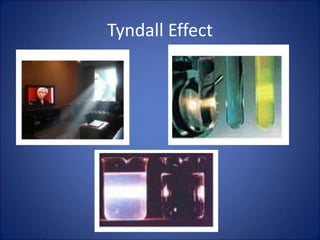
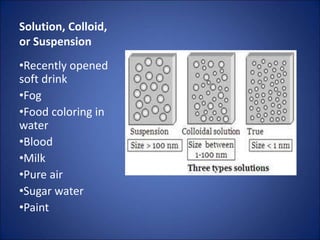
Solutions, colloids, and suspensions are three types of mixtures. Solutions are homogeneous mixtures with particles smaller than 1 nm that remain mixed and do not separate. Colloids have slightly larger particles from 1-100 nm that appear cloudy but also remain mixed. Suspensions have the largest particles over 100 nm that can separate upon standing and can be separated by filtration.