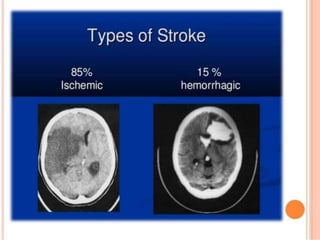
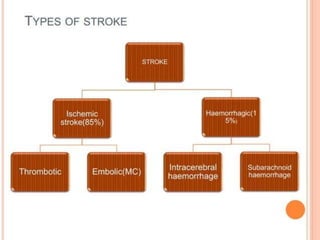
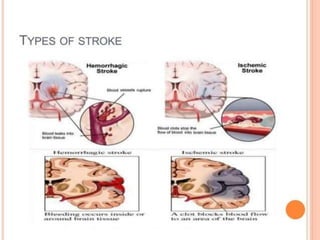
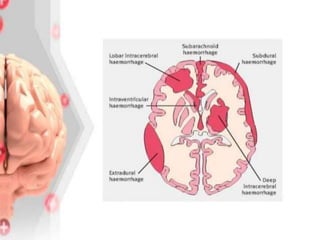
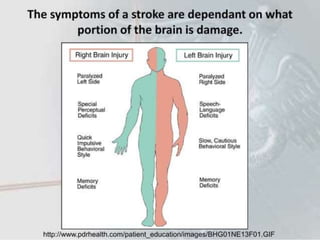
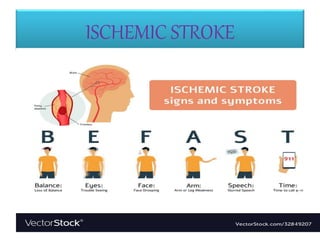
1) Ischemic stroke, which accounts for about 87% of stroke cases, occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, depriving brain cells of oxygen.
2) The main types of ischemic stroke are thrombotic, caused by blood clots; embolic, caused by clots traveling from other parts of the body to the brain; and artery to artery embolism.
3) Common risk factors for ischemic stroke include atherosclerosis, atrial fibrillation, heart attack, and hypercoagulable disorders.