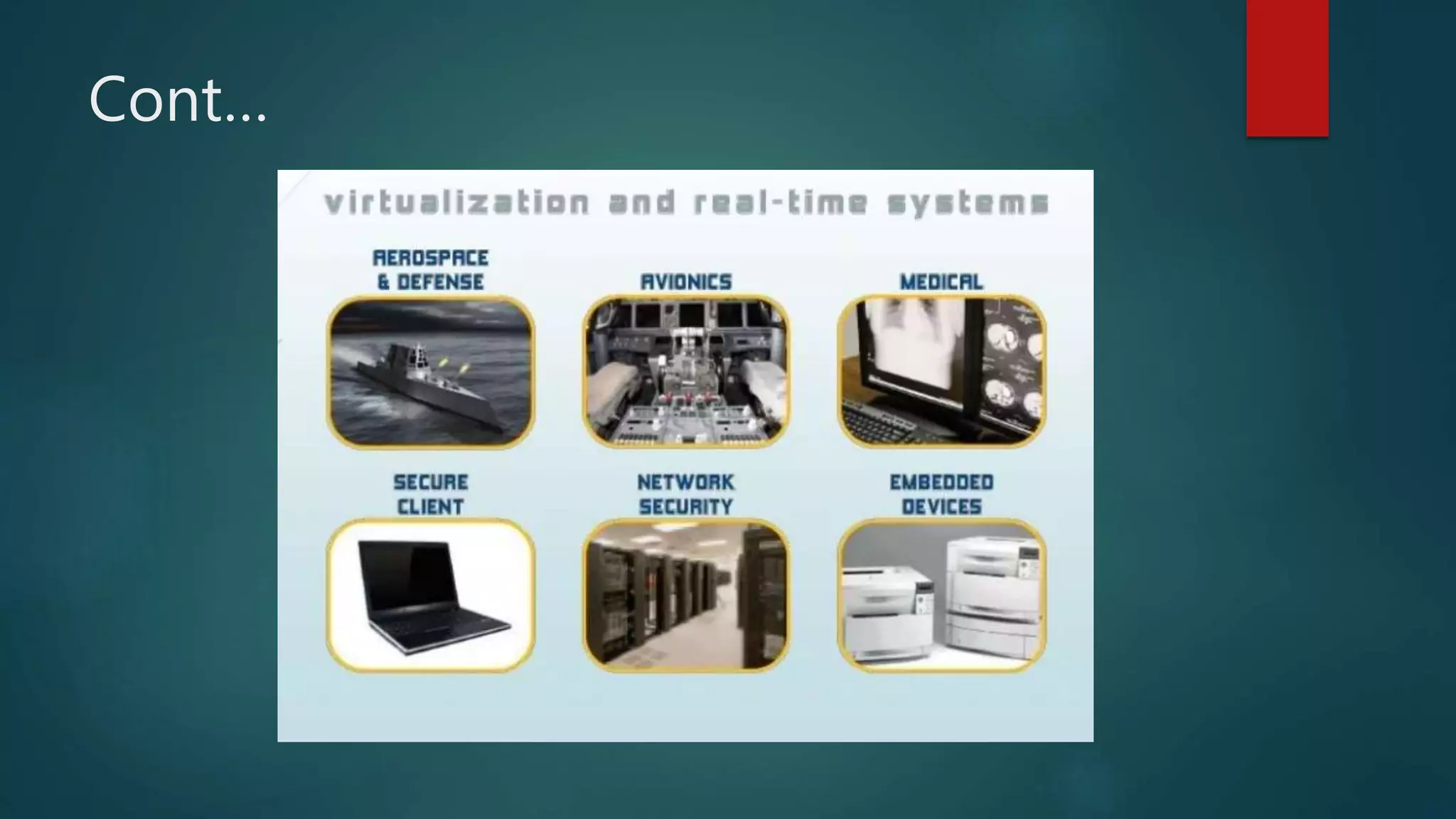
![[6] REAL TIME OPERATING SYSTEM [6]
Is a multitasking operating system that aims an executing
real-time applications’
The main objective of real-time operating system is their
quick and predictable response to events.
In it, the time interval required to process and respond to
inputs is so small that is controls the environment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/types-of-operating-system-221027110028-22972569/75/Types-of-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-17-2048.jpg)

![Summary [1]
Single User
Two types:
Single user, single task- Designed to manage the computer so that one user can effectively do one
thing at a time.
Single user, multi tasking- Designed with a single user in mind but can deal with many applications
running ant the same time.
Multi User - Allows many different users to take advantages of the computer’s resources
simultaneously, Allows multiple users to access the computer system at the same time. Time
sharing system and the internet servers as the multi users systems.
Multitasking - Allows more than one program to run concurrently. The task share commonly
processing resources, such as a CPU and main memory. In the process, only one CPU is
involved, but it switches from one program to another so quickly that it gives the appearance
of executing all the programs at the same time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/types-of-operating-system-221027110028-22972569/75/Types-of-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-20-2048.jpg)
![Summary [2]
Multi Processing - Multiprocessing, in general, refers to the utilization of multiple CPUs
in a single computer system. Enables several programs to run concurrently. The term
also refers to the ability of a system to support more that one processor and/or the
ability to allocate task between them.
Embedded - Designed to be used in embedded computer systems. Are able to operate
with a limited number of resources on small machines like PDAs (personal device
assistant). Are very compact and extremely efficient by design.
Real Time - Is a multitasking operating system that aims an executing real-time
applications’. The main objective of real-time operating system is their quick and
predictable response to events. In it, the time interval required to process and respond
to inputs is so small that is controls the environment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/types-of-operating-system-221027110028-22972569/75/Types-of-OPERATING-SYSTEM-pptx-21-2048.jpg)